
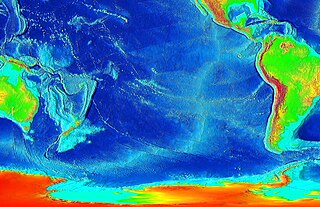
Seafloor spreading, or seafloor spread, is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.

A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface, and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000–4,000 m (3,300–13,100 ft) in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least 1,000 m (3,281 ft) above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface, such flat-top seamounts are called "guyots" or "tablemounts".

The Tonga Trench is an oceanic trench located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It is the deepest trench in the Southern hemisphere and the second deepest on Earth after the Mariana Trench. The fastest plate-tectonic velocity on Earth is occurring at this location, as the Pacific plate is being subducted westward in the trench.

Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount is an active submarine volcano about 22 mi (35 km) off the southeast coast of the island of Hawaii. The top of the seamount is about 3,200 ft (975 m) below sea level. This seamount is on the flank of Mauna Loa, the largest active subaerial shield volcano on Earth. Kamaʻehuakanaloa is the newest volcano in the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, a string of volcanoes that stretches about 3,900 mi (6,200 km) northwest of Kamaʻehuakanaloa. Unlike most active volcanoes in the Pacific Ocean that make up the active plate margins on the Pacific Ring of Fire, Kamaʻehuakanaloa and the other volcanoes of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain are hotspot volcanoes and formed well away from the nearest plate boundary. Volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands arise from the Hawaii hotspot, and as the youngest volcano in the chain, Kamaʻehuakanaloa is the only Hawaiian volcano in the deep submarine preshield stage of development.
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise, at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific plate to the west from the North American plate, the Rivera plate, the Cocos plate, the Nazca plate, and the Antarctic plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55°S130°W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-south-west towards Antarctica, near New Zealand. Much of the rise lies about 3,200 km (2,000 mi) off the South American coast and reaches a height about 1,800–2,700 m (5,900–8,900 ft) above the surrounding seafloor.

A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about 2,600 meters (8,500 ft) and rises about 2,000 meters (6,600 ft) above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin.
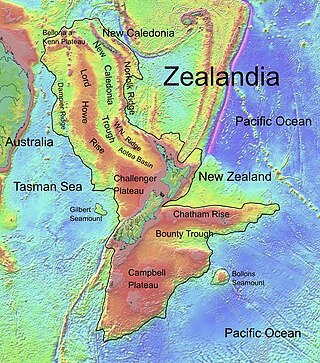
The Lord Howe Rise is a deep sea plateau which extends from south west of New Caledonia to the Challenger Plateau, west of New Zealand in the south west of the Pacific Ocean. To its west is the Tasman Basin and to the east is the New Caledonia Basin. Lord Howe Rise has a total area of about 1,500,000 km2 (580,000 sq mi), and generally lies about 750 to 1,200 metres under water. It is part of Zealandia, a much larger continent that is now mostly submerged, and so is composed of continental crust. Some have included the 3,500 m (11,500 ft) deep New Caledonia Basin as within the rise, given its continental crust origin, and this would give a larger total area of 1,950,000 km2 (750,000 sq mi).
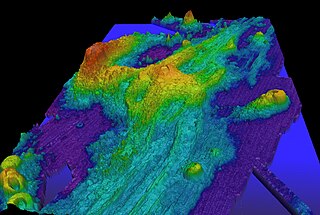
Axial Seamount is a seamount, submarine volcano, and underwater shield volcano in the Pacific Ocean, located on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, approximately 480 km (298 mi) west of Cannon Beach, Oregon. Standing 1,100 m (3,609 ft) high, Axial Seamount is the youngest volcano and current eruptive center of the Cobb–Eickelberg Seamount chain. Located at the center of both a geological hotspot and a mid-ocean ridge, the seamount is geologically complex, and its origins are still poorly understood. Axial Seamount is set on a long, low-lying plateau, with two large rift zones trending 50 km (31 mi) to the northeast and southwest of its center. The volcano features an unusual rectangular caldera, and its flanks are pockmarked by fissures, vents, sheet flows, and pit craters up to 100 m (328 ft) deep; its geology is further complicated by its intersection with several smaller seamounts surrounding it.
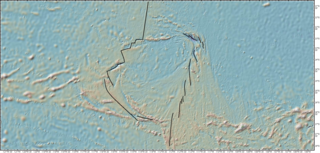
The Easter plate is a tectonic microplate located to the west of Easter Island off the west coast of South America in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, bordering the Nazca plate to the east and the Pacific plate to the west. It was discovered from looking at earthquake distributions that were offset from the previously perceived Nazca-Pacific Divergent boundary. This young plate is 5.25 million years old and is considered a microplate because it is small with an area of approximately 160,000 square kilometres (62,000 sq mi). Seafloor spreading along the Easter microplate's borders have some of the highest global rates, ranging from 50 to 140 millimetres /yr.

