
The First Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the First Italo-Abyssinian War, or simply in Italy as the Abyssinian War, was a war fought between Italy and Ethiopia from 1895 to 1896. It originated from the disputed Treaty of Wuchale, which the Italians claimed turned Ethiopia into an Italian protectorate. Full-scale war broke out in 1895, with Italian troops from Italian Eritrea achieving initial successes against Tigrayan warlords at Coatit, Senafe and Debra Ailà, until they were reinforced by a large Ethiopian army led by Emperor Menelik II. The Italian defeat came about after the Battle of Adwa, where the Ethiopian army dealt the outnumbered Italian soldiers and Eritrean askaris a decisive blow and forced their retreat back into Eritrea. The war concluded with the Treaty of Addis Ababa. Because this was one of the first decisive victories by African forces over a European colonial power, this war became a preeminent symbol of pan-Africanism and secured Ethiopia's sovereignty until the Second Italo-Ethiopian War of 1935–37.

The Battle of Omdurman was fought during the Anglo-Egyptian conquest of Sudan between a British–Egyptian expeditionary force commanded by British Commander-in-Chief (sirdar) major general Horatio Herbert Kitchener and a Sudanese army of the Mahdist State, led by Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, the successor to the self-proclaimed Mahdi, Muhammad Ahmad. The battle took place on 2 September 1898, at Kerreri, 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) north of Omdurman.

The Mahdist State, also known as Mahdist Sudan or the Sudanese Mahdiyya, was a state based on a religious and political movement launched in 1881 by Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah against the Khedivate of Egypt, which had ruled Sudan since 1821. After four years of struggle, the Mahdist rebels overthrew the Ottoman-Egyptian administration and established their own "Islamic and national" government with its capital in Omdurman. Thus, from 1885 the Mahdist government maintained sovereignty and control over the Sudanese territories until its existence was terminated by the Anglo-Egyptian forces in 1898.

The Battle of Atbara also known as the Battle of the Atbara River took place during the Mahdist War. Anglo-Egyptian forces defeated 15,000 Mahdists on the banks of the River Atbara. The battle proved to be the turning point in the reconquest of Sudan by the British and Egyptian coalition.

Osman Digna was a follower of Muhammad Ahmad, the self-proclaimed Mahdi, in Sudan, who became his best known military commander during the Mahdist War. He was claimed to be a descendant from the Abbasid family. As the Mahdi's ablest general, he played an important role in the fate of General Charles George Gordon and the end of Turkish-Egyptian rule in Sudan.

The Mahdist War was a war between the Mahdist Sudanese, led by Muhammad Ahmad bin Abdullah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam, and the forces of the Khedivate of Egypt, initially, and later the forces of Britain. After four years of revolt, the Mahdist rebels overthrew the Ottoman-Egyptian administration with the fall of Khartoum and gained control over Sudan. The Mahdist State launched several unsuccessful invasions of their neighbours, expanding the scale of the conflict to also include the Italian Empire, the Congo Free State and the Ethiopian Empire. They also faced significant internal rebellion. Anglo-Egyptian forces reconquered Sudan in 1898 and the Mahdist state collapsed following defeat at the battle of Omdurman. The last organised resistance from the Mahdists ended the next year, leading to the creation of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1899–1956), a de jure condominium of the British Empire, and the Kingdom of Egypt, in which Britain had de facto control over Sudan.

The Battle of Toski (Tushkah) was part of the Mahdist War. It took place on August 3, 1889, in southern Egypt between the Anglo-Egyptian forces and the Mahdist forces of the Sudan.

The Battle of Gallabat, also known as the Battle of Metemma, was fought on 9–10 March 1889 during the Mahdist War between the Mahdist Sudanese and Ethiopian forces. It is a critical event in Ethiopian history because Nəgusä Nägäst Yohannes IV was killed in this battle, and because it was the last major battle on the Ethiopian front of the Mahdist War. The fighting occurred at the site of the twin settlements of Gallabat and Metemma.

The Battle of Ferkeh occurred during the Mahdist War in which an army of Mahdists was surprised and routed by Egyptian forces, led by Sir Herbert Kitchener, on 7 June 1896. It was the first significant action of the reconquest of Sudan, which culminated in the September 1898 Battle of Omdurman.

