
Bismarckjugend, 'Bismarck Youth', was an anti-Marxist youth movement in Weimar Germany. Bismarckjugend was the youth wing of the monarchist German National People's Party (DNVP).

Bismarckjugend, 'Bismarck Youth', was an anti-Marxist youth movement in Weimar Germany. Bismarckjugend was the youth wing of the monarchist German National People's Party (DNVP).
The organization was founded in Hanover in 1922, through the unification of various local youth groups close to DNVP. DNVP was the last of the established parties in the Reichstag to have a national youth wing of its own. The organization was politically completely dependent on the DNVP. The youth movement was initially led by Wilhelm Kube. Bismarckjugend branches were at first centred in the industrial areas of Germany. Later the movement spread its wings to the rural eastern regions of the country. [1] [2]
Soon after the founding of the national youth organization (in 1922), Hermann Otto Sieveking became its chairman. Under Sieveking's leadership, the organization developed a paramilitary character. It also began to organize annual national youth meetings. [1]
By mid-1923 Bismarckjugend entered a period of continuous decay. Generally DNVP was associated with the old order and was unpopular amongst the younger generation. [2]

In July 1928 the seventh national youth meeting of Bismarcksjugend has held in Friedrichsruh to commemorate the 30th anniversary of Otto von Bismarck's death. Friedrichsruh is the site of Bismarck's mausoleum. The meeting had particular importance to the mother party, as it was an important event to show strength after the meagre electoral result for DNVP in May the same year. [1] By the end of the 1920s Bismarckjugend had been revitalized and had expanded its membership. [2]
In the 1933 National Socialist take-over, parties other than the NSDAP either dissolved themselves or were banned. On June 27, 1933 a 'Friendly Agreement' was signed between the DNVP (renamed in 1932 into German National Front (DNF)) and the NSDAP, following which the DNF dissolved itself. [3] In 1935, the wearing of the Bismarckjugend uniform was banned by law. [4]
At the time of the founding of the organization, its name was National League of Youth Groups of the German National People's Party (Reichsverband der Jugendgruppen der Deutschnationalen Volkspartei). In the autumn of 1922 the name Bismarck Youth of the German National People's Party (Bismarckjugend der Deutschnationalen Volkspartei) was adopted, in short Bismarckjugend. [2] The name referred to Otto von Bismarck, and sought to link the organization with Bismarck's historical legacy. Bismarck's grandson Otto gave his permission to the organization to use his grandfather's name. [1]
Bismarckjugend organized men and women between the ages of 14 and 25. By 1928, the organization had 800 local organizations around Germany. Its total membership had reached 42,000, making it the second largest youth movement in the country at the time (after the SPD Socialist Worker Youth, Sozialistische Arbeiter-Jugend). Generally the movement had a stronger appeal in Protestant areas. Strongholds included Berlin, Magdeburg, Hesse, Thuringia, Lower Saxony, Pomerania, Württemberg and Hamburg. [1]
Most of the members came from bourgeois or noble families. However the single largest affiliate body of the movement, the Bismarck League Berlin, had an overwhelmingly working class membership. As of 1922 the Bismarck League Berlin had around 6,000 affiliates, approximately 80% from working-class families. The Berlin affiliate had been founded in 1920. [1]
Bismarckjugend published Deutsches Echo ('German Echo'). [1]

The German People's Party was a conservative-liberal political party during the Weimar Republic that was the successor to the National Liberal Party of the German Empire. Along with the left-liberal German Democratic Party (DDP), it represented political liberalism in Germany between 1918 and 1933.

The German Democratic Party was a liberal political party in the Weimar Republic, considered centrist or centre-left. Along with the right-liberal German People's Party, it represented political liberalism in Germany between 1918 and 1933. It was formed in 1918 from the Progressive People's Party and the liberal wing of the National Liberal Party, both of which had been active in the German Empire.

