Related Research Articles

While recreational use, possession and trade of non-medicinal drugs described by the Opium Law are all technically illegal under Dutch law, official policy since the late 20th century has been to openly tolerate all recreational use while tolerating the other two under certain circumstances. This pragmatic approach was motivated by the idea that a drug-free Dutch society is unrealistic and unattainable, and efforts would be better spent trying to minimize harm caused by recreational drug use. As a result of this gedoogbeleid, the Netherlands is typically seen as much more tolerant of drugs than most other countries.

The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law is a common means of attempting to prevent the recreational use of certain intoxicating substances.

Ontario is the largest city in Malheur County, Oregon, United States. It lies along the Snake River at the Idaho border. The population was 11,366 at the 2010 census. The city is the largest community in the region of far eastern Oregon, also known as the Western Treasure Valley.
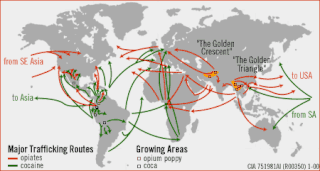
The illegal drug trade or drug trafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through the use of drug prohibition laws. The think tank Global Financial Integrity's Transnational Crime and the Developing World report estimates the size of the global illicit drug market between US$426 and US$652 billion in 2014 alone. With a world GDP of US$78 trillion in the same year, the illegal drug trade may be estimated as nearly 1% of total global trade. Consumption of illegal drugs is widespread globally and it remains very difficult for local authorities to thwart its popularity.

Border trade, in general, refers to the flow of goods and services across the border between different jurisdictions. In this sense, border trade is a part of the normal trade that flows through the ordinary export/import legal and logistical frameworks of nations and smaller jurisdictions. However border trade specifically refers to the increase in trade in areas where crossing borders is relatively easy and where products are significantly less expensive on one side of the border than the other – often because of significant variations in taxation levels on goods. Common items involved in border trade include alcohol, tobacco, medication, recreational drugs, automobiles, automotive fuel, groceries, furniture and clothing.
This article is intended to give an overview of several arguments for and against drug prohibition.

Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant. Native to Central and South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various traditional medicines for centuries. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive component of cannabis, which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD). Cannabis can be used by smoking, vaporizing, within food, or as an extract.
Drug policy reform, also known as drug law reform, generally refers to proposed changes to the laws and regulations that governments promulgate with respect to substances that have psychoactive effects or a real or perceived potential to be used for recreational or other non-medical reasons. Proponents of drug policy reform frequently argue that prohibition of recreational drugs—such as cannabis, opioids, cocaine, amphetamines and hallucinogens—has been ineffective and counterproductive and that substance use is better responded to by implementing practices for harm reduction and increasing the availability of addiction treatment. Another reform proposed is to introduce a regulatory regime for the production, marketing, and distribution of some or all currently illegal drugs in a manner analogous to that for alcohol and tobacco.

Cannabis in Canada is legal for both recreational and medicinal purposes. Medicinal use of cannabis was legalized nationwide under conditions outlined in the Marihuana for Medical Purposes Regulations, later superseded by the Access to Cannabis for Medical Purposes Regulations, issued by Health Canada and seed, grain, and fibre production was permitted under licence by Health Canada. The federal Cannabis Act came into effect on 17 October 2018 and made Canada the second country in the world, after Uruguay, to formally legalize the cultivation, possession, acquisition and consumption of cannabis and its by-products. Canada is the first G7 and G20 nation to do so.

A dispensary is an office in a school, hospital, industrial plant, or other organization that dispenses medications, medical supplies, and in some cases even medical and dental treatment. In a traditional dispensary set-up, a pharmacist dispenses medication per the prescription or order form. The English term originated from the medieval Latin noun dispensaria and is cognate with the Latin verb dispensare, 'to distribute'.

In the United States, the non-medical use of cannabis is legalized in 19 states and decriminalized in 12 states as of May 2022. Decriminalization refers to a policy of reduced penalties for cannabis offenses, typically involving a civil penalty for possessing small amounts, instead of criminal prosecution or the threat of arrest. In jurisdictions without penalty the policy is referred to as legalization, although the term decriminalization is sometimes used for this purpose as well.

