Related Research Articles

In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The biceps or biceps brachii is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join to form a single muscle belly which is attached to the upper forearm. While the biceps crosses both the shoulder and elbow joints, its main function is at the elbow where it flexes the forearm and supinates the forearm. Both these movements are used when opening a bottle with a corkscrew: first biceps screws in the cork (supination), then it pulls the cork out (flexion).

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.
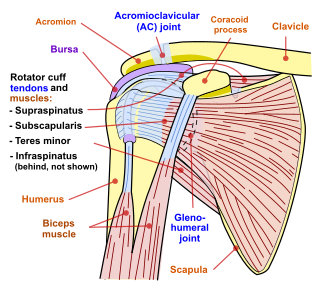
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.
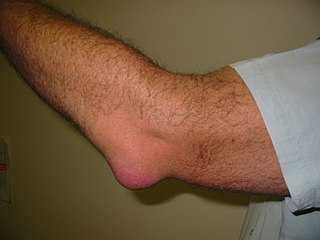
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursae rest at the points where internal functionaries, such as muscles and tendons, slide across bone. Healthy bursae create a smooth, almost frictionless functional gliding surface making normal movement painless. When bursitis occurs, however, movement relying on the inflamed bursa becomes difficult and painful. Moreover, movement of tendons and muscles over the inflamed bursa aggravates its inflammation, perpetuating the problem. Muscle can also be stiffened.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it has two parts, one of which forms part of the hamstrings muscle group.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.
The flexor pollicis longus is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population.
The pronator teres is a muscle that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm. It has two attachments, to the medial humeral supracondylar ridge and the ulnar tuberosity, and inserts near the middle of the radius.
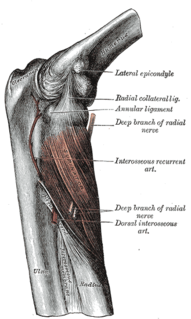
In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius. Its function is to supinate the forearm.

Snapping hip syndrome, also referred to as dancer's hip, is a medical condition characterized by a snapping sensation felt when the hip is flexed and extended. This may be accompanied by a snapping or popping noise and pain or discomfort. Pain often decreases with rest and diminished activity. Snapping hip syndrome is commonly classified by the location of the snapping as either extra-articular or intra-articular.
The knee examination, in medicine and physiotherapy, is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with knee pain or a history that suggests a pathology of the knee joint.

The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the Supinator, and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm. The deep branch provides motor function to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which is mostly the extensor muscles of the hand.
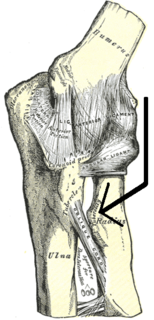
Beneath the neck of the radius, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into:

The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa, and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term elbow is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates forelimb plus joint is used.
Ischial bursitis is inflammation of the synovial bursa located between gluteus maximus muscle and ischial tuberosity.
In the skeleton of humans and other animals, a tubercle, tuberosity or apophysis is a protrusion or eminence that serves as an attachment for skeletal muscles. The muscles attach by tendons, where the enthesis is the connective tissue between the tendon and bone. A tuberosity is generally a larger tubercle.
References
- ↑ "Definition: Bicipitoradial Bursa". MediLexicon. Open Publishing. 30 April 2005. Archived from the original on 8 November 2016. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
- 1 2 3 Kegels, Lore; Van Oyen, Jan; Siemons; Verdonk, René (June 2006). "Bicipitoradial bursitis. A case report" (PDF). Acta Orthopaedica Belgica. 72 (3): 362–365. PMID 16889153. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2012.
- ↑ Sofka, Carolyn M.; Adler, Ronald S. (July 2004). "Sonography of Cubital Bursitis". American Journal of Roentgenology. 183 (1): 51–53. doi:10.2214/ajr.183.1.1830051. ISSN 1546-3141. PMID 15208108.