
James I the Conqueror was King of Aragon, Count of Barcelona and Lord of Montpellier from 1213 to 1276; King of Majorca from 1231 to 1276; and Valencia from 1238 to 1276. His long reign of 62 years is not only the longest of any Iberian monarch, but one of the longest monarchical reigns in history, ahead of Hirohito but remaining behind Queen Victoria and Ferdinand III of Naples and Sicily. He saw the expansion of the Crown of Aragon in three directions: Languedoc to the north, the Balearic Islands to the southeast, and Valencia to the south. By a treaty with Louis IX of France, he achieved the renunciation of any possible claim of French suzerainty over the County of Barcelona and the other Catalan counties, while he renounced northward expansion and taking back the once Catalan territories in Occitania and vassal counties loyal to the County of Barcelona, lands that were lost by his father Peter II of Aragon in the Battle of Muret during the Albigensian Crusade and annexed by the Kingdom of France, and then decided to turn south. His great part in the Reconquista was similar in Mediterranean Spain to that of his contemporary Ferdinand III of Castile in Andalusia. One of the main reasons for this formal renunciation of most of the once Catalan territories in Languedoc and Occitania and any expansion into them is the fact that he was raised by the Knights Templar crusaders, who had defeated his father fighting for the Pope alongside the French, so it was effectively forbidden for him to try to maintain the traditional influence of the Count of Barcelona that previously existed in Occitania and Languedoc.

Ramon Muntaner was a Catalan mercenary and writer who wrote the Crònica, a chronicle of his life, including his adventures as a commander in the Catalan Company. He was born at Peralada.

Peter III of Aragon was King of Aragon, King of Valencia, and Count of Barcelona from 1276 to his death. At the invitation of some rebels, he conquered the Kingdom of Sicily and became King of Sicily in 1282, pressing the claim of his wife, Constance II of Sicily, uniting the kingdom to the crown.

Almogavars is the name of a class of light infantry soldier originated in the Crown of Aragon used in the later phases of the Reconquista, during the 13th and 14th centuries.

Peter IV, called the Ceremonious, was from 1336 until his death the king of Aragon, Sardinia-Corsica, and Valencia, and count of Barcelona. In 1344, he deposed James III of Majorca and made himself King of Majorca.
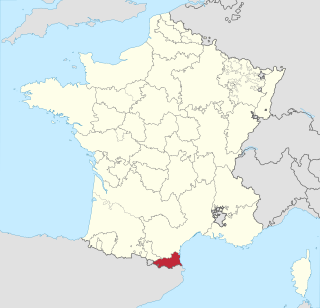
Roussillon was a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of the region of Northern Catalonia or French Catalonia, corresponding roughly to the present-day southern French département of Pyrénées-Orientales in the former region of Languedoc-Roussillon.

The Kingdom of Majorca was a realm on the east coast of Spain, which included certain Mediterranean islands, and which was founded by James I of Aragon, also known as James the Conqueror. In a will written in 1262 after the death of his firstborn son Alfonso, he ceded the kingdom to his son James. The disposition was maintained during successive versions of his will and so when James I died in 1276, the Crown of Aragon passed to his eldest son Peter, known as Peter III of Aragon or Peter the Great. The Kingdom of Majorca passed to James, who reigned under the name of James II of Majorca. After 1279, Peter III of Aragon established that the King of Majorca was a vassal to the king of Aragon. The title continued to be employed by the Aragonese and Spanish monarchs until its dissolution by the 1715 Nueva Planta decrees.

Catalan literature is the name conventionally used to refer to literature written in the Catalan language. The focus of this article is not just the literature of Catalonia, but literature written in Catalan from anywhere, so that it includes writers from Andorra, the Valencian Community, Balearic Islands and other territories where any Catalan variant is spoken.
The naval Battle of Les Formigues (Catalan) took place probably in the early morning of 4 September 1285 near Les Formigues Islands, Catalonia, about 85 km northeast of Barcelona, when a Catalan-Sicilian galley fleet commanded by Roger of Lauria defeated a French and Genoese galley fleet commanded by Guilhem de Lodeva, Henry di Mari, and John de Orrea.

The Llibre dels fets is the autobiographical chronicle of the reign of James I of Aragon (1213–1276). It is written in Old Catalan in the first person and is the first chronologically of the four works classified as The Four Great Catalan Chronicles, all belonging to the early medieval Crown of Aragon, and its first royal dynasty, the House of Barcelona. James I inherited as a child the titles of King of Aragon, Count of Barcelona, and Lord of Montpellier, but also became by conquest King of Majorca and King of Valencia. James emphasises in his chronicles his conquest of Majorca (1229) and of Valencia (1238).

