
Cache Creek is a historic transportation junction and incorporated village 354 kilometres (220 mi) northeast of Vancouver in British Columbia, Canada. It is on the Trans-Canada Highway in the province of British Columbia at a junction with Highway 97. The same intersection and the town that grew around it was at the point on the Cariboo Wagon Road where a branch road, and previously only a trail, led east to Savona's Ferry on Kamloops Lake. This community is also the point at which a small stream, once known as Riviere de la Cache, joins the Bonaparte River.
The Bonaparte Plateau, in British Columbia, Canada, is a subarea of the larger Cariboo Plateau which extends to the Quesnel River and lies between the Cariboo Mountains on the east and the Fraser River on the west. The Cariboo Plateau is a subarea of the Interior Plateau, aka the Fraser Plateau.

Amukta is a small yet mountainous island in the Islands of Four Mountains group lying between the Fox Islands and the Andreanof Islands in the Aleutian Islands. The nearest islands to it are Yunaska and Seguam Island; it is separated from Seguam Island by Amukta Pass. The small island of Chagulak lies directly northeast of it. The island reaches a total height of 3,461 feet (1,055 m). The island measures 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) long and 8.3 kilometres (5.2 mi) wide.

The Gover Stream is an approximately 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) long stream located in mid south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.

The River Lemon is a 16-kilometre (9.9 mi) river in the county of Devon in southwest England. It is a tributary of the River Teign, starting on Dartmoor by Haytor, and ending in Newton Abbot. It rises on the south-east side of Dartmoor near Haytor, joins with the River Sig and the Langworthy Brook at Sigford, then passes the village of Bickington. Lower down, it is joined by the Kestor Brook and it then flows through the woods in Bradley Valley, past the manor house of Bradley, and through the town of Newton Abbot where it flows through a 400-metre-long tunnel below the town centre. Just below the town, the river joins the River Teign at 50.517°N 3.607°W, near the head of its estuary.

The Bonaparte Indian Band a.k.a. Bonaparte First Nation, is a member band of the Shuswap Nation Tribal Council of the Secwepemc (Shuswap) people.
The Skeetchestn Indian Band is a member of the Secwepemc (Shuswap) Nation, located in the Central Interior region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Its main Indian reserve is located at Savona, British Columbia. The reserve was set up in the 1860s when the government of the then-Colony of British Columbia established an Indian Reserve system. The Skeetchestn is a member government of the Shuswap Nation Tribal Council.
The Morice River is the outflow of Morice Lake south west of Houston, British Columbia, Canada. Morice Lake and Morice River are named after Father Adrien-Gabriel Morice Geographic Name details The Morice has many small creeks joining it along its length, but retains the clear glacial hue for its length. The Morice river continues on to the town of Houston at which point the river is joined by a small tributary river called "The Little Bulkley" and the two rivers joined become the Bulkley River. They become the Bulkley, not the Morice despite the fact the Morice is larger. This was done by Poudrier, a government cartographer who, it is rumoured, never saw the region.

Podlesie is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Walim, within Wałbrzych County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland.
Hat Creek is a tributary of the Bonaparte River in British Columbia, Canada, joining that stream at Carquile, which is also known as Lower Hat Creek and is the site of the Hat Creek Ranch heritage museum and visitor centre. The Hat Creek basin includes a broad upper plateau area encircled by the gentle but high summits of the Clear Range and, to its east, the Cornwall Hills; this area is known as Upper Hat Creek. Adjacent to Upper Hat Creek is the gateway to Marble Canyon and a rancherie of the Pavilion First Nation, who are both a St'at'imc and Secwepemc people. During the Fraser Canyon and Cariboo Gold Rushes an important trail northwards from the lower Fraser Canyon led from Foster Bar on the Fraser via Laluwissen Creek into Upper Hat Creek, then via the creek to the Bonaparte River. The economy of the basin is ranching-based and includes some of the oldest ranches in the British Columbia Interior. On the northwest edge of the Upper Hat Creek basin there is a large lignite deposit and several exploratory pits, some dating back to the 19th century but some more recent, part of an intended, but now shelved Hat Creek coal-thermal proposal.
The Deadman River, also known as the Deadman's River, Deadman Creek or Deadman's Creek, is a tributary of the Thompson River in the British Columbia Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is about 70 kilometres (43 mi) in length.

The River Inny is a small river in east Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is a tributary of the River Tamar and is about twenty miles (32 km) long from its source near Davidstow on the eastern flank of Bodmin Moor to its confluence with the Tamar at Inny Foot near Dunterton.
Cache Creek, originally Rivière de la Cache, is a tributary of the Bonaparte River in the Thompson Country of the Interior of British Columbia, Canada, joining that river at the town of Cache Creek, British Columbia, which is located at the junction of the Trans-Canada and Cariboo Highways.

The Stein River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia.
The Nicoamen River is a tributary of the Thompson River in the southern Interior of British Columbia, Canada, located 15 kilometres (9 mi) upstream from its confluence with the Thompson at Lytton.

Pilica is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Warka, within Grójec County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It lies approximately 4 kilometres (2 mi) north-east of Warka, 28 km (17 mi) east of Grójec, and 50 km (31 mi) south of Warsaw.
The Landor River is a river in the Gascoyne region of Western Australia.
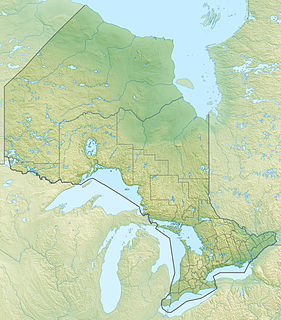
The Ekwan River is a river in Kenora District in northwestern Ontario, Canada. It travels about 500 kilometres (311 mi) from its source at Zumar Lake on the Canadian Shield, through the Hudson Bay Lowlands, northeast and then east, to its mouth on James Bay.

The St Austell River properly known as the River Vinnick, but historically called The White River, is a 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) long river located in south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. 50.337°N 4.793°W. The river has also been known as the "red river" due to tin streaming and mining activity upstream.
















