Related Research Articles

The Blackfoot Confederacy, Niitsitapi, or Siksikaitsitapi, is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Blackfeet people: the Siksika ("Blackfoot"), the Kainai or Blood, and two sections of the Peigan or Piikani – the Northern Piikani (Aapátohsipikáni) and the Southern Piikani. Broader definitions include groups such as the Tsúùtínà (Sarcee) and A'aninin who spoke quite different languages but allied with or joined the Blackfoot Confederacy.

The Kainai Nation is a First Nations band government in southern Alberta, Canada, with a population of 12,965 members in 2024, up from 11,791 in December 2013.

The Blackfoot language, also called Siksiká is an Algonquian language spoken by the Blackfoot or Niitsitapi people, who currently live in the northwestern plains of North America. There are four dialects, three of which are spoken in Alberta, Canada, and one of which is spoken in the United States: Siksiká / ᓱᖽᐧᖿ (Blackfoot), to the southeast of Calgary, Alberta; Kainai / ᖿᐟᖻ, spoken in Alberta between Cardston and Lethbridge; Aapátohsipikani / ᖳᑫᒪᐦᓱᑯᖿᖹ, to the west of Fort MacLeod which is Brocket (Piikani) and Aamsskáápipikani / ᖳᐢᔈᖿᑯᑯᖿᖹ, in northwestern Montana. The name Blackfoot probably comes from the blackened soles of the leather shoes that the people wore.

The Bow River is a river in Alberta, Canada. It begins within the Canadian Rocky Mountains and winds through the Alberta foothills onto the prairies, where it meets the Oldman River, the two then forming the South Saskatchewan River. These waters ultimately flow through the Nelson River into Hudson Bay. The Bow River runs through the city of Calgary, taking in the Elbow River at the historic site of Fort Calgary near downtown. The Bow River pathway, developed along the river's banks, is considered a part of Calgary's self-image.

The Siksika Nation is a First Nation in southern Alberta, Canada. The name Siksiká comes from the Blackfoot words sik (black) and iká (foot), with a connector s between the two words. The plural form of Siksiká is Siksikáwa. The Siksikáwa are the northernmost of the Niitsítapi, all of whom speak dialects of Blackfoot, an Algonquian language.

The Piikani Nation is a First Nation, representing the Indigenous people in Canada known as the Northern Piikani or simply the Peigan.

The Tsuutʼina Nation, also spelled Tsuu Tʼina or Tsu Tʼina, is a First Nation band government in Alberta, Canada. The Tsuu T'ina Nation 145 reserve is located directly west of Calgary, with its eastern edge directly adjacent to the southwest city limits. Their traditional territory spans a much larger area in southern Alberta. The land area of the current reserve is 283.14 km2, and it had a population of 1,982 in the 2001 Canadian census. The northeast portion of the reserve was used as part of CFB Calgary, a Canadian Army base, from 1910 to 1998. In 2006, the land was returned to the Nation by the Government of Canada.
First Nations in Alberta are a group of people who live in the Canadian province of Alberta. The First Nations are peoples recognized as Indigenous peoples or Plains Indians in Canada excluding the Inuit and the Métis. According to the 2011 Census, a population of 116,670 Albertans self-identified as First Nations. Specifically there were 96,730 First Nations people with registered Indian Status and 19,945 First Nations people without registered Indian Status. Alberta has the third largest First Nations population among the provinces and territories. From this total population, 47.3% of the population lives on an Indian reserve and the other 52.7% live in urban centres. According to the 2011 Census, the First Nations population in Edmonton totalled at 31,780, which is the second highest for any city in Canada. The First Nations population in Calgary, in reference to the 2011 Census, totalled at 17,040. There are 45 First Nations or "bands" in Alberta, belonging to nine different ethnic groups or "tribes" based on their ancestral languages.
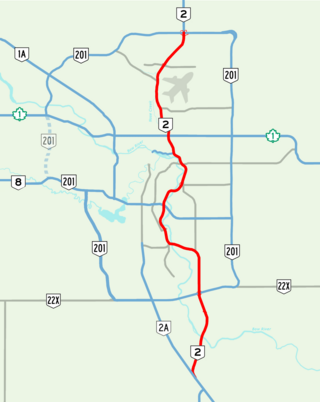
Deerfoot Trail is a 46.4-kilometre (28.8 mi) freeway segment of Highway 2 in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. It stretches the entire length of the city from south to north and links suburbs to downtown via Memorial Drive and 17 Avenue SE. The freeway begins south of Calgary where it splits from Macleod Trail, crosses the Bow River into city limits, and reaches the Stoney Trail ring road. Crisscrossing twice more with the river, it intersects Glenmore Trail and Memorial Drive; the former is a major east–west expressway while the latter is a freeway spur into downtown. In north Calgary, it crosses Highway 1 and passes Calgary International Airport before ending at a second interchange with Stoney Trail. Highway 2 becomes the Queen Elizabeth II Highway as it continues north into Rocky View County towards Red Deer and Edmonton.
Hugh Aylmer Dempsey, was a Canadian historian, an author and the Chief Curator Emeritus of the Glenbow Museum in Calgary, Alberta. Dempsey authored more than 20 books, focusing primarily on the history of people of the Blackfoot Confederacy. He received an honorary doctorate from the University of Calgary and was made an honorary chief of the Kainai Blackfoot in 1967. For his contributions to the study of the Plains Indians, Dempsey was awarded membership in the Order of Canada in 1975.
Blackfoot Trail is a super-4 expressway in Calgary, Alberta. It is named for the Blackfoot Confederacy, and more specifically the Siksika Nation, located east of Calgary. The road runs from 17 Avenue SE in the north, where Blackfoot Trail meets Deerfoot Trail, to Southland Drive in the south. It is the historical alignment of Highway 2 in south Calgary. The section of Blackfoot Trail between 19 Street SE and Deerfoot Trail is a former alignment, and still technically part of, 17 Avenue SE; however, it is generally referred to as being part of Blackfoot Trail.