The Battle of Coatit was fought on 13 January 1895 between Italy and Ethiopian proxies led by Tigrayan Prince Ras Mengesha Yohannes in what is now Eritrea. It was the opening battle of the First Italo–Ethiopian War, and was a significant victory for the Italians, as they rebuffed an invasion force.
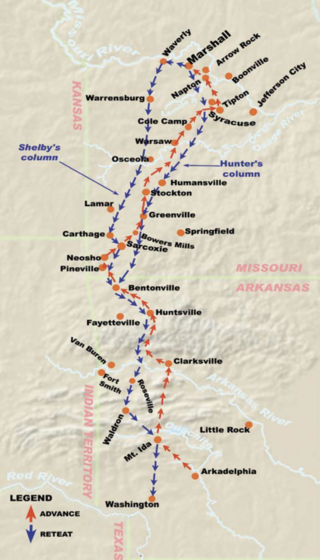
Shelby's Raid, also known as Shelby's Great Raid, was a Confederate cavalry incursion into Arkansas and Missouri during the American Civil War in 1863. Led by Colonel Joseph Orville Shelby, the raid took place from August 21, 1863, to November 3, 1863, covering over 800 miles across territories in west central and northwest Arkansas, as well as southwest and west central Missouri.

The unification of Saudi Arabia was a military and political campaign in which the various tribes, sheikhdoms, city-states, emirates, and kingdoms of most of the central Arabian Peninsula were conquered by the House of Saud, or Al Saud. Unification started in 1902 and continued until 1932, when the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was proclaimed under the leadership of Abdulaziz, known in the West as Ibn Saud, creating what is sometimes referred to as the Third Saudi State, to differentiate it from the Emirate of Diriyah, the First Saudi State and the Emirate of Nejd, the Second Saudi State, also House of Saud states.

The Royal Corps Of Eritrean Colonial Troops were indigenous soldiers from Eritrea, who were enrolled as askaris in the Royal Corps of Colonial Troops of the Royal Italian Army during the period 1889–1941.

The Second Battle of Agordat was fought in late December 1893, between Italian colonial troops and Mahdists from Sudan. Emir Ahmed Ali campaigned against the Italian forces in eastern Sudan and led about 10,000–12,000 men east from Kassala. This force encountered 2,400 Italians and their Eritrean askaris at Agordat, west of Asmara, commanded by Colonel Arimondi. Over 1,000 Dervishes, including the Emir, were killed in severe fighting. The outcome of the battle constituted "...the first decisive victory yet won by Europeans against the Sudanese revolutionaries,..."
The First Battle of Agordat, which took place on 27 June 1890 was the first battle between Italy and the Mahdist State. Fighting began when a force of one-thousand Mahdists attacked tribes that had signed protectorates with the Kingdom of Italy. The Sudanese continued on to the wells at Agordat, where they were met by two companies of Italian-led ascari. The battle that ensued was an Italian victory, with around 250 Mahdists being killed. Italian losses were three dead and eight wounded. Author Sean McLachlan attributes the Mahdists' defeat at both Agordat and the upcoming Battle of Serobeti (1892) to their "inferior weaponry and fire discipline".

The Battle of Agordat was fought near Agordat in Eritrea from 26 to 31 January 1941, by the Italian army and Royal Corps of Colonial Troops against British, Commonwealth and Indian forces, during the East African Campaign of the Second World War. The British had the advantage of breaking Italian codes and cyphers before the offensive and received copious amounts of information from Italian sources on the order of battle and plans of the Regia Aeronautica and the Italian army.

Giuseppe Edoardo Arimondi, OSML, OMS, OCI was an Italian general, mostly known for his role during the First Italo-Ethiopian War. He was one of the few European commanders who gained a victory over the Mahdists before Kitchener's Expedition, soundly defeating them at Agordat in 1893. After a long and successful colonial service, he died in combat at Adwa, and was posthumously awarded the Gold Medal of Military Valour.

The siege of Taormina in 902 ended the conquest of the Byzantine city of Taormina, in northeastern Sicily, by the Aghlabids. The campaign was led by the deposed Aghlabid emir, Ibrahim II, as a form of armed pilgrimage and holy war. Ibrahim's forces defeated the Byzantine garrison in a hard-fought battle in front of the city walls, and laid siege to the city. Left unsupported by the Byzantine government, Taormina capitulated on 1 August. The population was massacred or sold into slavery. The fall of this last major Byzantine stronghold signalled the completion of the Muslim conquest of Sicily, which had been ongoing since the 820s, although some minor Byzantine outposts survived until the 960s.
The Battle of Segheneyti, or Saganèiti, was a small clash fought on August 8, 1888 between the troops of the Kingdom of Italy and Abyssinian irregulars towards the end of the Italo-Ethiopian War of 1887-1889. The battle resulted in the destruction of Italian attachment that was deployed to Segheneyti.

Domenico Turitto was an Italian major who was part of the Royal Colonial Corps of Eritrea. He participated in the Mahdist War as he commanded the 1st Indigenous Infantry Battalion, occupying the city of Kassala and distinguishing himself at the Battle of Kassala. During the First Italo-Ethiopian War, Turitto commanded the vanguard of the Indigenous brigade under the command of Matteo Albertone before being killed in the battle. He was also a recipient of the Silver and Bronze Medals of Military Valor and a knight of the Order of Saints Maurice and Lazarus.


















