
The Battle of Peleliu, codenamed Operation Stalemate II by the US military, was fought between the United States and Japan during the Mariana and Palau Islands campaign of World War II, from 15 September to 27 November 1944, on the island of Peleliu.

The Battle of Leyte in the Pacific campaign of World War II was the amphibious invasion of the island of Leyte in the Philippines by American forces and Filipino guerrillas under the overall command of General Douglas MacArthur, who fought against the Imperial Japanese Army in the Philippines led by General Tomoyuki Yamashita. The operation, codenamed King Two, launched the Philippines campaign of 1944–45 for the recapture and liberation of the entire Philippine Archipelago and to end almost three years of Japanese occupation.

The Battle of Tinian was part of the Pacific campaign of World War II. It was fought between the United States and Japan on the island of Tinian in the Mariana Islands from 24 July until 1 August 1944. The battle saw napalm used for the first time.

Operation Chronicle was the Allied invasion of Woodlark and Kiriwina Islands, in the South West Pacific, during World War II. The operation was a subordinate action that formed part of the wider Operation Cartwheel, the advance towards Rabaul. An early planning name for this operation was Operation Coronet. Preliminary actions commenced on 23–24 June 1943 when small reconnaissance parties were landed on both islands. The main operation was executed without opposition on 30 June 1943. Around 16,800 personnel took part, divided into two forces. The United States Army provided the majority of ground troops, which were supported by a United States Marine Corps defense battalion as well as U.S. and Australian aircraft and naval vessels.

The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945.

The Battle of Cape Gloucester was fought in the Pacific theater of World War II between Japanese and Allied forces on the island of New Britain, Territory of New Guinea, between 26 December 1943 and 16 January 1944. Codenamed Operation Backhander, the US landing formed part of the wider Operation Cartwheel, the main Allied strategy in the South West Pacific Area and Pacific Ocean Areas during 1943–1944. It was the second landing the US 1st Marine Division had conducted during the war thus far, after Guadalcanal. The objective of the operation was to capture the two Japanese airfields near Cape Gloucester that were defended by elements of the Japanese 17th Division.

The 4th Reconnaissance Battalion is a reserve reconnaissance battalion in the United States Marine Corps. It falls under the 4th Marine Division and Marine Forces Reserve.

The Battle of Biak was part of the Western New Guinea campaign of World War II, fought between the United States Army and the Japanese Army from 27 May to 17 August 1944. Taking place on the island of Biak, in Geelvink Bay, in present-day Indonesia, it was part of General Douglas MacArthur's South West Pacific Area's offensive drive to clear New Guinea in preparation for an invasion of the Philippines. It was the first major effort by the Japanese to allow uncontested landings for the purpose of creating a kill zone inland. The main Allied objective was to capture the island so that they could construct airfields there. The battle resulted in the capture of the island by Allied forces, which were then used to support operations elsewhere in the Pacific.

The Battle of Arawe was fought between Allied and Japanese forces during the New Britain campaign of World War II. The battle formed part of the Allied Operation Cartwheel and was a diversion before a larger landing at Cape Gloucester in late December 1943. The Japanese military was expecting an Allied offensive in western New Britain and was reinforcing the region at the time of the Allied landing in the Arawe area on 15 December 1943. The Allies secured Arawe after about a month of intermittent fighting with the outnumbered Japanese force.

This is the complete order of battle of Allied and Japanese forces during the Borneo campaign of 1945. As the campaign was fought in three geographically separate areas and the same air and naval units supported more than one of these battles the order of battle is split into the three areas.
As it turned out these operations were different from those that had gone before. The minefields were heavier and, for the first time in any Pacific campaign, man-made obstacles had been laid off the beaches.

The Battle of Hollandia was an engagement between Allies of World War II and Japanese forces during World War II. The majority of the Allied force was provided by the United States, with the bulk of two United States Army infantry divisions being committed on the ground. Air and naval support consisted largely of U.S. assets, although Australia also provided air support during preliminary operations and a naval bombardment force.