Der Stahlhelm, Bund der Frontsoldaten, commonly known as Der Stahlhelm, was a German First World War veteran's organisation existing from 1918 to 1935. In the late days of the Weimar Republic, it was closely affiliated to the monarchist German National People's Party (DNVP), placed at party gatherings in the position of armed security guards.
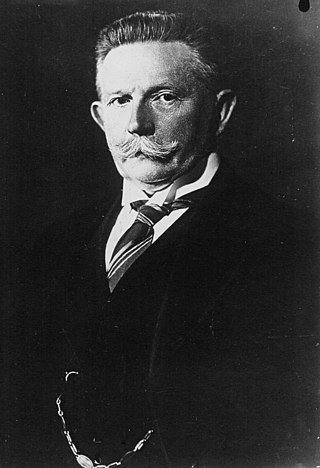
Alfred Ernst Christian Alexander Hugenberg was an influential German businessman and politician. An important figure in nationalist politics in Germany during the first three decades of the twentieth century, Hugenberg became the country's leading media proprietor during the 1920s. As leader of the German National People's Party, he played a part in helping Adolf Hitler become chancellor of Germany and served in his first cabinet in 1933, hoping to control Hitler and use him as his tool. The plan failed, and by the end of 1933 Hugenberg had been pushed to the sidelines. Although he continued to serve as a guest member of the Reichstag until 1945, he wielded no political influence. Following World War II, he was interned by the British in 1946 and classified as "exonerated" in 1951 after undergoing denazification.

The Centre Party, officially the German Centre Party and also known in English as the Catholic Centre Party, is a Christian democratic political party in Germany. It was most Influential in the German Empire and Weimar Republic. Formed in 1870, it successfully battled the Kulturkampf waged by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck against the Catholic Church. It soon won a quarter of the seats in the Reichstag, and its middle position on most issues allowed it to play a decisive role in the formation of majorities. The party name Zentrum (Centre) originally came from the fact that Catholic representatives would take up the middle section of seats in parliament between the social democrats and the conservatives.

The German National People's Party was a national-conservative and monarchist political party in Germany during the Weimar Republic. Before the rise of the Nazi Party, it was the major nationalist party in Weimar Germany. It was an alliance of conservative, nationalist, monarchist, völkisch, and antisemitic elements supported by the Pan-German League. Ideologically, the party was described as subscribing to authoritarian conservatism, German nationalism, monarchism, and from 1931 onwards also to corporatism in economic policy. It held anti-communist, anti-Catholic, and antisemitic views. On the left–right political spectrum, it belonged on the right-wing, and is classified as far-right in its early years and then again from the late 1920s when it moved back rightward.

The Frontier March of Posen–West Prussia was a province of Prussia from 1920/1922 to 1938, covering most of lands of historical Greater Poland that were not included in the Second Polish Republic. Posen–West Prussia was established in 1922 as a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, formed from merging three remaining non-contiguous territories of Posen and West Prussia, which had lost the majority of their territory to the Second Polish Republic following the Greater Poland Uprising. From 1934, Posen–West Prussia was de facto ruled by Brandenburg until it was dissolved by Nazi Germany, effective 1 October 1938 and its territory divided between the provinces of Pomerania, Brandenburg and Silesia. Schneidemühl was the provincial capital. Today, lands of the province are entirely contained within Poland.

The Bavarian People's Party was a Catholic political party in Bavaria during the Weimar Republic. After the collapse of the German Empire in 1918, it split away from the national-level Catholic Centre Party and formed the BVP in order to pursue a more conservative and particularist Bavarian course. It consistently had more seats in the Bavarian state parliament than any other party and provided all Bavarian minister presidents from 1920 on. In the national Reichstag it remained a minor player with only about three percent of total votes in all elections. The BVP disbanded shortly after the Nazi seizure of power in early 1933.
The Conservative People's Party was a short-lived conservative and Christian democratic political party of the moderate right in the last years of the Weimar Republic. It broke away from the German National People's Party (DNVP) in July 1930 as a result of the DNVP's increasing shift to the right under the leadership of Alfred Hugenberg. It remained a numerically insignificant minor party but was represented in the governments of Heinrich Brüning (1930–1932). The KVP folded on 31 March 1933 after it ran out of funds.
In the fourteen years the Weimar Republic was in existence, some forty parties were represented in the Reichstag. This fragmentation of political power was in part due to the use of a peculiar proportional representation electoral system that encouraged regional or small special interest parties and in part due to the many challenges facing the nascent German democracy in this period.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 5 March 1933, after the Nazi seizure of power on 30 January and just six days after the Reichstag fire. The election saw Nazi stormtroopers unleash a widespread campaign of violence against the Communist Party (KPD), left-wingers, trade unionists, the Social Democratic Party and the Centre Party. They were the last multi-party elections in a united Germany until 1990.

