Related Research Articles

The Monon Railroad, also known as the Chicago, Indianapolis, and Louisville Railway from 1897 to 1971, was an American railroad that operated almost entirely within the state of Indiana. The Monon was merged into the Louisville and Nashville Railroad in 1971, and much of the former Monon right of way is owned today by CSX Transportation. In 1970, it operated 540 miles (870 km) of road on 792 miles (1,275 km) of track; that year it reported 1320 million ton-miles of revenue freight and zero passenger-miles.

The Southern Railway was a class 1 railroad based in the Southern United States between 1894 and 1982, when it merged with the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) to form the Norfolk Southern Railway. The railroad was the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894.

The Florida West Coast Railroad was a 13-mile (21-kilometre) railroad owned by CSF Acquisition, Inc., which acquired it from CSX on December 13, 1987 as its first acquisition. Archived 2004-10-18 at the Wayback Machine It ran west from a CSX line at Newberry to Trenton.
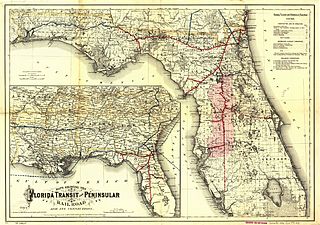
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.

The Georgia Southwestern Railroad is a Class III short line railroad company that operates over 234 miles (377 km) of track in southwestern Georgia and southeastern Alabama. Beginning in 1989 as a division of the South Carolina Central Railroad on a pair of former CSX Transportation lines, the railroad has since undergone a number of transformations through abandonments and acquisitions, before arriving at its current form. The railroad was formerly a RailAmerica property before going independent, and in 2008 it was acquired by Genesee & Wyoming Inc.
The Wilmington and Weldon Railroad (W&W) name began use in 1855, having been originally chartered as the Wilmington and Raleigh Railroad in 1834. When it opened in 1840, the line was the longest railroad in the world with 161.5 miles (259.9 km) of track. It was constructed in 4 ft 8 in gauge. At its terminus in Weldon, North Carolina, it connected with the Seaboard and Roanoke Railroad and the Petersburg Railroad. The railroad also gave rise to the city of Goldsboro, North Carolina, the midpoint of the W&W RR and the railroad intersection with the North Carolina Railroad. It’s been more than 50 years since passenger rail linked Wilmington and Raleigh, but there’s a renewed push to bring back a passenger route between the two cities. The latest feasibility study, prepared by Florida-based firm WGI Inc., compares two potential route options linking Wilmington with Raleigh: a western route through Fayetteville and an eastern route through Goldsboro.
The Charleston and Savannah Railway was a 19th-century American railroad serving the coastal states of South Carolina and Georgia and running through part of the South Carolina Lowcountry. Its name varied slightly over time:

The East Tennessee Railway, L.P. is a short line railroad connecting CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway in Johnson City, Tennessee. Since 2005, the railroad has been owned by Genesee and Wyoming, an international operator of short line railroads, as part of its Rail Link group. The railroad uses a single diesel locomotive, SW1200 #214, to serve a small number of industries and a transloading facility, as well as to provide interchange services between NS and CSX.
Pickens Railway is a shortline railroad that has operated on two separate divisions in the Upstate Region of South Carolina:

The Carolina Piedmont Railroad is a class III railroad and subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming Inc. operating in the Upstate region of South Carolina. From an interchange with CSX Transportation at Laurens the railroad runs 34 miles (55 km) to the northwest, terminating at East Greenville.
Cliffside Railroad was a Class III railroad operating freight service in southwestern North Carolina from 1905 until service ended in 1987. The line was formally abandoned in 1992.
The Greenville and Northern Railroad was a shortline railroad formerly operating between Travelers Rest and Greenville, South Carolina, 11.3 miles (18.2 km). The railroad was part of the Pinsly Railroad Company after 1957 before being purchased by RailTex in 1997. Operations ended in February 1998 and the railroad was abandoned in 2005.
The Port Royal Railroad was a South Carolina railroad that was constructed following the American Civil War. The line was chartered in 1856 but wasn't built until 1870. By 1871, it ran from Port Royal, South Carolina, to Yemassee, South Carolina. It was extended to Augusta, Georgia in 1873. That same year, the company declared bankruptcy and was sold to the new Port Royal and Augusta Railway in 1878.
The Barnwell Railway was a shortline railroad that served western South Carolina in the late 19th century.
The Carolina Midland Railway was a railroad that served western South Carolina in the late 19th century.
The Edgefield, Trenton and Aiken Railroad was a railroad that served South Carolina immediately after the end of the Reconstruction Era of the United States.
The Blackville and Alston Railroad was a South Carolina railroad company chartered in the latter half of the 19th century.
The Union and Glenn Springs Railroad was a South Carolina railroad that served the Upstate region of the state in the early part of the 20th century.

The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Chicago, Illinois; Kansas City, Missouri; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; St. Louis, Missouri; and Toledo, Ohio.

The Prisma Health Swamp Rabbit Trail is a 19.9-mile (32.0 km) multi-use rail trail in Greenville County, South Carolina, that largely follows the bed of a former railroad that had been nicknamed after the indigenous swamp rabbit. South-to-north the current trail begins at Greenville Technical College, crosses the city of Greenville, proceeds through Falls Park and the campus of Furman University, and ends about a mile north of the Travelers Rest city limits.
References
- ↑ Abandoned Rails, The Former Swamp Rabbit Line
- ↑ Abandoned Rails, The Former Swamp Rabbit Line
- ↑ Abandoned Rails, The Former Swamp Rabbit Line
- ↑ South Carolina Railroads, Carolina Midland Railway Archived 2009-05-24 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Poor's Manual of Railroads, 1892
- ↑ South Carolina Railroads, Blackville, Alston & Newberry Railroad Archived November 21, 2008, at the Wayback Machine