
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity ; the sustainable use of its components; and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. Its objective is to develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, and it is often seen as the key document regarding sustainable development.

Environmental laws are laws that protect the environment. Environmental law is the collection of laws, regulations, agreements and common law that governs how humans interact with their environment. This includes environmental regulations; laws governing management of natural resources, such as forests, minerals, or fisheries; and related topics such as environmental impact assessments. Environmental law is seen as the body of laws concerned with the protection of living things from the harm that human activity may immediately or eventually cause to them or their species, either directly or to the media and the habits on which they depend.

Biodiversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than one-fifth of Earth's terrestrial area and contain about 50% of the world's species. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity for both marine and terrestrial taxa.

Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests and woodlands for associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management plays an essential role in the creation and modification of habitats and affects ecosystem services provisioning.

Bioprospecting is the exploration of natural sources for small molecules, macromolecules and biochemical and genetic information that could be developed into commercially valuable products for the agricultural, aquaculture, bioremediation, cosmetics, nanotechnology, or pharmaceutical industries. In the pharmaceutical industry, for example, almost one third of all small-molecule drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 1981 and 2014 were either natural products or compounds derived from natural products.
The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, is a comprehensive international agreement in harmony with the Convention on Biological Diversity, which aims at guaranteeing food security through the conservation, exchange and sustainable use of the world's plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (PGRFA), the fair and equitable benefit sharing arising from its use, as well as the recognition of farmers' rights. It was signed in 2001 in Madrid, and entered into force on 29 June 2004.
In situ conservation is the on-site conservation or the conservation of genetic resources in natural populations of plant or animal species, such as forest genetic resources in natural populations of tree species. This process protects the inhabitants and ensures the sustainability of the environment and ecosystem.

Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, groups and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where it is possible, to repair damage and reverse trends.

The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research is a research and development (R&D) organisation in India to promote scientific, industrial and economic growth. Headquartered in New Delhi, it was established as an autonomous body in 1942 under the aegis of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (DSIR), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India. CSIR is among the largest publicly funded R&D organisations in the world. CSIR has pioneered sustained contribution to science and technology (S&T) human resource development in India.
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK), folk knowledge, and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities.

The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) is an autonomous organisation or governmental agency under the MoEFCC, Government of India. Headquartered in Dehradun, its functions are to conduct forestry research; transfer the technologies developed to the states of India and other user agencies; and to impart forestry education. The council has 9 research institutes and 4 advanced centres to cater to the research needs of different bio-geographical regions. These are located at Dehradun, Shimla, Ranchi, Jorhat, Jabalpur, Jodhpur, Bengaluru, Coimbatore, Prayagraj, Chhindwara, Aizawl, Hyderabad and Agartala.

The East Kolkata Wetlands, are a complex of natural and human-made wetlands lying east of the city of Calcutta (Kolkata), of West Bengal in India. The wetlands cover 125 square kilometres and include salt marshes, and agricultural fields, sewage farms and settling ponds. The wetlands are also used to treat Kolkata's sewage, and the nutrients contained in the wastewater sustain fish farms and agriculture.

Natural resource management (NRM) is the management of natural resources such as land, water, soil, plants and animals, with a particular focus on how management affects the quality of life for both present and future generations (stewardship).

The environment of India comprises some of the world's most biodiverse ecozones. The Deccan Traps, Gangetic Plains and the Himalayas are the major geographical features. The country faces different forms of pollution as its major environmental issue and is more vulnerable to the effects of climate change being a developing nation. India has laws protecting the environment and is one of the countries that signed the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) treaty. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change and each particular state forest departments plan and implement environmental policies throughout the country.
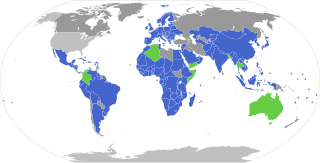
The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity, also known as the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS), is a 2010 supplementary agreement to the 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD). Its aim is the implementation of one of the three objectives of the CBD: the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources, thereby contributing to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity. It sets out obligations for its contracting parties to take measures in relation to access to genetic resources, benefit-sharing and compliance.

The National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) is a statutory autonomous body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Government of India established in 2003 to implement the provisions under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, after India signed Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) in 1992.

Plant genetic resources describe the variability within plants that comes from human and natural selection over millennia. Their intrinsic value mainly concerns agricultural crops.

Biopiracy is the unauthorized appropriation of knowledge and genetic resources of farming and indigenous communities by individuals or institutions seeking exclusive monopoly control through patents or intellectual property. While bioprospecting is the act of exploring natural resources for undiscovered chemical compounds with medicinal or anti-microbial properties, commercial success from bioprospecting leads to the company's attempt at protecting their intellectual property rights on indigenous medicinal plants, seeds, genetic resources, and traditional medicines.
Digital sequence information (DSI) is a placeholder term used in international policy fora, particularly the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), to refer to data derived from dematerialized genetic resources (GR).

The Forestry Department, also referred to as the Forest Department, is a department overseen by the Ministry of Primary Resources and Tourism (MPRT). Through the department practices sustainable forest management to ensure that forest resources can be used and utilized continuously in addition to balancing environmental, economic and social interests as well as the well-being of the people and the country.















