
Benjamin Frank Adair (1852 - March 28, 1902) was a lawyer who served in the Arkansas House of Representatives in 1891 representing Pulaski County. [1] [2]

Benjamin Frank Adair (1852 - March 28, 1902) was a lawyer who served in the Arkansas House of Representatives in 1891 representing Pulaski County. [1] [2]
Adair's father had the same name and was the owner of his mother. His father moved the family to Oberlin, Ohio, when Arkansas outlawed free people of color (Arkansas's Free Negro Expulsion Act of 1859). The father freed his family. [1] He was included in a photo montage of African American state legislators serving in Arkansas in 1891 published in The Freeman newspaper in Indianapolis. [3] He was a Democrat. [4] Adair died March 28, 1902, from a suspected heart failure after suffering from heart issues. [5]

John Mercer Langston was an American abolitionist, attorney, educator, activist, diplomat, and politician. He was the founding dean of the law school at Howard University and helped create the department. He was the first president of what is now Virginia State University, a historically black college. He was elected a U.S. Representative from Virginia and wrote From the Virginia Plantation to the National Capitol; Or, the First and Only Negro Representative in Congress From the Old Dominion.

Hernando De Soto Money was an American politician from the state of Mississippi.

The history of Arkansas began millennia ago when humans first crossed into North America. Many tribes used Arkansas as their hunting lands but the main tribe was the Quapaw, who settled in the Arkansas River delta upon moving south from Illinois. Early French explorers gave the territory its name, a corruption of Akansea, which is a phonetic spelling from the Illinois language word for the Quapaw. This phonetic heritage explains why "Arkansas" is pronounced so differently than the U.S. state of "Kansas" even though they share the same spelling.
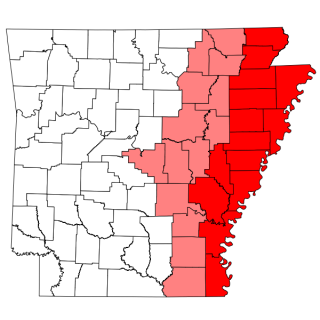
The Arkansas Delta is one of the six natural regions of the state of Arkansas. Willard B. Gatewood Jr., author of The Arkansas Delta: Land of Paradox, says that rich cotton lands of the Arkansas Delta make that area "The Deepest of the Deep South."

James Hunter Young was an American soldier and politician from North Carolina. He was a colonel in the Third North Carolina Regiment during the Spanish–American War and served in the North Carolina House of Representatives. He was a Republican.

John Gray Lucas was a lawyer and a state legislator in Arkansas during the early 20th century. He was appointed Assistant U.S. attorney in Cook County in 1934. Born in Marshall, Texas, in 1864, he eventually moved to Pine Bluff, Arkansas. He graduated from Branch Normal College of Arkansas Industrial University. He then got his law degree from Boston University School of Law in 1887, graduating with honors as the only African-American student in his class. He moved to Chicago.
Lycurgus Johnson (1818–1876) was an American cotton planter and large slaveholder in the Arkansas Delta during the antebellum years. Born to the powerful political and planter Johnson family in Scott County, Kentucky, he became the owner and developer of the Lakeport Plantation in Chicot County, Arkansas. It bordered the west bank of the Mississippi River.
The Arkansas State Press was an African-American newspaper published from 1941 to 1959. Dubbed "Little Rock's leading African-American newspaper," its owners and editors were Daisy Bates and L. C. Bates. According to historians, the newspaper was "believed by many to be instrumental in bringing about the desegregation of the Little Rock public schools."

Walter "Wiley" Jones was a businessman in Pine Bluff, Arkansas, who was one of the wealthiest African-Americans in his state. He owned the first streetcar company in Pine Bluff and a park in the city which housed the fairgrounds. A devotee of horse racing, he owned stables and a race track on the park grounds. He also owned a saloon. He was active in civic affairs and was an advocate for civil rights.

Josephine Beall Willson Bruce was a women's rights activist in the late 1890s and early 1900s. She spent a majority of her time working for the National Organization of Afro-American Women. She was a prominent socialite in Washington, D.C., throughout most of her life where she lived with her husband, United States Senator Blanche Bruce. In addition to these accomplishments, she was the first Black teacher in the public school system in Cleveland, and she eventually became a highly regarded educator at Tuskegee University in Alabama.
Reuben C. Weddington was an American state representative in Arkansas. A Republican, he served in the Arkansas House of Representatives in 1891. He represented Desha County.
G. W. Watson was an American politician. He was a member of the Arkansas Legislature in 1891 He represented Crittenden County. Watson was included in a photo montage of African American state legislators serving in Arkansas in 1891 published in the Indianapolis Freeman.

John H. Carr was a farmer and member of the Arkansas Legislature in 1891. He represented Phillips County, Arkansas. He served in the Arkansas House of Representatives in 1891.
Jacob N. Donohoo was an American state politician and banker in Arkansas. He served several terms in the Arkansas House of Representatives after first winning election in 1876 when he was 22. He helped fundraise for the Masonic Temple in Pine Bluff, part of the Sovereign Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons.
Henry Augustus Johnson was an American justice of the peace, sheriff, and state legislator in Arkansas.
William Demosthenes Crum, alternatively known as William Demos Crum, was an American physician and diplomat.
Willard Badgett Gatewood Jr. was a history professor emeritus at the University of Arkansas and an author.

The 1892 Arkansas gubernatorial election was held on September 5, 1892.

African Americans have played an essential role in the history of Arkansas, but their role has often been marginalized as they confronted a society and polity controlled by white supremacists. As slaves in the United States, they were considered property and were subjected to the harsh conditions of forced labor. After the Civil War and the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Reconstruction Amendments to the U.S. Constitution, African Americans gained their freedom and the right to vote. However, the rise of Jim Crow laws in the 1890s and early 1900s led to a period of segregation and discrimination that lasted into the 1960s. Most were farmers, working their own property or poor sharecroppers on white-owned land, or very poor day laborers. By World War I, there was steady emigration from farms to nearby cities such as Little Rock and Memphis, as well as to St. Louis and Chicago.
John Frances Cook Sr. (1810–1855) was an American pastor and educator. He was the first African-American Presbyterian minister in Washington D.C. and the head of the District's Smothers School. John F. Cook School in Washington, D.C., was named in his honor.