Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade, is the buildup of fluid in the pericardium, resulting in compression of the heart. Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically include those of obstructive shock including shortness of breath, weakness, lightheadedness, and cough. Other symptoms may relate to the underlying cause.
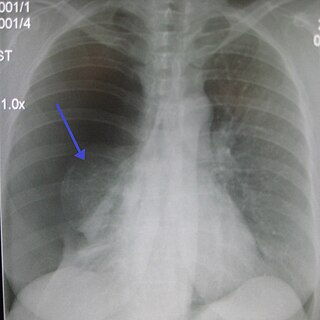
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, and the amount of air in the space between chest wall and lungs increases; this is called a tension pneumothorax. This can cause a steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. This leads to a type of shock called obstructive shock, which can be fatal unless reversed. Very rarely, both lungs may be affected by a pneumothorax. It is often called a "collapsed lung", although that term may also refer to atelectasis.

Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause.

Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the nose, past the throat, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the mouth. Abraham Louis Levin invented the NG tube. Nasogastric tube is also known as Ryle's tube in Commonwealth countries, after John Alfred Ryle.

A chest tube is a surgical drain that is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space or the mediastinum in order to remove clinically undesired substances such as air (pneumothorax), excess fluid, blood (hemothorax), chyle (chylothorax) or pus (empyema) from the intrathoracic space. An intrapleural chest tube is also known as a Bülau drain or an intercostal catheter (ICC), and can either be a thin, flexible silicone tube, or a larger, semi-rigid, fenestrated plastic tube, which often involves a flutter valve or underwater seal.

A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure to gain access into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by surgeons to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, or the esophagus, or for access to the thoracic aorta or the anterior spine. The purpose of a thoracotomy is the first step used to facilitate thoracic surgeries including lobectomy or pneumonectomy for lung cancer or to gain thoracic access in major trauma.

A hemothorax is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may include reduced breath sounds on the affected side and a rapid heart rate. Hemothoraces are usually caused by an injury, but they may occur spontaneously due to cancer invading the pleural cavity, as a result of a blood clotting disorder, as an unusual manifestation of endometriosis, in response to a collapsed lung, or rarely in association with other conditions.

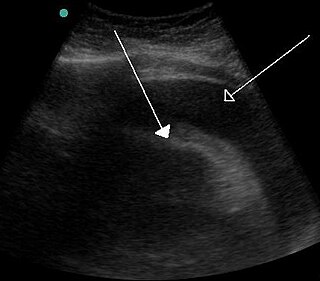
A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of the serous membrane enclose the pericardial cavity between them. This pericardial space contains a small amount of pericardial fluid. The fluid is normally 15-50 mL in volume. The pericardium, specifically the pericardial fluid provides lubrication, maintains the anatomic position of the heart in the chest, and also serves as a barrier to protect the heart from infection and inflammation in adjacent tissues and organs.
Hemopneumothorax, or haemopneumothorax is the condition of having air in the chest cavity (pneumothorax) and blood in the chest cavity (hemothorax). A hemothorax, pneumothorax, or the combination of both can occur due to an injury to the lung or chest.

Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical trauma or impactful force to a body part, often occurring with road traffic collisions, direct blows, assaults, injuries during sports, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound and bruise.

A chest injury, also known as chest trauma, is any form of physical injury to the chest including the ribs, heart and lungs. Chest injuries account for 25% of all deaths from traumatic injury. Typically chest injuries are caused by blunt mechanisms such as direct, indirect, compression, contusion, deceleration, or blasts- caused by motor vehicle collisions or penetrating mechanisms such as stabbings.
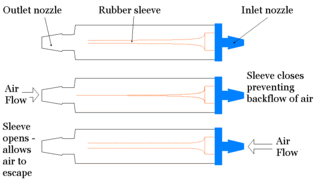
A flutter valve is a one-way valve used in respiratory medicine to prevent air from travelling back along a chest tube. One can also use a chest drainage management system, which typically enables vacuum to be applied along with quantifying the effluent. However, it is much larger with more tubing, which may encumber the patient.

Penetrating trauma is an injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound. The penetrating object may remain in the tissues, come back out the way it entered, or pass through the tissues and exit from another area. An injury in which an object enters the body or a structure and passes all the way through is called a perforating injury, while penetrating trauma implies that the object does not pass through. Perforating trauma is associated with an entrance wound and an often larger exit wound.

In medicine, a port is a small medical appliance that is installed beneath the skin. A catheter connects the port to a vein. Under the skin, the port has a septum through which drugs can be injected and blood samples can be drawn many times, usually with less discomfort for the patient than a more typical "needle stick".
A thoracostomy is a small incision of the chest wall, with maintenance of the opening for drainage. It is most commonly used for the treatment of a pneumothorax. This is performed by physicians, paramedics, and nurses usually via needle thoracostomy, manually using a hemostat and the provider's finger, or with the insertion of a thoracostomy tube.

A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut. An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung, while pulmonary contusion does not. Pulmonary laceration is commonly caused by penetrating trauma but may also result from forces involved in blunt trauma such as shear stress. A cavity filled with blood, air, or both can form. The injury is diagnosed when collections of air or fluid are found on a CT scan of the chest. Surgery may be required to stitch the laceration, to drain blood, or even to remove injured parts of the lung. The injury commonly heals quickly with few problems if it is given proper treatment; however it may be associated with scarring of the lung or other complications.

Subcutaneous emphysema occurs when gas or air accumulates and seeps under the skin, where normally no gas should be present. Subcutaneous refers to the subcutaneous tissue, and emphysema refers to trapped air pockets resembling the pneumatosis seen in pulmonary emphysema. Since the air generally comes from the chest cavity, subcutaneous emphysema usually occurs around the upper torso, such as on the chest, neck, face, axillae and arms, where it is able to travel with little resistance along the loose connective tissue within the superficial fascia. Subcutaneous emphysema has a characteristic crackling-feel to the touch, a sensation that has been described as similar to touching warm Rice Krispies. This sensation of air under the skin is known as subcutaneous crepitation, a form of Crepitus.

Tracheobronchial injury is damage to the tracheobronchial tree. It can result from blunt or penetrating trauma to the neck or chest, inhalation of harmful fumes or smoke, or aspiration of liquids or objects.
Prehospital ultrasound is the specialized application of ultrasound by paramedics, to guide immediate care and treatment procedures. Like conventional ultrasound, it is a device that produces cyclic sound pressure to penetrate a medium (flesh) and reveal details about the inner structure of the medium.
In medicine, vascular access is a means of accessing the bloodstream through the peripheral or central blood vessels in order to obtain blood or deliver medications including chemotherapy. A vascular access procedure involves insertion of a sterile plastic tube called a catheter into a blood vessel. Types of catheters can be either peripherally or centrally located. Peripheral catheters are approximately one inch (25 mm) long and are inserted into the small veins of the forearm. Central catheters are bigger and longer and are inserted into the large veins of the extremities, neck, or chest. Central venous catheters are the primary modality used for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents. The duration of central venous catheterization is dependent on the type of treatment given.