Blackfoot Crossing Historical Park is a complex of historic sites on the Siksika 146 Indian reserve in Alberta, Canada. This crossing of the Bow River was traditionally a bison-hunting and gathering place for the Siksika people and their allies in the Blackfoot Confederacy.
Rilee Many Bears is a Canadian-born First Nations runner from Siksika Nation, Alberta, a part of the Blackfoot Confederacy. Many Bears, now 22 years of age, was presented with the name Iinomaahka, meaning Running Buffalo, during a naming ceremony while the Siksika Nation celebrated his achievements in running.
Brittney Bear Hat is a half Blackfoot, half Cree artist. She makes work in a variety of media, including photography, installation and video, as a means to explore how memory and personal identity construct her Native identity.
Richelle Bear Hat is a Blackfoot and Cree artist, based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, on Treaty 7 territory. Bear Hat's work explores the ancestral transmission of knowledge, memory, and Indigenous relationships to land. According to curator Kristy Trinier, "her practice investigates ideas surrounding family relationships and the types of knowledge that are capable of being passed through them. These ideas are explored through the use of photography, transfers, video and paper based works. It is important to use materials and means of production that support the transference of memory and provide a platform for storytelling."
Making Treaty 7 is an arts collective that stemmed from the Calgary's nomination as one of the Cultural Capitals of Canada in 2012. The collective seeks to draw attention on the creation of Treaty 7 and its continuing effects on Indigenous populations of Alberta, in hopes of dispelling misunderstandings, myths and falsities that originate from a lack of awareness. The collective produces works of art and theatre projects to encourage greater attention to this ongoing dialogue. It has been described by CTV News as "one of the city's – and the country's – most important companies."
Adrian Stimson is an artist and a member of the Siksika Nation.
Roy Little Chief was a Canadian Siksika elder and former Chief of the Siksika Nation from 1981 to 1983. He was a longtime activist for the rights of First Nations and indigenous people in Canada.
Miiksikaʼam is a Siksika Indigenous elder, policeman, and veteran from Alberta, Canada.

Maggie Black Kettle was a Canadian community leader in the Siksika Nation. She taught traditional crafts, dance, and the Blackfoot language in Calgary. She was a storyteller, and appeared in film and television programs in her later years.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-09-19. Retrieved 2017-09-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Meet Noran Calf Robe, Indian Village Tipi Owner from Siksika Nation – Blog". Archived from the original on 2017-07-27.
- ↑ "Meet Noran Calf Robe, Indian Village Tipi Owner from Siksika Nation – Blog". Archived from the original on 2017-07-27.
- ↑ "Home | Calgary Herald". Archived from the original on 2016-10-19.
- ↑ "Ben Calf Robe Society | Our Children are Sacred". bcrsociety.ab.ca. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ↑ "Meet Noran Calf Robe, Indian Village Tipi Owner from Siksika Nation – Blog". Archived from the original on 2017-07-27.
- ↑ "A short biography of K'sitew". www.medicinereiki.com. Archived from the original on 11 December 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ↑ "Meet Noran Calf Robe, Indian Village Tipi Owner from Siksika Nation – Blog". Archived from the original on 2017-07-27.
- ↑ "Ben Calf Robe Society | Our Children are Sacred". bcrsociety.ab.ca. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 13 January 2022.
- ↑ "Edmonton Catholic Schools". Archived from the original on 2017-09-19.
- ↑ "Ben Calf Robe celebrates its landmark 35th Annual Powwow on May 7". 19 April 2016. Archived from the original on 2017-09-19.