
Colchicaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes 15 genera with a total of about 285 known species according to Christenhusz and Byng in 2016.

Moringa is the sole genus in the plant family Moringaceae. It contains 13 species, which occur in tropical and subtropical regions of Africa and Asia and that range in size from tiny herbs to massive trees. Moringa species grow quickly in many types of environments.

Actaea, commonly called baneberry, bugbane and cohosh, is a genus of flowering plants of the family Ranunculaceae, native to subtropical, temperate and subarctic regions of Europe, Asia and North America.

Jeffrey Barry Harborne FRS was a British chemist who specialised in phytochemistry. He was Professor of Botany at the University of Reading, 1976–93, then Professor emeritus. He contributed to more than 40 books and 270 research papers and was a pioneer in ecological biochemistry, particularly in the complex chemical interactions between plants, microbes and insects.
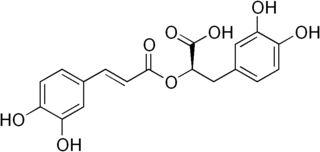
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.

The Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics is an annual scientific journal published by Annual Reviews. The journal was established in 1970 as the Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics and changed its name beginning in 2003. It publishes invited review articles on topics considered to be timely and important in the fields of ecology, evolutionary biology, and systematics. As of 2023, Journal Citation Reports gave the journal a 2022 impact factor of 11.8, ranking it third of 169 journals in the "Ecology" category and third of 52 journals in "Evolutionary Biology".

Evolutionary physiology is the study of the biological evolution of physiological structures and processes; that is, the manner in which the functional characteristics of individuals in a population of organisms have responded to natural selection across multiple generations during the history of the population. It is a sub-discipline of both physiology and evolutionary biology. Practitioners in the field come from a variety of backgrounds, including physiology, evolutionary biology, ecology, and genetics.

Plantago maritima, the sea plantain, seaside plantain or goose tongue, is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. It has a subcosmopolitan distribution in temperate and Arctic regions, native to most of Europe, northwest Africa, northern and central Asia, northern North America, and southern South America.

Forrer's grass frog or Forrer's leopard frog is a species of frog in the family Ranidae found in Mexico and Central America through Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua to Costa Rica. It is a widespread and common frog found in lowland and seasonal tropical forests. It can also adapt to man-made habitats such as flooded agricultural lands and other water content systems. Reproduction requires permanent pools and lagoons.

Alvaradoa is a genus of plants in the family Picramniaceae.

The Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society is a scientific journal publishing original papers relating to the taxonomy of all plant groups and fungi, including anatomy, biosystematics, cytology, ecology, ethnobotany, electron microscopy, morphogenesis, palaeobotany, palynology and phytochemistry.

Polygodial is chemical compound found in dorrigo pepper, mountain pepper, horopito, canelo, paracress, water-pepper, and Dendrodoris limbata.

Biebersteinia is a genus containing five species, of herbs in the flowering plant order Sapindales. They occur from East Mediterranean to West Siberia and Central Asia. They are normally stemless and have tuberous rhizomes.
Theodore Garland Jr. is a biologist specializing in evolutionary physiology at the University of California, Riverside.

Scorzoneroides or hawkbits is a genus of plants of the tribe Cichorieae within the family Asteraceae.

Verbascoside is a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.
Tony Swain (1922–1987) was a chemist known for his definition of a plant polyphenol with Bate-Smith, Haslam and White, which includes specific structural characteristics common to all phenolics having a tanning property. It is referred to as the White–Bate-Smith–Swain–Haslam (WBSSH) definition.

Homoisoflavonoids (3-benzylidenechroman-4-ones) are a type of phenolic compounds occurring naturally in plants.
An attractant is any chemical that attracts an organism, e.g. i) synthetic lures; ii) aggregation and sex pheromones ; and iii) synomone















