Related Research Articles
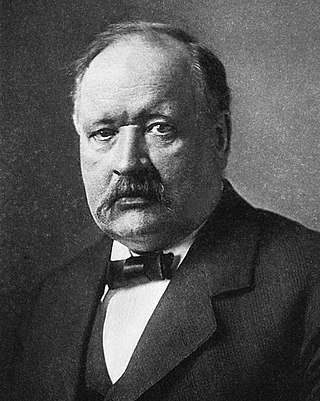
Svante August Arrhenius was a Swedish scientist. Originally a physicist, but often referred to as a chemist, Arrhenius was one of the founders of the science of physical chemistry. He received the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1903, becoming the first Swedish Nobel laureate. In 1905, he became the director of the Nobel Institute, where he remained until his death.

Paleoclimatology is the scientific study of climates predating the invention of meteorological instruments, when no direct measurement data were available. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important to understand natural variation and the evolution of the current climate.

There is a nearly unanimous scientific consensus that the Earth has been consistently warming since the start of the Industrial Revolution, that the rate of recent warming is largely unprecedented, and that this warming is mainly the result of a rapid increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) caused by human activities. The human activities causing this warming include fossil fuel combustion, cement production, and land use changes such as deforestation, with a significant supporting role from the other greenhouse gases such as methane and nitrous oxide. This human role in climate change is considered "unequivocal" and "incontrovertible".
Hermann Flohn was a climatologist. Flohn was professor at the University of Bonn and head of the department at the Institute of Meteorology of Bonn University. He produced about 360 publications. Flohn was member in numerous scientific societies such as the Bavarian Academy, the Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, the New York Academy of Sciences, and the Royal Academy of Belgium.
Catastrophe or catastrophic comes from the Greek κατά (kata) = down; στροφή (strophē) = turning. It may refer to the following:

Sir John Theodore Houghton was a Welsh atmospheric physicist who was the co-chair of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) scientific assessment working group which shared the Nobel Peace Prize in 2007 with Al Gore. He was lead editor of the first three IPCC reports. He was professor in atmospheric physics at the University of Oxford, former Director General at the Met Office and founder of the Hadley Centre.

Ernest Ronald Oxburgh, Baron Oxburgh, is an English geologist, geophysicist and politician. Lord Oxburgh is well known for his work as a public advocate in both academia and the business world in addressing the need to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and develop alternative energy sources as well as his negative views on the consequences of current oil consumption.
Zbigniew Jaworowski was a Polish physician, radiologist and alpinist. He chaired the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation in 1981 and 1982. He was an investigator for projects by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the International Atomic Energy Agency. Later in his career, Jaworowski disputed that ionizing radiation from the Chernobyl disaster was a major catastrophe for human health and wrote that the movement to remove lead from gasoline was based on a "stupid and fraudulent myth". Outside of his expertise in radiology, Jaworowski published articles criticizing mainstream climate science, including in magazines published by Lyndon LaRouche.
Umm al Binni lake is a mostly dry lake within the Central Marshes in Maysan Governorate in southern Iraq. The 3.4 km (2.1 mi) wide lake is approximately 45 km (28 mi) northwest of the Tigris–Euphrates confluence. Because of its shape, location, and other details, it was first conjectured by Sharad Master, a geoarchaeologist, to represent an impact crater. However, these claims have been disputed, with other studies finding subsidence of the underlying rock a more plausible explanation.

Syun-Ichi Akasofu is the founding director of the International Arctic Research Center of the University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF), serving in that position from the center's establishment in 1998 until January 2007. Previously he had been director of the university's Geophysical Institute from 1986.
George Kukla was a climatologist who was senior research scientist at the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University. Kukla was a member of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences prior to emigrating to the US, and a pioneer in the field of astronomical climate forcing. In 1972 he became a central figure in convincing the United States government to take the dangers of climate change seriously.

A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanently and drastically curtail humanity's existence or potential is known as an "existential risk".

The history of the scientific discovery of climate change began in the early 19th century when ice ages and other natural changes in paleoclimate were first suspected and the natural greenhouse effect was first identified. In the late 19th century, scientists first argued that human emissions of greenhouse gases could change Earth's energy balance and climate. The existence of the greenhouse effect, while not named as such, was proposed as early as 1824 by Joseph Fourier. The argument and the evidence were further strengthened by Claude Pouillet in 1827 and 1838. In 1856 Eunice Newton Foote demonstrated that the warming effect of the sun is greater for air with water vapour than for dry air, and the effect is even greater with carbon dioxide.

The Global Warming Policy Foundation (GWPF) is a charitable organisation in the United Kingdom whose aims are to challenge what it calls "extremely damaging and harmful policies" envisaged by governments to mitigate anthropogenic global warming. The GWPF, and some of its prominent members individually, have been characterised as practising and promoting climate change denial.

David Morrison is an American astronomer, a senior scientist at the Solar System Exploration Research Virtual Institute, at NASA Ames Research Center in Mountain View, California. Morrison is the former director of the Carl Sagan Center for Study of Life in the Universe at the SETI Institute and of the NASA Lunar Science Institute. He is the past Director of Space at NASA Ames. Morrison is credited as a founder of the multi-disciplinary field of astrobiology. Morrison is best known for his work in risk assessment of near Earth objects such as asteroids and comets. Asteroid 2410 Morrison was named in his honor. Morrison is also known for his "Ask an Astrobiologist" series on NASA's website where he provides answers to questions submitted by the public. He has published 12 books and over 150 papers primarily on planetary science, astrobiology and near Earth objects.