Roger-Bernard III was the Count of Foix from 1265 to his death. He was the son of Roger IV of Foix and Brunissende of Cardona. He entered into conflicts with both Philip III of France and Peter III of Aragon, who held him in captivity for a time. He was nevertheless a distinguished poet and troubadour.

The Gesta comitum Barcinonensium is a Latin chronicle composed in three stages by some monks of Santa Maria de Ripoll and recounting the reigns of the Counts of Barcelona from Wifred I (878–97) to James II (1291–1327), as late as 1299. It is the fawning history of the dynasty known as the House of Barcelona. In presenting the rulers of the county of Barcelona as the descendants of Charlemagne, the monks sought to justify their independent policy with respect to the King of France, their nominal sovereign. The Gesta is the chronological backbone.

The Mural paintings of the Conquest of Majorca is a group of Gothic paintings, created on 1285-1290, conserved at the National Art Museum of Catalonia, in Barcelona, Spain.

The conquest of the island of Majorca on behalf of the Roman Catholic kingdoms was carried out by King James I of Aragon between 1229 and 1231. The pact to carry out the invasion, concluded between James I and the ecclesiastical and secular leaders, was ratified in Tarragona on 28 August 1229. It was open and promised conditions of parity for all who wished to participate.

The Battle of Portopí was an open field military conflict between the Almohad troops that occupied the island of Majorca and the Christian army led by King James I the Conqueror with the aim of annexing it to the Crown of Aragon in order to expand their domain. It was carried out at various points in the current Sierra de Na Burguesa, approximately halfway between the current resort town of Santa Ponsa and the City of Majorca. It was the second major battle in the campaign for the conquest of the island of Majorca initiated by the Aragonese king.
ʿAlī was, according to the Llibre dels fets, "a Saracen ... from La Palomera" who defected during the conquest of Majorca and swam out to the fleet of King James I of Aragon with intelligence about the island. The Llibre is an eyewitness account written by James himself. The story, however, is much more developed in the later account of Bernat Desclot. According to Desclot, ʿAlī was the majordomo of the "king of Majorca". He chose to defect when his mother, an astronomer, warned him that James would conquer the island. In reality, his choice was probably based on opposition to Abū Yaḥyā. He and his family would certainly have preserved their property by siding with the conquerors.

The Chronicle of Ramon Muntaner, written by the Catalan burgher and administrator Ramon Muntaner in Xirivella, Kingdom of Valencia, in 1325–1328, is the longest in the series of four "great" Catalan-language chronicles of the 13th and 14th centuries. It narrates events relating to the history of the Crown of Aragon and to Muntaner's personal career in Iberia, Sicily, the Aegean and North Africa and spans the period from the conception of James I of Aragon in May 1207 to the coronation of Alfonso IV of Aragon in April 1328. Its character of "mirror of princes" and "mirror of citizens" has been pointed out by scholars.

Macalda di Scaletta was a Sicilian baroness and lady-in-waiting during the Angevin and Aragonese periods. The daughter of Giovanni di Scaletta and a Sicilian noblewoman, Macalda was noted for her political conduct, inclination to betray marriage, and for her promiscuous sexual habits; because of this dissoluteness, even having a brush with "suspicion of incest," tended to morph into an "exhibitionism veined with nymphomania." She was the wife of the Grand Justiciar of the Kingdom of Sicily, Alaimo da Lentini.
The Four Great Catalan Chronicles were written between the late 13th century and the mid 14th century. The Chronicles narrate events of the lives of James I of Aragon, Bernat Desclot, Ramon Muntaner and Pere el Cerimoniós. The four chronicles were written with the same purpose: to justify the political actions of the rulers as well as passing their political knowledge onto their descendants. They are among the most complete historiographical sets of documents of medieval Europe, and are valued by historians for their detailed descriptions of the social and political aspects of Catalan feudal society.
Denis of Hungary, was a Hungarian-born Aragonese knight and nobleman in the 13th century. Born into a prominent family in the Kingdom of Hungary, he escorted Queen Violant of Hungary to the Kingdom of Aragon in 1235, where he settled down and faithfully served James I of Aragon during the Reconquista. Integrating into the local elite, Denis was the eponymous ancestor of the prominent Dionís (Dionisii) noble family. In Canals, Valencia, a street is named after him.




