The Harzburg Front was a short-lived radical right-wing, anti-democratic political alliance in Weimar Germany, formed in 1931 as an attempt to present a unified opposition to the government of Chancellor Heinrich Brüning. It was a coalition of the national conservative German National People's Party (DNVP) under millionaire press-baron Alfred Hugenberg with Adolf Hitler's National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP), the leadership of Der Stahlhelm paramilitary veterans' association, the Agricultural League and the Pan-German League organizations.

The Free State of Prussia was one of the constituent states of Germany from 1918 to 1947. The successor to the Kingdom of Prussia after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, it continued to be the dominant state in Germany during the Weimar Republic, as it had been during the empire, even though most of Germany's post-war territorial losses in Europe had come from its lands. It was home to the federal capital Berlin and had 62% of Germany's territory and 61% of its population. Prussia changed from the authoritarian state it had been in the past and became a parliamentary democracy under its 1920 constitution. During the Weimar period it was governed almost entirely by pro-democratic parties and proved more politically stable than the Republic itself. With only brief interruptions, the Social Democratic Party (SPD) provided the Minister President. Its Ministers of the Interior, also from the SPD, pushed republican reform of the administration and police, with the result that Prussia was considered a bulwark of democracy within the Weimar Republic.
The Agricultural League or National Rural League was a German agrarian association during the Weimar Republic which was led by landowners with property east of the Elbe. It was allied with the German National People's Party and later the National Socialist German Workers' Party
Reinhold Quaatz was a German conservative politician who was active during the Weimar Republic. Although associated with right-wing and völkisch tendencies, Quaatz was half-Jewish in ancestry.
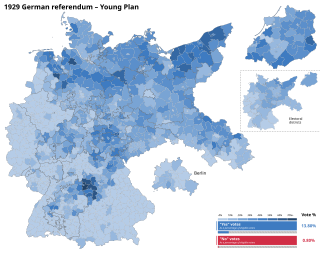
The 1929 German Referendum was an attempt during the Weimar Republic to use popular legislation to annul the agreement in the Young Plan between the German government and the World War I opponents of the German Reich regarding the amount and conditions of reparations payments. The referendum was the result of the initiative "Against the Enslavement of the German People " launched in 1929 by right-wing parties and organizations. It called for an overall revision of the Treaty of Versailles and stipulated that government officials who accepted new reparation obligations would be committing treason.

The 1931 Prussian Landtag referendum was an attempt to prematurely dissolve the sitting session of the Landtag (parliament) of the Weimar German state of Prussia. The referendum, which took place according to Article 6 of the 1920 Prussian Constitution, was triggered by a petition launched in the spring of 1931 by the anti-republican veterans' organization Der Stahlhelm. It was supported by several right-wing parties including the Nazis, as well as by the Communist Party of Germany (KPD). Even though 93.9% of those voting on 9 August 1931 opted to dissolve the Landtag, the referendum failed because the turnout of 39.2% did not meet the minimum 50% requirement.
The presidential cabinets were a succession of governments of the Weimar Republic whose legitimacy derived exclusively from presidential emergency decrees. From April 1930 to January 1933, three chancellors, Heinrich Brüning, Franz von Papen, and Kurt von Schleicher were appointed by President Paul von Hindenburg, and governed without the consent of the Reichstag, Germany's lower house of parliament. After Schleicher's tenure, the leader of the Nazis Adolf Hitler succeeded to the chancellorship and regained the consent of the Reichstag by obtaining a majority in the March 1933 German federal election with DNVP.
Herbert von Bismarck was a German lawyer and politician. In 1930 he switched to national politics, serving between 1930 and 1933 as a Member of the Reichstag in Berlin. He represented the conservative-nationalist DNVP (party). During a couple of months at the start of 1933 he served very briefly as secretary of state at the Prussian Interior Ministry before being placed in "temporary retirement". After the war he returned to public life between 1948 and 1952 as the first spokesman for the new Pommersche Landsmannschaft, an association created to represent the interests of those who had been expelled from their homes in Pomerania.