
Castlefield is an inner-city conservation area in Manchester, North West England. The conservation area which bears its name is bounded by the River Irwell, Quay Street, Deansgate and Chester Road. It was the site of the Roman era fort of Mamucium or Mancunium which gave its name to Manchester. It was the terminus of the Bridgewater Canal, the world's first industrial canal, built in 1764; the oldest canal warehouse opened in 1779. The world's first passenger railway terminated here in 1830, at Liverpool Road railway station and the first railway warehouse opened here in 1831.

Severn Trent plc is a water company based in Coventry, England. It supplies 4.6 million households and business across the Midlands and Wales.

Rochdale is a town in Greater Manchester, England, and the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale. In the 2021 census the town had a population of 111,261, compared to 223,773 for the wider borough. Rochdale is in the foothills of the South Pennines and lies in the dale (valley) of the River Roch, 5 miles (8 km) northwest of Oldham and 10 miles (16 km) northeast of Manchester.

The Croydon Canal ran 9+1⁄4 miles (15 km) from Croydon, via Forest Hill, to the Grand Surrey Canal at New Cross in south London, England. It opened in 1809 and closed in 1836, the first canal to be abandoned by an Act of Parliament.

Milnrow is a town within the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale, in Greater Manchester, England. It lies on the River Beal at the foothills of the South Pennines, and forms a continuous urban area with Rochdale. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) east of Rochdale town centre, 10 miles (16.1 km) north-northeast of Manchester, and spans from Windy Hill in the east to the Rochdale Canal in the west. Milnrow is adjacent to junction 21 of the M62 motorway, and includes the village of Newhey, and hamlets at Tunshill and Ogden.

The River Irwell is a tributary of the River Mersey in north west England. It rises at Irwell Springs on Deerplay Moor, approximately 1+1⁄2 miles north of Bacup and flows southwards for 39 mi (63 km) to meet the Mersey near Irlam. The Irwell marks the boundary between Manchester and Salford, and its lower reaches have been canalised and now form part of the Manchester Ship Canal.

Littleborough is a village in the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England, in the upper Roch Valley by the foothills of the South Pennines, 3 miles (4.8 km) northeast of Rochdale and 13 miles (20.9 km) northeast of Manchester; Milnrow and the M62 motorway are to the south, and the rural uplands of Blackstone Edge to the east. According to the 2001 census, Littleborough, and its suburbs of Calderbrook, Shore and Smithy Bridge, had a population of 13,807.

The Rochdale Canal is in Northern England, between Manchester and Sowerby Bridge, part of the connected system of the canals of Great Britain. Its name refers to the town of Rochdale through which it passes.

United Utilities Group plc (UU), the United Kingdom's largest listed water company, was founded in 1995 as a result of the merger of North West Water and NORWEB. The group manages the regulated water and waste water network in North West England, which includes Cumbria, Greater Manchester, Lancashire, Merseyside, most of Cheshire and a small area of Derbyshire, which have a combined population of more than seven million.

Hollingworth Lake is a 130-acre (53 ha) reservoir at Smithy Bridge in Littleborough, Greater Manchester, England. It was originally built as the main water source for the Rochdale Canal, but developed as a tourist resort from the 1860s. Hotels were built around it, helped by the arrival of the railway in 1839, which brought day-trippers and weekend visitors from Manchester, Bradford and Leeds.

Blackstone Edge is a gritstone escarpment at 472 metres (1,549 ft) above sea level in the Pennine hills surrounded by moorland on the boundary between Greater Manchester and West Yorkshire in England.

Toddbrook Reservoir, a feeder for the Peak Forest Canal, opened in 1838. It is sited above the town of Whaley Bridge in the Derbyshire High Peak area of England. The reservoir is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) providing habitats for herons, ducks and other animals and fish, while rare mosses and liverworts grow on its shores, particularly short-lived species that grow on seasonally exposed mud. The reservoir is used for sailing and angling. The Peak District Boundary Walk runs around the eastern end of the reservoir. The reservoir is owned by the Canal & River Trust and, like the nearby Combs Reservoir, is a feeder reservoir for the Peak Forest Canal. The feeder runs through Whaley Bridge, and with the Combs feed enters the canal system in a pool close to the transhipment shed at the Whaley Bridge canal basin.

The transport infrastructure of Greater Manchester is built up of numerous transport modes and forms an integral part of the structure of Greater Manchester and North West England – the most populated region outside of South East England which had approximately 301 million annual passenger journeys using either buses, planes, trains or trams in 2014. Its position as a national city of commerce, education and cultural importance means the city has one of the largest and most thorough transport infrastructures which is heavily relied upon by its 2.8 million inhabitants in the Greater Manchester conurbation and further afield in the North West region. Public transport comes under the jurisdiction of Transport for Greater Manchester.

The Engine Arm or Birmingham Feeder Arm near Smethwick, West Midlands, England, is a short canal which was originally part of a feeder tunnel for a pumping engine. When the Smethwick flight of locks were reduced from six to three, the pumping engine was moved to a new site, which allowed part of the feeder tunnel to be opened up and made navigable, so that coal supplies for the engine could be delivered by barge. The Engine Arm also supplied the pumped water to the 473-foot (144 m) Wolverhampton level of the lowered summit. The arm was extended between 1825 and 1830 by Thomas Telford to carry water from Rotton Park Reservoir to the Old Main Line of the BCN Main Line Canal, and the Engine Arm Aqueduct was inserted to carry it over the new main line constructed at that time, which was 20 feet (6.1 m) lower. The arm is now managed by the Canal and River Trust and the basin beyond the site of the pumping station, which was replaced by a new engine house near Brasshouse Lane bridge in 1892, is used for residential moorings.

Rochdale was, from 1856 to 1974, a local government district coterminate with the town of Rochdale in the northwest of England.
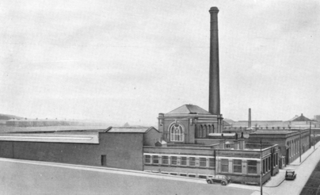
Harp Mill was a former cotton spinning mill in the Castleton, Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England. Queensway, Castleton was a hub of cotton mills including the three 't', Th'Arrow, Th'Harp, and Th'Ensor. The 1908 Castleton map includes: Marland Cotton Mill, Castleton Cotton Mill, Globe Works, Arrow Cotton Mill, Harp Cotton Mill, Globe Leather Works, Castleton Size Works and Castleton Iron Works. Th'Harp was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. The site now houses industrial units.

Mars Mill was a former cotton spinning mill in Castleton, Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England. Castleton joined the Borough of Rochdale in 1899. Queensway, Castleton was a hub of cotton mills; Mars, Marland, and Castleton Mill were a group of three. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in 1935 and passed to Courtaulds in 1964 and demolished in the 1990s; Marland survived until 2004.
The Grand Contour Canal in England and Wales was intended to enhance and upgrade the British canal system, but was never built. This canal was proposed in 1943, and again ten years later, by J F Pownall. Pownall observed that there was a natural 'contour' down the spine of England, around the 300 ft level that connected several of the most populated areas. He put forward the idea that this contour could be used to define the course of a large European sized canal which contained no locks except at its entry and exit points. It would also serve as a water grid capable of distributing domestic water supply around England as need arises.



















