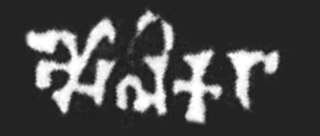Samudragupta (Gupta script: Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta, was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India, and is regarded among the greatest rulers of India. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Licchavi princess Kumaradevi, he greatly expanded his dynasty's political and military power.

Yashodharman was ruler of the Malava Empire in North India, from 515 until his death in 545. He belonged to the Second Aulikara dynasty. He conquered much of the Indian subcontinent between c. 530–540 according to the Mandsaur pillar inscription.

Eran is an ancient town and archaeological site in the Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It was one of the ancient mints for Indian dynasties as evidenced by the diverse coins excavated here. The site has 5th and 6th-century Gupta era temples and monuments, particularly the colossal stone boar with sages and scholars depicted on the body of the sculpture. The inscription stones found at Eran are important to reconstructing the chronology of Gupta Empire history. Eran or Erakina was the capital of Erakina (Airikina) Pradesha or Airkina Vishaya, an administrative division of the Gupta Empire.

Toramana also called Toramana Shahi Jauvla was a king of the Alchon Huns who ruled in northern India in the late 5th and the early 6th century CE. Toramana consolidated the Alchon power in Punjab, and conquered northern and central India including Eran in Madhya Pradesh. Toramana used the title "Great King of Kings", equivalent to "Emperor", in his inscriptions, such as the Eran boar inscription.

NarasimhaguptaBaladitya was the Gupta Emperor from 495 to 530 CE. He was son of Purugupta and probably the successor of Budhagupta.

Budhagupta was a Gupta emperor and the successor of Kumaragupta II. He was the son of Purugupta and was succeeded by Narasimhagupta.
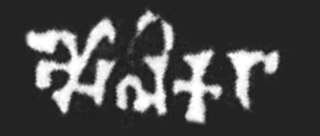
The Aulikaras, were an ancient clan that ruled the Kingdom of Daśapura between the 4th-century CE and 6th-century CE.

Purugupta was an emperor of the Gupta dynasty in northern India. Purugupta was a son of the Gupta emperor Kumaragupta I by his queen Anantadevi. He succeeded his half-brother Skandagupta. No inscription of Purugupta has been found so far. He is known from the Bhitari silver-copper seal of his grandson Kumaragupta III and Nalanda clay sealings of his sons Narasimhagupta and Budhagupta and his grandson Kumaragupta III. From the Saranath Buddha image inscription, it is concluded that he was succeeded by Kumaragupta II. According to Hornell and Raychaudhary, Prakashaditya was another title of Purugupta, although this has now been disproven by Pankaj Tandon, who has definitively shown that Prakashaditya was the Hun king Toramana.
The Gwalior Inscription of Mihirakula is a Sanskrit inscription recording the construction of a Surya temple from stone on the Gopa hill of Gwalior. Though now referred with the name of Mihirakula, the temple and the inscription was commissioned by Matricheta. The original temple is lost, and the inscribed red-sandstone slab was found in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham in the porch of another temple, and published in 1861. This inscribed stone from Gwalior was moved shortly after its discovery to the Kolkata museum for preservation. Several translations of it have been published thereafter. It is damaged, its script is the northern class of ancient Gupta script and the entire composition is in poetic verse.

The Alchon Huns, also known as the Alkhan, Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alakhana, and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and Central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India.

The Eran boar inscription of Toramana, is a stone inscription found in Eran in the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is 8 lines of Sanskrit, the first three of which are in meter and the rest in prose, written in a North Indian script. It is carved on the neck of a freestanding 11 feet (3.4 m) high red sandstone Varaha statue, a zoomorphic iconography of Vishnu avatar, and dated to the 6th century. The inscription names king Toramana, ruler of the Alchon Huns, as ruling over Malwa and records that a Dhanyaviṣṇu is dedicating a stone temple to Narayana (Vishnu).

