Related Research Articles

Mandarin is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language of China. Because Mandarin originated in North China and most Mandarin dialects are found in the north, the group is sometimes referred to as Northern Chinese. Many varieties of Mandarin, such as those of the Southwest and the Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the standard language. Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers.
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning – that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information and to convey emphasis, contrast and other such features in what is called intonation, but not all languages use tones to distinguish words or their inflections, analogously to consonants and vowels. Languages that have this feature are called tonal languages; the distinctive tone patterns of such a language are sometimes called tonemes, by analogy with phoneme. Tonal languages are common in East and Southeast Asia, Africa, the Americas and the Pacific.

Yue is a group of similar Sinitic languages spoken in Southern China, particularly in Liangguang.

Middle Chinese or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the Qieyun, a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The Swedish linguist Bernard Karlgren believed that the dictionary recorded a speech standard of the capital Chang'an of the Sui and Tang dynasties. However, based on the more recently recovered preface of the Qieyun, most scholars now believe that it records a compromise between northern and southern reading and poetic traditions from the late Northern and Southern dynasties period. This composite system contains important information for the reconstruction of the preceding system of Old Chinese phonology.

Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of mainland China. The varieties are typically classified into several groups: Mandarin, Wu, Min, Xiang, Gan, Hakka and Yue, though some varieties remain unclassified. These groups are neither clades nor individual languages defined by mutual intelligibility, but reflect common phonological developments from Middle Chinese.
Jyutping is a romanisation system for Cantonese developed by the Linguistic Society of Hong Kong (LSHK), an academic group, in 1993. Its formal name is the Linguistic Society of Hong Kong Cantonese Romanization Scheme. The LSHK advocates for and promotes the use of this romanisation system.
Taishanese, alternatively romanized in Cantonese as Toishanese or Toisanese, in local dialect as Hoisanese or Hoisan-wa, is a dialect of Yue Chinese native to Taishan, Guangdong. Although it is related to Cantonese, Taishanese has little mutual intelligibility with the latter. Taishanese is also spoken throughout Sze Yup, located on the western fringe of the Pearl River Delta in Guangdong China. In the late 19th century and early 20th century, most of the Chinese emigration to North America originated from Sze Yup, the area where this variety is natively spoken. Thus, up to the mid-20th century, Taishanese was the dominant variety of the Chinese language spoken in Chinatowns in Canada and the United States. It was formerly the lingua franca of the overseas Chinese residing in the United States.
Historical Chinese phonology deals with reconstructing the sounds of Chinese from the past. As Chinese is written with logographic characters, not alphabetic or syllabary, the methods employed in Historical Chinese phonology differ considerably from those employed in, for example, Indo-European linguistics; reconstruction is more difficult because, unlike Indo-European languages, no phonetic spellings were used.

Cantonese is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou and its surrounding area in Southeastern China. It is the traditional prestige variety of the Yue Chinese dialect group, which has over 80 million native speakers. While the term Cantonese specifically refers to the prestige variety, it is often used to refer to the entire Yue subgroup of Chinese, including related but largely mutually unintelligible languages and dialects such as Taishanese.

Pinghua is a pair of Sinitic languages spoken mainly in parts of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, with some speakers in Hunan province. Pinghua is a trade language in some areas of Guangxi, where it is spoken as a second language by speakers of Zhuang languages. Some speakers of Pinghua are officially classified as Zhuang, and many are genetically distinct from most other Han Chinese. The northern subgroup of Pinghua is centered on Guilin and the southern subgroup around Nanning. Southern Pinghua has several notable features such as having four distinct checked tones, and using various loanwords from the Zhuang languages, such as the final particle wei for imperative sentences.
General Chinese is a diaphonemic orthography invented by Yuen Ren Chao to represent the pronunciations of all major varieties of Chinese simultaneously. It is "the most complete genuine Chinese diasystem yet published". It can also be used for the Korean, Japanese, and Vietnamese pronunciations of Chinese characters, and challenges the claim that Chinese characters are required for interdialectal communication in written Chinese.