Drug liberalization is a drug policy process of decriminalizing or legalizing the use or sale of controlled drugs. Variations of drug liberalization include: drug legalization, drug re-legalization and drug decriminalization. Proponents of drug liberalization argue that the legalization of these would make them more widely available, eradicating the illegal drug market and reducing the law enforcement costs and incarceration rates.

Cannabis in Colorado has been legal for medical use since 2000 and for recreational use since late 2012. On November 7, 2000, 54% of Colorado voters approved Amendment 20, which amended the State Constitution to allow the use of marijuana in the state for approved patients with written medical consent. Under this law, patients may possess up to 2 ounces (57 g) of medical marijuana and may cultivate no more than six marijuana plants. Patients who are caught with more than this in their possession may argue "affirmative defense of medical necessity" but are not protected under state law with the rights of those who stay within the guidelines set forth by the state. The Colorado Amendment 64, which was passed by voters on November 6, 2012, led to recreational legalization in December 2012 and state-licensed retail sales in January 2014. The policy has led to cannabis tourism. There are two sets of policies in Colorado relating to cannabis use: those for medicinal cannabis and for recreational drug use along with a third set of rules governing hemp.

Colorado Amendment 64 was a successful popular initiative ballot measure to amend the Constitution of the State of Colorado, outlining a statewide drug policy for cannabis. The measure passed on November 6, 2012, and along with a similar measure in Washington state, marked "an electoral first not only for America but for the world."

Cannabis in Massachusetts is legal for medical and recreational use. It also relates to the legal and cultural events surrounding the use of cannabis. A century after becoming the first U.S. state to criminalize recreational cannabis, Massachusetts voters elected to legalize it in 2016.

Cannabis in Nevada became legal for recreational use on January 1, 2017, following the passage of Question 2 on the 2016 ballot. The first licensed sales of recreational cannabis began on July 1, 2017.

The use of cannabis as a recreational drug has been outlawed in many countries for several decades. As a result of long-fought legalization efforts, several countries such as Uruguay and Canada, as well as several states in the US, have legalized the production, sale, possession, and recreational and/or medical usage of cannabis. The broad legalization of cannabis in this fashion can have numerous effects on the economy and society in which it is legalised.

The Cannabis Act (C-45) of June, 2018 paved the way for the legalization of cannabis in Canada on 17 October 2018. Police and prosecution services in all Canadian jurisdictions are currently capable of pursuing criminal charges for cannabis marketing without a licence issued by Health Canada. The Supreme Court of Canada has held that the federal Parliament has the power to criminalize the possession of cannabis and that doing so does not infringe upon the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The Ontario Court of Appeal and the Superior Court of Ontario have, however, held that the absence of a statutory provision for medical marijuana is unconstitutional, and to that extent the federal law is of no force and/or effect if a prescription is obtained. The recreational use of cannabis has been legalized by the federal government, and took effect on 17 October 2018.

Cannabis in Canada has been legal for medicinal purposes since 2001 under conditions outlined in the Marihuana for Medical Purposes Regulations. This was superseded by the Access to Cannabis for Medical Purposes Regulations, issued by Health Canada while seed, grain, and fibre production were permitted under licence by Health Canada.
Since 2012, various jurisdictions in the United States have legalized cannabis for recreational use. Because there are no border controls between U.S. states and citizens are allowed to travel freely between them, this has resulted in the proliferation of cannabis dispensaries located in towns that border states where cannabis remains illegal. These dispensaries can often be a significant source of revenue for the local economy of a city; for example, the city of Ontario, Oregon generated $100 million in cannabis sales less than two years after allowing dispensaries.
References
- ↑ Border Effects Among EU Countries: Do National Identity and Cultural Differences Matter?
- ↑ "Do Borders Really Slash Trade? A Meta-Analysislast=" (PDF). doi:10.1057/s41308-016-0001-5. hdl: 2027.42/132988 .
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ The Border-Town Effect: Dispensaries Boom on State Line
- ↑ Pot sales boom in Ontario, top $100 million – fueled in part by Idaho customers