Sridharavarman was a Saka (Indo-Scythian) ruler of Central India, around the areas of Vidisa, Sanchi and Eran in the 4th century CE, just before the Gupta Empire expansion in these areas. He calls himself a general and "righteous conqueror" in an inscription, and Rajan ('King') and Mahaksatrapa in a probably later inscription at Eran, suggesting that he may have been a high-ranked officer who later rose to the rank of a King.

The Battle of Sondani was a large military encounter fought in 528 CE, between the Alchon Hun king Mihirakula and a confederation of Indian rulers led by King Yashodharman of Malwa and King Narasimhagupta of the Gupta Empire.
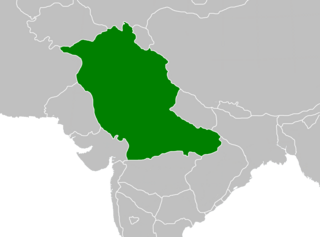
The Kingdom of Daśapura was a kingdom in Central India ruled by the Aulikara dynasty during the classical era and the early medieval era. It was established by Jayavarman in 350 AD. The name Malava Empire is applied to the territorial conquests of Yashodharman, who reigned between 515 and 545 AD.

The Kingdom of Valabhi was an early medieval kingdom in Western India from 475 to 776. It was founded by Bhatarka, a general in the Magadhan Empire, and ruled by the Maitraka dynasty.
The First Battle of Eran was a key engagement of the First Hunnic War that took place in 498 CE at Airikana (Eran), India. It was fought between the Gupta Empire and the invading army of Alchon Huns. The battle involved the Emperor Budhagupta, his viceroys, and Toramana, an acclaimed Hunnic king. The confrontation had significant consequences for the political and territorial situation in the region. The conflict concluded with a victory for the Alchon Huns that influenced subsequent events in the region.
The Second Battle of Eran, around 510 CE, marked a significant conflict between Emperor Bhanugupta of the Gupta Empire and the Huna invaders led by Toramana. The battle, commemorated in the Eran inscription, resulted in the death of Bhanugupta's general, Goparaja. It was pivotal in either halting the Huna advance into eastern Malwa or attempting to expel them from the region. The battle marked the first of a series of setbacks for the Huna conqueror. During his struggle against the invader, Bhanugupta may have received support from King Prakāśadharman, the ruler of Mandasor.

Goparaja was a feudatory chief during the Gupta Empire, remembered for his bravery and tragic demise in the Second Battle of Eran in 510 CE. He fought alongside King Bhanugupta against the Huna ruler Toramana. A memorial inscription at Eran commemorates his valor and the sacrifice of his wife, who performed sati.

A Brahmin and a feudatory of the Gupta Empire, Mātṛviṣṇu is prominently mentioned in several inscriptions of Eran, Central India, who valiantly fought along with the emperor Bhanugupta in the First Battle of Eran in which he was martyred. In 484 CE, he is described as being a maharaja and the Vishayapati of Eran under the reign of Maharaja Surasmichandra, who governed the region between the Yamuna and the Narmada River. He comes from a family of pious Brahmins performing religious and spiritual duties; his grandfather was Indraviṣṇu and his forefather was Varuṇaviṣṇu, both known for their participation in studies of scripture and enactment of sacrificial rites.

Dhanyaviṣṇu was a local leader, a Brahmin and vassal under the Huna ruler Toramana, noted in the Eran Stone Boar Inscription from the early 6th century. He was the grandson of Maharaja Indravisnu and the younger sibling of Maharaja Mātṛviṣṇu. He is recognized for continuing the religious and architectural endeavors by his family. Dhanyaviṣṇu is particularly known for finishing a large Varaha statue and managing the building of a temple for Narayana at Eran, which is on the southern side of the River Bina. His survival after the Gupta Empire's fall and his choice to follow Toramana shows a time of political change and the ongoing hope during a period of declining power.