Related Research Articles

Iridium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal with a density of 22.56 g/cm3 (0.815 lb/cu in) as defined by experimental X-ray crystallography. 191Ir and 193Ir are the only two naturally occurring isotopes of iridium, as well as the only stable isotopes; the latter is the more abundant. It is one of the most corrosion-resistant metals, even at temperatures as high as 2,000 °C (3,630 °F).

Osmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, mostly in platinum ores. Osmium is the densest naturally occurring element. When experimentally measured using X-ray crystallography, it has a density of 22.59 g/cm3. Manufacturers use its alloys with platinum, iridium, and other platinum-group metals to make fountain pen nib tipping, electrical contacts, and in other applications that require extreme durability and hardness.

Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them.

Platinum is a chemical element; it has symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish platina, a diminutive of plata "little silver".

Rhodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isotope, which is 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal or as an alloy with similar metals and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals. Rhodium is a group 9 element.
A period 5 element is one of the chemical elements in the fifth row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fifth period contains 18 elements, beginning with rubidium and ending with xenon. As a rule, period 5 elements fill their 5s shells first, then their 4d, and 5p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as rhodium.

In the United States, the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) operates an awards program based on the certified number of albums and singles sold through retail and other ancillary markets. Other countries have similar awards. Certification is not automatic; for an award to be made, the record label must first request certification. The audit is conducted against net shipments after returns, which includes albums sold directly to retailers and one-stops, direct-to-consumer sales and other outlets.
The platinum-group metals (PGMs), also known as the platinoids, platinides, platidises, platinum group, platinum metals, platinum family or platinum-group elements (PGEs), are six noble, precious metallic elements clustered together in the periodic table. These elements are all transition metals in the d-block.

The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the arsenides, the antimonides, the bismuthinides, the sulfarsenides and the sulfosalts. Sulfide minerals are inorganic compounds.
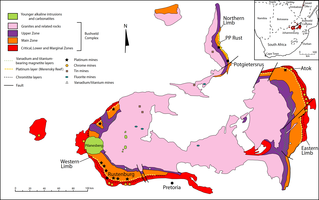
The Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) is the largest layered igneous intrusion within the Earth's crust. It has been tilted and eroded forming the outcrops around what appears to be the edge of a great geological basin: the Transvaal Basin. It is approximately two billion years old and is divided into four limbs: northern, eastern, southern and western. It comprises the Rustenburg Layered suite, the Lebowa Granites and the Rooiberg Felsics, that are overlain by the Karoo sediments. The site was first publicised around 1897 by Gustaaf Molengraaff who found the native South African tribes residing in and around the area.

The Merensky Reef is a layer of igneous rock in the Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) in the North West, Limpopo, Gauteng and Mpumalanga provinces of South Africa which together with an underlying layer, the Upper Group 2 Reef (UG2), contains most of the world's known reserves of platinum group metals (PGMs) or platinum group elements (PGEs)—platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium. The Reef is 46 cm thick and bounded by thin chromite seams or stringers. The composition consists predominantly of cumulate rocks, including leuconorite, anorthosite, chromitite, and melanorite.

Feklistova or Feklistov Island is one of the Shantar Islands in Sea of Okhotsk. With an area of 372 square kilometres, it is the second largest in the archipelago.

