
A kit car is an automobile available as a set of parts that a manufacturer sells and the buyer then assembles into a functioning car. Usually, many of the major mechanical systems such as the engine and transmission are sourced from donor vehicles or purchased new from other vendors. Kits vary in completeness, consisting of as little as a book of plans, or as much as a complete set with all components to assemble into a fully operational vehicle such as those from Caterham.
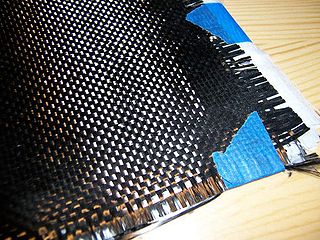
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres are fibers about 5 to 10 micrometers (0.00020–0.00039 in) in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber, basalt fibers, or plastic fibers.
Fiberglass or fibreglass is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinyl ester resin—or a thermoplastic.

Ultrasonic welding is an industrial process whereby high-frequency ultrasonic acoustic vibrations are locally applied to work pieces being held together under pressure to create a solid-state weld. It is commonly used for plastics and metals, and especially for joining dissimilar materials. In ultrasonic welding, there are no connective bolts, nails, soldering materials, or adhesives necessary to bind the materials together. When used to join metals, the temperature stays well below the melting point of the involved materials, preventing any unwanted properties which may arise from high temperature exposure of the metal.
Fibre-reinforced plastic is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibres. The fibres are usually glass, carbon, aramid, or basalt. Rarely, other fibres such as paper, wood, boron, or asbestos have been used. The polymer is usually an epoxy, vinyl ester, or polyester thermosetting plastic, though phenol formaldehyde resins are still in use.

A spoiler is an automotive aerodynamic device whose intended design function is to 'spoil' unfavorable air movement across the body of a vehicle in motion, usually manifested as lift, turbulence, or drag. Spoilers on the front of a vehicle are often called air dams.
Royalex was a composite material, comprising an outer layer of vinyl and hard acrylonitrile butadiene styrene plastic (ABS) and an inner layer of ABS foam. The layers are bonded by heat treatment. It was used to manufacture durable, mid-priced canoes. Its supplier closed out production of the material in 2014.

Automotive design is the process of developing the appearance of motor vehicles, including automobiles, motorcycles, trucks, buses, coaches, and vans.

Ruf Automobile GmbH is a German car manufacturer. Formerly using Porsche bodies in white to build cars, today they build vehicles on their own bodies and chassis. They also manufacture performance parts for various Porsche models, including the 911, Boxster, and Cayman.

Hexcel Corporation is an American public industrial materials company, based in Stamford, Connecticut. The company develops and manufactures structural materials. Hexcel was formed from the combination of California Reinforced Plastics, Ciba Composites and Hercules Composites Products Division. The company sells its products in commercial, military and recreational markets for use in commercial and military aircraft, space launch vehicles and satellites, wind turbine blades, sports equipment and automotive products. Hexcel works with Airbus Group, The Boeing Company, and others. Since 1980, the firm has publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol HXL.
Fiberfab was an American automotive manufacturer established in 1964. Starting with accessories and body parts, they progressed to making kit cars and fully assembled automobiles. They became one of the longest lasting kit car manufacturers.
The JimenezNovia W16 is a French one off sports car built in 1995 by Ramon Jimenez, a French motorcycle racer from Vaucluse. It reportedly cost £600,000 ($855,000) and took ten years to develop. It features an aerodynamic body with center locking wheels, scissor doors and carbon fiber parts which Jimenez developed himself.
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers, carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic, also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications.
Briggs Automotive Company (BAC) Limited is a British car manufacturer that created Mono, a road-legal sports car with only one seat. BAC is based in the city of Liverpool, United Kingdom, Mono cars are exported to 47 countries.

Tailored fiber placement (TFP) is a textile manufacturing technique based on the principle of sewing for a continuous placement of fibrous material for composite components. The fibrous material is fixed with an upper and lower stitching thread on a base material. Compared to other textile manufacturing processes fiber material can be placed near net-shape in curvilinear patterns upon a base material in order to create stress adapted composite parts.
The Automobili Lamborghini Advanced Composite Structures Laboratory (ACSL), commonly referred to as the Lamborghini Lab, was a research and development facility based in Seattle, Washington from 2007 to 2018, which focused on the development of carbon fiber composite technologies for Automobili Lamborghini S.p.A. The ACSL also designed and developed carbon fiber products for other organizations in other industries. The hallmark technology pioneered by the Lamborghini Lab is the forged composite technology.

Paolo Feraboli is a carbon fiber technology inventor and businessman. He is the founder and CTO of Gemini Composites, LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Mitsubishi Chemical Carbon Fiber and Composites, and founder and former Director of the Automobili Lamborghini Advanced Composite Structures Laboratory (ACSL). He is known for having invented the Forged Composite technology, and his contributions to the Lamborghini Sesto Elemento and Aventador programs.
CFSMC, or Carbon Fiber Sheet Molding Compound, is a ready to mold carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite material used in compression molding. While traditional SMC utilizes chopped glass fibers in a polymer resin, CFSMC utilizes chopped carbon fibers. The length and distribution of the carbon fibers is more regular, homogeneous, and constant than the standard glass SMC. CFSMC offers much higher stiffness and usually higher strength than standard SMC, but at a higher cost.

The Aria FXE is an American mid-engined sports car manufactured by American automotive design and engineering company Aria Group. The car is loosely named after Ed Taylor, former Vice President of Design at General Motors. The FXE is Aria's first production car, and was unveiled at the 2017 Los Angeles Auto Show.

The Ruf SCR is a rear-engined sports car manufactured by German automobile manufacturer Ruf Automobile. Introduced in 2018, the styling of the SCR 2018 is inspired by the Porsche 911 (964) and its introduction pays homage to the original Ruf SCR, but the new SCR uses a completely bespoke carbon-fibre monocoque chassis and body work.











