
Sulfur (also spelled sulphur in British English) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature.

In physical geography, a fjord or fiord is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, British Columbia (Canada), Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland (Denmark), the Faroe Islands (Denmark), Montenegro, Iceland, Ireland, Kamchatka (Russia), the Kerguelen Islands (France), Newfoundland and Labrador (Canada), New Zealand, Norway, Novaya Zemlya (Russia), Nunavut (Canada), Quebec (Canada), Argentina, Russia, South Georgia Island, Tasmania (Australia), Scotland and the states of Washington, Maine, and Alaska. Norway's coastline is estimated to be 29,000 km (18,000 mi) long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only 2,500 km (1,600 mi) long excluding the fjords.

A fumarole is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planets from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcanic activity, but fumarole activity can also precede a volcanic eruption and has been used for eruption prediction. Most fumaroles die down within a few days or weeks of the end of an eruption, but a few are persistent, lasting for decades or longer. An area containing fumaroles is known as a fumarole field.

Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

The geothermal areas of Yellowstone include several geyser basins in Yellowstone National Park as well as other geothermal features such as hot springs, mud pots, and fumaroles. The number of thermal features in Yellowstone is estimated at 10,000. A study that was completed in 2011 found that a total of 1,283 geysers have erupted in Yellowstone, 465 of which are active during an average year. These are distributed among nine geyser basins, with a few geysers found in smaller thermal areas throughout the Park. The number of geysers in each geyser basin are as follows: Upper Geyser Basin (410), Midway Geyser Basin (59), Lower Geyser Basin (283), Norris Geyser Basin (193), West Thumb Geyser Basin (84), Gibbon Geyser Basin (24), Lone Star Geyser Basin (21), Shoshone Geyser Basin (107), Heart Lake Geyser Basin (69), other areas (33). Although famous large geysers like Old Faithful are part of the total, most of Yellowstone's geysers are small, erupting to only a foot or two. The hydrothermal system that supplies the geysers with hot water sits within an ancient active caldera. Many of the thermal features in Yellowstone build up sinter, geyserite, or travertine deposits around and within them.

Liquid fuels are combustible or energy-generating molecules that can be harnessed to create mechanical energy, usually producing kinetic energy; they also must take the shape of their container. It is the fumes of liquid fuels that are flammable instead of the fluid. Most liquid fuels in widespread use are derived from fossil fuels; however, there are several types, such as hydrogen fuel, ethanol, and biodiesel, which are also categorized as a liquid fuel. Many liquid fuels play a primary role in transportation and the economy.

Axel Heiberg Island is an uninhabited island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in the Arctic Ocean, it is the 32nd largest island in the world and Canada's seventh largest island. According to Statistics Canada, it has an area of 43,178 km2 (16,671 sq mi). It is named after Axel Heiberg.
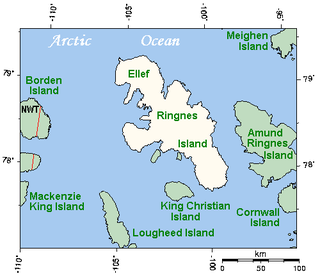
Ellef Ringnes Island is an uninhabited island and one of the Sverdrup Islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. A member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands and Arctic Archipelago, it is located in the Arctic Ocean, east of Borden Island, and west of Amund Ringnes Island. It has an area of 11,295 km2 (4,361 sq mi), making it the 69th largest island in the world and Canada's 16th largest island. Its highest mount is 260 m (850 ft).

The Claus process is the most significant gas desulfurizing process, recovering elemental sulfur from gaseous hydrogen sulfide. First patented in 1883 by the chemist Carl Friedrich Claus, the Claus process has become the industry standard.
The oil and gas industry is usually divided into three major sectors: upstream, midstream, and downstream. The downstream sector is the refining of petroleum crude oil and the processing and purifying of raw natural gas, as well as the marketing and distribution of products derived from crude oil and natural gas. The downstream sector reaches consumers through products such as gasoline or petrol, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel oil, heating oil, fuel oils, lubricants, waxes, asphalt, natural gas, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as well as naphtha and hundreds of petrochemicals.

The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which the sulfur moves between rocks, waterways and living systems. It is important in geology as it affects many minerals and in life because sulfur is an essential element (CHNOPS), being a constituent of many proteins and cofactors, and sulfur compounds can be used as oxidants or reductants in microbial respiration. The global sulfur cycle involves the transformations of sulfur species through different oxidation states, which play an important role in both geological and biological processes. Steps of the sulfur cycle are:

Lake Hazen is a freshwater lake in the northern part of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada, north of the Arctic Circle. It is the largest lake north of the Arctic Circle by volume. By surface area it is third largest, after Lake Taymyr in Russia and Lake Inari in Finland.

Sulfur water is a condition where water is exposed to hydrogen sulfide gas, giving a distinct "rotten egg" smell. This condition has different purposes in culture varying to health and implications to plumbing.

Natural-gas processing is a range of industrial processes designed to purify raw natural gas by removing contaminants such as solids, water, carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), mercury and higher molecular mass hydrocarbons (condensate) to produce pipeline quality dry natural gas for pipeline distribution and final use. Some of the substances which contaminate natural gas have economic value and are further processed or sold. Hydrocarbons that are liquid at ambient conditions: temperature and pressure (i.e., pentane and heavier) are called natural-gas condensate (sometimes also called natural gasoline or simply condensate).
Greely Fiord is a natural inlet in the west of Ellesmere Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut in the Arctic Archipelago. To the south lies the Cañon Fiord and the Agassiz Ice Cap. To the northwest is Borup Fiord and Tanquary Fiord is northeast.
Borup Fiord is located on Ellesmere Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut Canada. The mouth of the fiord opens into Greely Fiord. To the west is Oobloyah Bay and to the north is the Neil Peninsula and the Neil Icecap. The eastern arm, known as Esayoo Bay leads to Borup Fiord Pass. Detailed studies of the Borup Fiord area between Oobloyah Bay and Esayoo Bay have been done in summer 1988 by geographers from Heidelberg University.
Sulfur production in the United States was 9.04 million metric tons of sulfur content in 2014, all of it recovered as a byproduct, from oil refineries, natural gas processing plants, and metal smelters. The United States was second in the world in sulfur production in 2014, behind China. The sulfur recovered was marketed in the forms of native (elemental) sulfur, and sulfuric acid. Total value was US$927 million in 2014.
Mars habitability analogue environments on Earth are environments that share potentially relevant astrobiological conditions with Mars. These include sites that are analogues of potential subsurface habitats, and deep subsurface habitats.

Nansen Land is a peninsula in far northwestern Greenland. It is a part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.
















