Related Research Articles

Transport in Liberia consist of 266 miles of railways, 6,580 miles of highways, seaports, 29 airports and 2 miles of pipeline for oil transportation. Busses and taxis are the main forms of ground transportation in and around Monrovia. Charter boats are also available.
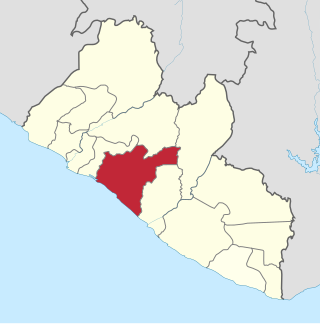
Grand Bassa is a county in the west-central portion of the West African nation of Liberia. One of 15 counties that comprise the first-level of administrative division in the nation, it has eight districts. Buchanan serves as the capital with the area of the county measuring 3,064 square miles (7,940 km2). As of the 2022 Census, it had a population of 293,557, making it the sixth most populous county in Liberia.
Iron ore production in Africa is dominated by South Africa, Mauritania and Algeria. Many countries possess iron ore deposits that are as yet untapped/unmined. Countries and companies currently involved in production are listed here; measurements are in tonnes per annum(year).

The Liberian-American-Swedish Mining Company (LAMCO) is a defunct Liberian corporation that mined for iron ore in the Nimba range in Liberia during the second half of the twentieth century. Founded in 1955 by American and Swedish investors, the company established the first large-scale mining operation in Liberia following the discovery in the 1950s of the Nimba ore body by geologist Sandy Clarke.
Railway stations in Guinea include:

Bong Town is a populated place in the Bong County of Liberia.

Railways in Liberia comprised two lines from the port of Monrovia in the northeast, and one line from the port of Buchanan in the centre. The lines were built principally to transport iron ore. By 2010, only the Bong mine railway was operational but the Lamco Railway was rebuilt by Arcelor Mittal and put back into service in 2011 as far as Tokadeh, Nimba County, allowing export of iron ore from the company's mine on the Guinean border via the Port of Buchanan.

The Brockman 2 mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 60 kilometres north-west of Tom Price. It should not be confused with Rio Tinto's Brockman 4 mine, also in the area.
The Nammuldi mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 60 kilometres north-west of Tom Price.

The Mount Tom Price mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, near the town of Tom Price.
The Mesa J mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 16 kilometres south-west of Pannawonica.
The Hope Downs mine is an iron ore mining complex located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. It comprises four large open-pit mines. The mines are co-owned by the Hancock Group and Rio Tinto, and the complex was named after Hope Hancock.

The Brockman 4 mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 60 km (37 mi) north-west of Tom Price. The mine, located near the existing Brockman mine, was opened in 2010. The mine is fully owned and operated by Rio Tinto Iron Ore, which owns many mines in the area. The mine is serviced by the Boolgeeda Airport.

Iron ore mining in Western Australia, in the 2018–19 financial year, accounted for 54 percent of the total value of the state's resource production, with a value of A$78.2 billion. The overall value of the minerals and petroleum industry in Western Australia was A$145 billion in 2018–19, a 26 percent increase on the previous financial year.
The Jimblebar mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 41 kilometres east of Newman.
The history of rail transport in Liberia began shortly after World War II, when the Freeport of Monrovia was completed, with limited rail access. It had been developed by American military forces.

The Tatanagar–Bilaspur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Tatanagar in the Indian state of Jharkhand and Bilaspur in Chhattisgarh. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through an industrial-mining area and handles high volumes of freight, particularly coal and iron ore.
The Putu mine is a large iron mine located in south-east Liberia in Grand Gedeh County. Putu represents one of the largest iron ore reserves in Liberia and in the world having estimated reserves of 2.37 billion tonnes of ore grading 34.1% iron metal.

The Kaunisvaara mine is a large iron mine located in northern Sweden in the village of Kaunisvaara in Norrbotten County. Kaunisvaara represents one of the largest iron ore reserves in Sweden and in the world having estimated reserves of 872 million tonnes of ore grading 32.7% iron metal.

The mining industry of Liberia has witnessed a revival after the civil war which ended in 2003. Gold, diamonds, and iron ore form the core minerals of the mining sector with a new Mineral Development Policy and Mining Code being put in place to attract foreign investments. In 2013, the mineral sector accounted for 11% of GDP in the country and the World Bank projected a further increase in the sector by 2017.
References
- ↑ "China's Wugang eyes H2 2013 startup for huge Liberia iron ore project". chinamining.org. 2012. Archived from the original on 2014-04-25. Retrieved 2013-06-14.
- ↑ "World rail infrastructure market October 2010". Railway Gazette International. 2010-10-21. Retrieved 2010-10-25.