The Battle of Noemfoor was part of the New Guinea campaign of World War II. It took place on the island of Noemfoor, in Dutch New Guinea, between 2 July and 31 August 1944. During the battle, Allied forces landed on the island to capture Japanese bases as part of their advance through the Pacific towards the Philippines. The initial landing was largely unopposed and the Japanese defenders withdrew inland as the US troops came ashore. Sporadic fighting took place over the course of two months as the Allies secured the three airfields on the island and pushed the surviving Japanese troops to the southeastern coast. The island was later used by the Allies to support operations around Sansapor and on Morotai.

The Battle of Morotai, part of the Pacific War, began on 15 September 1944, and continued until the end of the war in August 1945. The fighting started when United States and Australian forces landed on the southwest corner of Morotai, a small island in the Netherlands East Indies (NEI), which the Allies needed as a base to support the liberation of the Philippines later that year. The invading forces greatly outnumbered the island's Japanese defenders and secured their objectives in two weeks. Japanese reinforcements landed on the island between September and November, but lacked the supplies needed to effectively attack the Allied defensive perimeter. Intermittent fighting continued until the end of the war, with the Japanese troops suffering heavy loss of life from disease and starvation.

The United States Marine Corps's Amphibious Reconnaissance Battalion, formerly Company, was a Marine Corps special operations forces of United States Marine and Hospital corpsman that performed clandestine operation preliminary pre–D-Day amphibious reconnaissance of planned beachheads and their littoral area within uncharted enemy territory for the joint-Navy/Marine force commanders of the Pacific Fleet during World War II. Often accompanied by Navy Underwater Demolition Teams and the early division recon companies, these amphibious recon platoons performed more reconnaissance missions than any other single recon unit during the Pacific campaigns.

The Battle of Wickham Anchorage took place during the New Georgia campaign in the Solomon Islands during the Pacific War from 30 June – 3 July 1943. During the operation US Marines and US Army troops landed by ship around Oleana Bay on Vangunu Island and advanced overland towards the anchorage where they attacked a garrison of Imperial Japanese Navy and Army troops. The purpose of the attack by the US was to secure the lines of communication and supply between Allied forces involved in the New Georgia campaign and Allied bases in the southern Solomons. The US forces were successful in driving the Japanese garrison from the area and securing the anchorage, which would later be used to stage landing craft for subsequent operations.
The Scout and Sniper Company of 6th Marine Division was the division reconnaissance asset for the regimental commanders. It was created by former Marine Raider Major Anthony "Cold Steel" Walker to form a scout company from Company H from out of one of the regiments of 6th Marine Division. The Scout Company deactivated, along with 6th Marine Division, after the end of World War II.
Cape Opmarai Airfield is a disused airfield located near Sansapor, in Southwest Papua, Indonesia. It is abandoned and overgrown, disused since 1944.

Sausapor is a small town and administrative district (distrik) in the Tambrauw Regency of the province of Southwest Papua, Indonesia. The town is located on the northern coast of the Bird's Head Peninsula, also known as the Vogelkop Peninsula. The district covers an area of 457.47 km2, and, according to the mid 2023 official estimates, had a population of 7,226, giving it by far the highest population of any district in this sparely-populated regency. The 2020 Census had shown that there were 6,461 inhabitants in the district, of whom 1,063 lived in the main town of Sausapor and 1,293 in Emaos. Sausapor is a major breeding ground for sea turtles and bird habitat.
The IJA Amphibious Brigades were marines brigades of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. They were established in 1943. Although the Japanese invasion of Southeast Asia had been completed at the time of their founding, the Imperial General Headquarters (Daihon'ei) saw the need for flexible countermeasures to defend strategic islands in the Pacific Ocean from impending Allied invasion as the war situation deteriorated for the Japanese Empire.
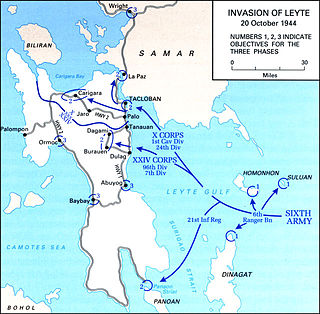
On 20 October 1944, troops of the United States Sixth Army under the direct command of Lieutenant General Walter Krueger, invaded the Philippine island of Leyte. This operation was the beginning of General Douglas MacArthur's fulfillment of his promise in March 1942 to the Filipino people that he would liberate them from Japanese rule.


