Mining in South Africa was once the main driving force behind the history and development of Africa's most advanced and richest economy. Large-scale and profitable mining started with the discovery of a diamond on the banks of the Orange River in 1867 by Erasmus Jacobs and the subsequent discovery of the Kimberley pipes a few years later. Gold rushes to Pilgrim's Rest and Barberton were precursors to the biggest discovery of all, the Main Reef/Main Reef Leader on Gerhardus Oosthuizen's farm Langlaagte, Portion C, in 1886, which kicked off the Witwatersrand Gold Rush and the subsequent rapid development of the gold field there.
The mineral industry of Russia is one of the world's leading mineral industries and accounts for a large percentage of the Commonwealth of Independent States' production of a range of mineral products, including metals, industrial minerals, and mineral fuels. In 2005, Russia ranked among the leading world producers or was a significant producer of a vast range of mineral commodities, including aluminum, arsenic, cement, copper, magnesium compounds and metals, nitrogen, palladium, silicon, nickel and vanadium.
Stanley Hay Umphray Bowie FRS was a Scottish geologist. He was considered a "world authority on uranium geology and a leader in the field of geochemistry and mineralogy". He developed methods and tools to identify opaque minerals using micro-indentation hardness and optical reflectance. He worked for the British Geological Survey between 1946 and 1977. The mineral bowieite was so named in recognition of his work on identification of opaque minerals.
Louis Jean-Pierre Cabri (born February 23, 1934, in Cairo) is an eminent Canadian scientist in the field of platinum group elements (PGE) mineralogy with expertise in precious metal mineralogy and base metals at the Canada Centre for Mineral and Energy Technology (CANMET). First as Research Scientist and later as Principal Scientist (1996–1999). In the 1970s he discovered two new Cu–Fe sulfide minerals, "mooihoekite" and "haycockite". In 1983 Russian mineralogists named a new mineral after him: cabriite (Pd2SnCu).
African Rainbow Minerals Limited is a mining company based in South Africa. ARM has interests in a wide range of mines, including platinum and platinum group metals (PGMs), iron, coal, copper, and gold. ARM's Goedgevonden coalmine near Witbank is a flagship of their joint venture with Xstrata, and produces 6.7 million tons of coal per year. Production is expanding at the Two Rivers platinum mine in Mpumalanga. ARM owns 20% of Harmony Gold, the 12th largest gold mining company in the world with three mining operations in South Africa. Patrice Motsepe is the executive chairman; Phillip Tobias is CEO.
Lt. Col. William Robert Royal was an American scuba diver in the United States Air Force and amateur archeologist. In 1959, Royal and Eugenie Clark found archaeologically, pale-ontologically, and geologically significant artifacts and human bones from at least 30 individuals in Little Salt Spring and Warm Mineral Springs. A partially burned log found in association with some of the human bones was radiocarbon dated to about 10,000 years ago. If the bones were the same age as the log, then the bones were the oldest known evidence of human occupation in Florida at the time.

The geology of Zimbabwe in southern Africa is centered on the Zimbabwe Craton, a core of Archean basement composed in the main of granitoids, schist and gneisses. It also incorporates greenstone belts comprising mafic, ultramafic and felsic volcanics which are associated with epiclastic sediments and iron formations. The craton is overlain in the north, northwest and east by Proterozoic and Phanerozoic sedimentary basins whilst to the northwest are the rocks of the Magondi Supergroup. Northwards is the Zambezi Belt and to the east the Mozambique Belt. South of the Zimbabwe Craton is the Kaapvaal Craton separated from it by the Limpopo Mobile Belt, a zone of deformation and metamorphism reflecting geological events from Archean to Mesoproterozoic times. The Zimbabwe Craton is intruded by an elongate ultramafic/mafic igneous complex known as the Great Dyke which runs for more than 500 km along a SSW/NNE oriented graben. It consists of peridotites, pyroxenites, norites and bands of chromitite.

Ferronickel platinum is a very rarely occurring minerals from the mineral class of elements (including natural alloys, intermetallic compounds, carbides, nitrides, phosphides and silicides) with the chemical composition Pt2FeNi and thus is chemically seen as a natural alloy, more precisely an intermetallic compound of platinum, nickel and iron in a ratio of 2:1:1.
References
- 1 2 Mindat.org
- ↑ Handbook of Mineralogy - Bowieite
- ↑ Webmineral.com - Bowieite
- ↑ The Times The Times, 10 Oct 2008, p81
- ↑ Parthé, E.; Hohnke, E.; Hulliger, F. (1 November 1967). "A new structure type with octahedron pairs for Rh2S3, Rh2Se3 and Ir2S3". Acta Crystallographica. 23 (5): 832–840. Bibcode:1967AcCry..23..832P. doi:10.1107/S0365110X67003767.