The "Knowledge Quarter" is an area of Liverpool city centre covering 450 acres, incorporating the vicinity around London Road, Islington, the so called 'Fabric District', Paddington Village and part of Canning.

Climate fiction is literature that deals with climate change. Generally speculative in nature but inspired by climate science, works of climate fiction may take place in the world as we know it, in the near future, or in fictional worlds experiencing climate change. The genre frequently includes science fiction and dystopian or utopian themes, imagining the potential futures based on how humanity responds to the impacts of climate change. Climate fiction typically involves anthropogenic climate change and other environmental issues as opposed to weather and disaster more generally. Technologies such as climate engineering or climate adaptation practices often feature prominently in works exploring their impacts on society.
The mid-24th century BCE climate anomaly is the period, between 2354 and 2345 BCE, of consistently reduced annual temperatures that are reconstructed from consecutive abnormally narrow, Irish oak tree rings. These tree rings are indicative of a period of catastrophically reduced growth in Irish trees during that period. This range of dates also matches the transition from the Neolithic to the Bronze Age in the British Isles and a period of widespread societal collapse in the Near East. It has been proposed that this anomalous downturn in the climate might have been the result of comet debris suspended in the atmosphere.

Jan Smit is a Dutch paleontologist. He was affiliated with the Faculty of Earth and Life Sciences at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam from 2003 to 2013 as a professor of event stratigraphy, studying rapid changes in the geological record related to mass extinctions.

Scenarios in which a global catastrophic risk creates harm have been widely discussed. Some sources of catastrophic risk are anthropogenic, such as global warming, environmental degradation, and nuclear war. Others are non-anthropogenic or natural, such as meteor impacts or supervolcanoes. The impact of these scenarios can vary widely, depending on the cause and the severity of the event, ranging from temporary economic disruption to human extinction. Many societal collapses have already happened throughout human history.
References
- 1 2 Davies, Nicky (13 April 2010). "Staff Profiles". Liverpool John Moores University. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010.
- ↑ Evans, Lloyd (9 April 2011). "'The global warming concern is over. Time for a return to sanity': a Spectator debate". The Spectator. No. 9528. Retrieved 4 August 2022.
- ↑ "Benny Peiser: Climate libel chill". The National Post. 12 March 2010.
- 1 2 Newman, Melanie (4 September 2008). "Debate is an endangered species, says climate critic". Times Higher Education Debate. Times Higher Education.
- 1 2 3 Wachmann, Doreen (2010). "Profile: Climate change does not pose immediate danger to the planet". Jerusalem Telegraph. Retrieved 22 May 2012.
- ↑ |editor1=Peiser, Benny J. |editor2=Trevor Palmer, and Mark E. Bailey (editors) (1998). Natural Catastrophes During Bronze Age Civilizations, BAR International Series 728. ISBN 0-86054-916-X. p. 251.
- ↑ Peiser, Benny J. 1993. Das dunkle Zeitalter Olympias: kritische Untersuchung der historischen, archäologischen und naturgeschichtlichen Probleme der griechischen Achsenzeit am Beispiel der antiken Olympischen Spiele. Frankfurt am Main: Lang 1993, 290 pp., ISBN 3-631-46522-X.
- ↑ Conference Schedule: "Reconsidering Velikovsky: The Role of Catastrophism in the Earth Sciences and the History of Mankind," University of Toronto, 17–19 August 1990.
- ↑ "Department staff page". John Moores University. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014.
- ↑ "Sir Arthur Backs Liverpool's Bid For Spaceguard Scope". Space Daily.
- ↑ "7107 Peiser (1980 PB1)". Nasa.
- ↑ Marshall, George (2015). Don't even think about it : why our brains are wired to ignore climate change (Paperback ed.). New York, NY. p. 92. ISBN 9781632861023 . Retrieved 3 August 2022.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ "CCNet homepage". Archived from the original on 7 May 2006.
- ↑ Guillory, J. (1998). Benny J. Peiser; Trevor E. Palmer; Mark E. Bailey (eds.). Natural Catastrophes during Bronze Age Civilisations: Archaeological, geological, Astronomical and Cultural Perspectives. Archaeopress. Vol. 34. Oxford, United Kingdom: British Archaeological Reports International Series. p. 252. Bibcode:1999M&PS...34.1029G. ISBN 978-0-86054-916-1.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ↑ "This House believes that alarmism has replaced science in the global warming debate". John Moores University. 19 May 2005. Archived from the original on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- ↑ "Can we go on building roads and runways and save the planet" (PDF). Local Transport Today. 30 November 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 July 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- ↑ "Global Warming from a Critical Perspective" (PDF). Vol. 13, no. 2. The University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut: New England Section Newsletter: American Physical Society (APS) and AAPT New England Sections. 19–20 October 2007. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
- ↑ Devlin, Hannah; Pagnamenta, Robin (1 December 2009). "Major cities at risk from rising sea level threat". The Times. London. Archived from the original on 3 December 2009. Retrieved 12 September 2009.
- ↑ Caroline Davies; Suzanne Goldenberg (24 November 2009). "The voices of climate change skeptics". The Guardian. London/Manchester. Retrieved 22 January 2010.