The protected areas of South Africa include national parks and marine protected areas managed by the national government, public nature reserves managed by provincial and local governments, and private nature reserves managed by private landowners. Most protected areas are intended for the conservation of flora and fauna. National parks are maintained by South African National Parks (SANParks). A number of national parks have been incorporated in transfrontier conservation areas.

The Pilanesberg Game Reserve is located north of Rustenburg in North West Province in South Africa. The park borders with the entertainment complex Sun City. The park is currently administered by the North West Parks and Tourism Board.

The bohor reedbuck is an antelope native to central Africa. The animal is placed under the genus Redunca and in the family Bovidae. It was first described by German zoologist and botanist Peter Simon Pallas in 1767. The bohor reedbuck has five subspecies. The head-and-body length of this medium-sized antelope is typically between 100–135 cm (39–53 in). Males reach approximately 75–89 cm (30–35 in) at the shoulder, while females reach 69–76 cm (27–30 in). Males typically weigh 43–65 kg (95–143 lb) and females 35–45 kg (77–99 lb). This sturdily built antelope has a yellow to grayish brown coat. Only the males possess horns which measure about 25–35 cm (9.8–13.8 in) long.

The Madikwe Game Reserve is a protected area in South Africa, part of the latest park developments in the country. Named after the Madikwe or Marico River, on whose basin it is located, it was opened in 1991 and comprises 750 km² of bushland north of the small town Groot-Marico up to the Botswana border.

The southern reedbuck, rietbok or common reedbuck is a diurnal antelope typically found in southern Africa. It was first described by Pieter Boddaert, a Dutch physician and naturalist, in 1785. It is placed in the genus Redunca and family Bovidae. This antelope has an average mass of 58 kg (128 lb) and a body length of about 134–167 cm (53–66 in).

The wildlife of Botswana refers to the flora and fauna of Botswana. Botswana is around 90% covered in savanna, varying from shrub savanna in the southwest in the dry areas to tree savanna consisting of trees and grass in the wetter areas. Even under the hot conditions of the Kalahari Desert, many different species survive; in fact the country has more than 2500 species of plants and 650 species of trees. Vegetation and its wild fruits are also extremely important to rural populations living in the desert and are the principal source of food, fuel and medicine for many inhabitants.

The wildlife of Zimbabwe occurs foremost in remote or rugged terrain, in national parks and private wildlife ranches, in miombo woodlands and thorny acacia or kopje. The prominent wild fauna includes African buffalo, African bush elephant, black rhinoceros, southern giraffe, African leopard, lion, plains zebra, and several antelope species.

The wildlife of Malawi is composed of the flora and fauna of the country. Malawi is a landlocked country in southeastern Africa, with Lake Malawi taking up about a third of the country's area. It has around 187 species of mammal, some 648 species of birds have been recorded in the country and around 500 species of fish, many of them endemic, are found in its lakes and rivers. About 20% of the country has been set aside as national parks and game and forest reserves.

The wildlife of Mozambique consists of the flora and fauna of this country in southeastern Africa. Mozambique has a range of different habitat types and an ecologically rich and diverse wildlife. This includes 236 species of mammal, 740 species of bird and 5,692 species of vascular plant. The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany hotspot, with significantly high levels of biodiversity, stretches from the southern tip of Mozambique into northeastern South Africa.

The wildlife of Zambia refers to the natural flora and fauna of Zambia. This article provides an overview, and outline of the main wildlife areas or regions, and compact lists of animals focusing on prevalence and distribution in the country rather than on taxonomy. More specialized articles on particular groups are linked from here.

The wildlife of Togo is composed of the flora and fauna of Togo, a country in West Africa. Despite its small size the country has a diversity of habitats; there are only remnants of the once more extensive rain forests in the south, there is Sudanian Savanna in the north-western part of the country and larger areas of Guinean forest-savanna mosaic in the centre and northeast. The climate is tropical with distinct wet and dry seasons. There are estimated to be over 3000 species of vascular plant in the country, and 196 species of mammal and 676 species of bird have been recorded there.

Lengwe National Park is a national park in Malawi located near the town of Chikwawa and about 40 miles southwest of Blantyre. Lengwe's topography is unusual for Malawi and consists of open deciduous forests and dense thickets. It is the home of the reclusive Nyala antelope.
North West Parks Board is a governmental organisation responsible for the management of protected areas and public nature reserves in North West Province, South Africa.

Oviston Nature Reserve is a protected area in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. The nature reserve is managed by Eastern Cape Parks. It is located on the southern shores of the Gariep Dam.
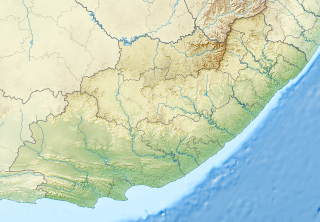
Tsolwana Nature Reserve is an 8,500 hectare nature reserve situated on the edge of the Winterberg Mountain range. It is located 60 km west of Queenstown, and 30 km south- east of Tarkastad in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa and is managed by Eastern Cape Parks Board. Its western boundary is formed by the upper Black Kei River. The reserve's name originates from the Xhosa word for "spike", due to the presence of the cone-shaped hill, Spitskop.

Dinder National Park is a national park and biosphere reserve in eastern Sudan, and is connected to Ethiopia's Alatash National Park.

Klipvoor Dam is a concrete gravity type dam located on the Moretele River, 55 km north of Brits, North West, South Africa. It was established in 1970. The main purpose of the dam is to serve for irrigation and its hazard potential has been ranked as high (3).

Gashaka-Gumti National Park (GGNP) is a national park in Nigeria, It was gazetted from two game reserves in 1991 and is Nigeria’s largest national park. It is located in the eastern provinces of Taraba and Adamawa to the border with Cameroon. The total area covers about 6,402 km2, much of the northern GGNP is savannah grassland, while the southern GGNP sector of the park has a rugged terrain characterized by very mountainous, steep slopes as well as deep valleys and gorges, and is home to montane forests. Altitude ranges from ranging from about 457 metres (1,499 ft) in the northern flatter corner of the park, up to 2,419 metres (7,936 ft) at Chappal Waddi, Nigeria’s highest mountain in the park's southern sections. It is an important water catchment area for the Benue River. There is abundant river flow even during the markedly dry season. Enclaves for local Fulani pastoralists exist within the park boundary that allow for farming and grazing.

Ruma National Park is the only terrestrial park in Kenya's Nyanza Province. Dubbed the "Last Retreat of the Roan Antelope", the park protects the only indigenous population of rare roan antelopes within Kenya. At present, the population is on the verge of extinction with individual populations numbering approximately 40. The park was established in 1966 as Lambwe Valley Game Reserve. It was later renamed “Ruma” after one of Kenya’s most powerful wizard, the much feared Gor Mahia who lived around the park. The park is located in the vast Lambwe Valley.
Kgaswane Mountain Reserve is a nature reserve of 5,300 hectares consisting of veld and mountains run by the North West Parks and Tourism Board and is located 5 km south-west of Rustenburg on the northern slopes of the Magaliesberg. Kgaswane is home to many species of flora and bird life and large and small mammals, and has been designated as a protected Ramsar site since 2019. The reserve has a number of camp sites, hikes and trails.



















