
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future.

Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, it is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity (electrowinning).
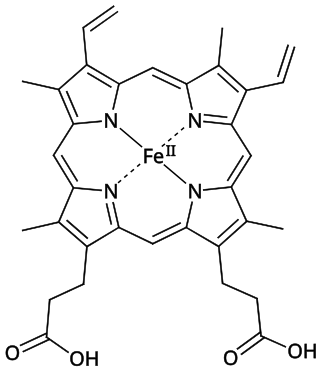
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key component of the hemoglobin protein, acting as a transport medium for electrons within the cells in the form of cytochromes, and facilitating oxygen enzyme reactions in various tissues. Too little iron can interfere with these vital functions and lead to morbidity and death.
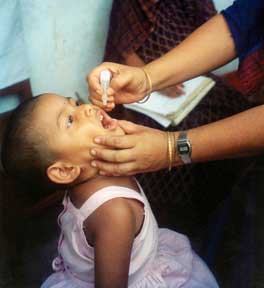
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all children be fully vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world, and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in 1988 to 33 in 2018.
Iron poisoning typically occurs from ingestion of excess iron that results in acute toxicity. Mild symptoms which occur within hours include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and drowsiness. In more severe cases, symptoms can include tachypnea, low blood pressure, seizures, or coma. If left untreated, iron poisoning can lead to multi-organ failure resulting in permanent organ damage or death.

Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, short of breath, or having decreased ability to exercise. Anemia that comes on quickly often has more severe symptoms, including confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out or increased thirst. Anemia is typically significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Children with iron deficiency anemia may have problems with growth and development. There may be additional symptoms depending on the underlying cause.

Iron(II) fumarate, also known as ferrous fumarate, is the iron(II) salt of fumaric acid, occurring as a reddish-orange powder, used to supplement iron intake. It has the chemical formula C4H2FeO4. Pure ferrous fumarate has an iron content of 32.87%, therefore one tablet of 300 mg iron fumarate will contain 98.6 mg of iron.
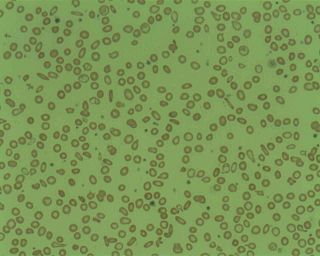
Microcytic anaemia is any of several types of anemia characterized by smaller than normal red blood cells. The normal mean corpuscular volume is approximately 80–100 fL. When the MCV is <80 fL, the red cells are described as microcytic and when >100 fL, macrocytic. The MCV is the average red blood cell size.

Iron supplements, also known as iron salts and iron pills, are a number of iron formulations used to treat and prevent iron deficiency including iron deficiency anemia. For prevention they are only recommended in those with poor absorption, heavy menstrual periods, pregnancy, hemodialysis, or a diet low in iron. Prevention may also be used in low birth weight babies. They are taken by mouth, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle. While benefits may be seen in days, up to two months may be required until iron levels return to normal.
Zinc toxicity is a medical condition involving an overdose on, or toxic overexposure to, zinc. Such toxicity levels have been seen to occur at ingestion of greater than 50 mg of zinc. Excessive absorption of zinc can suppress copper and iron absorption. The free zinc ion in solution is highly toxic to bacteria, plants, invertebrates, and even vertebrate fish. Zinc is an essential trace metal with very low toxicity in humans.
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a serum zinc level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in the serum concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe depletion, serum zinc is not a reliable biomarker for zinc status. Common symptoms include increased rates of diarrhea. Zinc deficiency affects the skin and gastrointestinal tract; brain and central nervous system, immune, skeletal, and reproductive systems.
Pharmacosmos is a pharmaceutical company specialized in treatment of iron deficiency anemia.

Panacea Biotec is an Indian multinational global generic and specialty pharmaceutical and vaccine maker. It has principal offices in New Delhi, Mumbai, and Lalru. It has business interests in research, development, manufacturing and marketing of pharmaceutical formulations, vaccines, biosimilars, and natural products.

Nutritional neuroscience is the scientific discipline that studies the effects various components of the diet such as minerals, vitamins, protein, carbohydrates, fats, dietary supplements, synthetic hormones, and food additives have on neurochemistry, neurobiology, behavior, and cognition.

Social Marketing Company is a Bangladeshi non-profit organisation which offers education and products for family planning, maternal and child health, and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) and AIDS. It is the largest social marketing company in Bangladesh.
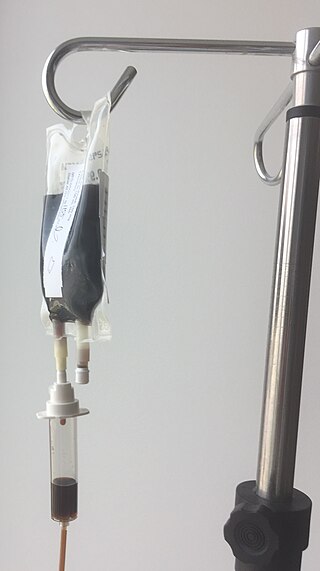
Intravenous iron sucrose is a commonly used treatment for iron deficiency anemia. Iron sucrose replaces iron in the blood to foster red blood cell production in patients with chronic kidney disease. Iron sucrose has the trade name Venofer.
Iron(III)-hydroxide polymaltose complex is a medication used to treat iron deficiency / iron deficiency anemia and belongs to the group of oral iron preparations. The preparation is a macromolecular complex, consisting of iron(III) hydroxide (trivalent iron, Fe3+, Fe(OH)3·H2O) and the carrier polymaltose and is available in solid form as a film-coated or chewable tablet and in liquid form as a syrup, drinkable solution, or drops. It is used for treating iron deficiency without anemia (latent iron deficiency) or with anemia (apparent iron deficiency). Prior to administration, the iron deficiency should be diagnostically established and verified via laboratory tests (e.g., low ferritin concentration, low transferrin saturation).
Vaccine shedding is a form of viral shedding which can occasionally occur following a viral infection caused by an attenuated vaccine. Illness in others resulting from transmission through this type of viral shedding is rare. Most vaccines are not attenuated vaccines, and therefore cannot cause vaccine-induced viral shedding, though the idea of shedding is a popular anti-vaccination myth.
DTaP-IPV-HepB vaccine is a combination vaccine whose generic name is diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis adsorbed, hepatitis B (recombinant) and inactivated polio vaccine or DTaP-IPV-Hep B. It protects against the infectious diseases diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, and hepatitis B.
Anemia is a condition in which blood has a lower-than-normal amount of red blood cells or hemoglobin. Anemia in pregnancy is a decrease in the total red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood during pregnancy. Anemia is an extremely common condition in pregnancy world-wide, conferring a number of health risks to mother and child. While anemia in pregnancy may be pathologic, in normal pregnancies, the increase in RBC mass is smaller than the increase in plasma volume, leading to a mild decrease in hemoglobin concentration referred to as physiologic anemia. Maternal signs and symptoms are usually non-specific, but can include: fatigue, pallor, dyspnea, palpitations, and dizziness. There are numerous well-known maternal consequences of anemia including: maternal cardiovascular strain, reduced physical and mental performance, reduced peripartum blood reserves, increased risk for peripartum blood product transfusion, and increased risk for maternal mortality.