The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split between the Sinitic languages and the rest of the family. This view is rejected by a number of researchers but has found phylogenetic support among others. The Greater Bai languages, whose classification is difficult, may be an offshoot of Old Chinese and thus Sinitic; otherwise Sinitic is defined only by the many varieties of Chinese unified by a common writing system, and usage of the term "Sinitic" may reflect the linguistic view that Chinese constitutes a family of distinct languages, rather than variants of a single language.
A checked tone, commonly known by the Chinese calque entering tone, is one of the four syllable types in the phonology of Middle Chinese. Although usually translated as "tone", a checked tone is not a tone in the phonetic sense but rather a syllable that ends in a stop consonant or a glottal stop. Separating the checked tone allows -p, -t, and -k to be treated as allophones of -m, -n, and -ng, respectively, since they are in complementary distribution. Stops appear only in the checked tone, and nasals appear only in the other tones. Because of the origin of tone in Chinese, the number of tones found in such syllables is smaller than the number of tones in other syllables. In Chinese phonetics, they have traditionally been counted separately.
The Shiqi dialect is a dialect of Yue Chinese. It is spoken by roughly 160,000 people in Zhongshan, Guangdong's Shiqi urban district. It differs slightly from Standard Cantonese, mainly in its pronunciation and lexicon.
The Cantonese Romanisation system known as Barnett–Chao is based on the principles of the Gwoyeu Romatzyh system (GR) developed by Chao Yuenren in the 1920s, which he modified in 1947. The B-C system is a modification in 1950 by K M A Barnett which was adopted by the School of Oriental and African Studies, London (SOAS).
The standard pronunciation of Cantonese is that of Guangzhou, also known as Canton, the capital of Guangdong Province. Hong Kong Cantonese is related to the Guangzhou dialect, and the two diverge only slightly. Yue dialects in other parts of Guangdong and Guangxi provinces, such as Taishanese, may be considered divergent to a greater degree.
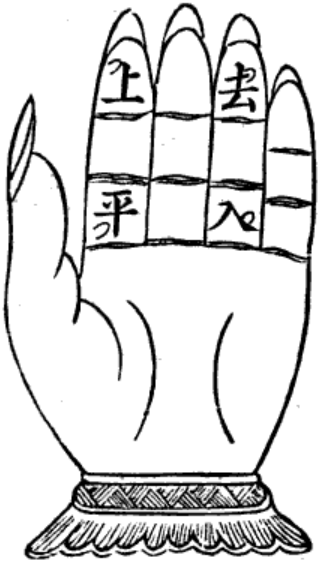
The four tones of Chinese poetry and dialectology are four traditional tone classes of Chinese words. They play an important role in Chinese poetry and in comparative studies of tonal development in the modern varieties of Chinese, both in traditional Chinese and in Western linguistics. They correspond to the phonology of Middle Chinese, and are named even or level, rising, departing or going, and entering or checked. They were reconstructed as mid, mid rising, high falling, and mid with a final stop consonant respectively. Due to historic splits and mergers, none of the modern varieties of Chinese have the exact four tones of Middle Chinese, but they are noted in rhyming dictionaries.
The Fuqing dialect, or Hokchia, is an Eastern Min dialect. It is spoken in the county-level city of Fuqing, China, situated within the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou. It is not completely mutually intelligible with the Fuzhou dialect.

Goulou is one of the principal groups of Yue dialects. It is spoken around the Guangxi–Guangdong border, and includes the dialects of Yulin and Bobai.
Proto-Min is a comparative reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Min group of varieties of Chinese. Min varieties developed in the relative isolation of the Chinese province of Fujian and eastern Guangdong, and have since spread to Taiwan, Southeast Asia, and other parts of the world. They contain reflexes of distinctions not found in Middle Chinese or most other modern varieties, and thus provide additional data for the reconstruction of Old Chinese.
References
- ↑ Lee, Gina (1993). Comparative, diachronic and experimental perspectives on the interaction between tone and the vowel in Standard Cantonese (PDF) (Ph.D. thesis). Ohio State University. p. 74. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-21.