The Izu–Bonin–Mariana (IBM) arc system is a tectonic plate convergent boundary in Micronesia. The IBM arc system extends over 2800 km south from Tokyo, Japan, to beyond Guam, and includes the Izu Islands, the Bonin Islands, and the Mariana Islands; much more of the IBM arc system is submerged below sealevel. The IBM arc system lies along the eastern margin of the Philippine Sea Plate in the Western Pacific Ocean. It is the site of the deepest gash in Earth's solid surface, the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench.

The Ocean Observatories Initiative (OOI) is a National Science Foundation (NSF) Major Research Facility composed of a network of science-driven ocean observing platforms and sensors in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This networked infrastructure measures physical, chemical, geological, and biological variables from the seafloor to the sea surface and overlying atmosphere, providing an integrated data collection system on coastal, regional and global scales. OOI's goal is to deliver data and data products for a 25-year-plus time period, enabling a better understanding of ocean environments and critical ocean issues.
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin.

Zealandia, also known as Te Riu-a-Māui (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust in Oceania that subsided after breaking away from Gondwana 83–79 million years ago. It has been described variously as a submerged continent, continental fragment, and microcontinent. The name and concept for Zealandia was proposed by Bruce Luyendyk in 1995, and satellite imagery shows it to be almost the size of Australia. A 2021 study suggests Zealandia is over a billion years old, about twice as old as geologists previously thought.
The volcanism of Eastern Canada includes the hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations in Eastern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Eastern Canada has very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions. The most capable large igneous provinces in Eastern Canada are Archean age greenstone belts containing a rare volcanic rock called komatiite.
The South China Sea Basin is one of the largest marginal basins in Asia. South China Sea is located to the east of Vietnam, west of Philippines and the Luzon Strait, and north of Borneo. Tectonically, it is surrounded by the Indochina Block on the west, Philippine Sea Plate on the east, Yangtze Block to the north. A subduction boundary exists between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Asian Plate. The formation of the South China Sea Basin was closely related with the collision between the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plates. The collision thickened the continental crust and changed the elevation of the topography from the Himalayan orogenic zone to the South China Sea, especially around the Tibetan Plateau. The location of the South China Sea makes it a product of several tectonic events. All the plates around the South China Sea Basin underwent clockwise rotation, subduction and experienced an extrusion process from the early Cenozoic to the Late Miocene.

The Adare Basin is a geologic structural basin located north-east of Cape Adare of Antarctica, for which its named, and north of the western Ross Sea. The Adare Basin is an extensional rift basin located along a seafloor spreading center that forms the failed arm of the Tertiary spreading ridge separating East and West Antarctica, known as the West Antarctic Rift System and similar in structure to the East Africa Rift System. Centrally located in the Adare Basin is the Adare Trough. The extension of this rift system is recorded in a series of magnetic anomalies which run along the seafloor at the extinct, north–south trending, Adare spreading axis. The Adare spreading system continues unbroken into the Northern Basin underlying the adjacent Ross Sea continental shelf.

The Bransfield Basin is a back-arc rift basin located off the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. The basin lies within a Northeast and Southwest trending strait that separates the peninsula from the nearby South Shetland Islands to the Northwest. The basin extends for more than 500 kilometres from Smith Island to a portion of the Hero fracture zone. The basin can be subdivided into three basins: Western, Central, and Eastern. The Western basin is 130 kilometres long by 70 kilometres wide with a depth of 1.3 kilometres, the Central basin is 230 kilometres long by 60 kilometres wide with a depth of 1.9 kilometres, and the Eastern basin is 150 kilometres long by 40 kilometres wide with a depth of over 2.7 kilometres. The three basins are separated by the Deception Island and Bridgeman Island. The moho depth in the region has been seismically interpreted to be roughly 34 kilometres deep.
Pito Seamount is a seamount in the Pacific Ocean. It rises to a depth of 2,250 metres (7,380 ft) and features hydrothermal activity in the form of black smokers, which were discovered in 1993.

The Havre Trough is a currently actively rifting back-arc basin about 100 km (62 mi) to 120 km (75 mi) wide, between the Australian Plate and Kermadec microplate. The trough extends northward from New Zealand's offshore Taupō Volcanic Zone commencing at Zealandia's continental shelf margin and continuing as a tectonic feature, as the Lau Basin which currently contains active seafloor spreading centers. Its eastern margin is defined by the Kermadec Ridge created by Pacific Plate subduction under the Kermadec microplate, while the western margin is the remnant Lau-Colville Ridge.

The South Fiji Basin is a large 4 to 4.7 km deep oceanic basin in the south-west Pacific Ocean, south of Fiji. It was formed from the then Indo-Australian plate and is delimited to the north west by the New Hebrides Trench, and the Hunter fracture zone, to the west by the Three Kings Ridge, to the east by the Lau-Colville Ridge, and to the south by the continental shelf of Zealandia.

















