
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi.2), including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, Enggano, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung and Krakatoa archipelago.

The Andaman Sea is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated from the Bay of Bengal to its west by the Andaman Islands and the Nicobar Islands. Its southern end is at Breueh Island just north of Sumatra, with the Strait of Malacca further southeast.

Hudson Strait in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut and Resolution Island, off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km (470 mi) long with an average width of 125 km (78 mi), varying from 70 km (43 mi) at the eastern entrance to 240 km (150 mi) at Deception Bay.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.
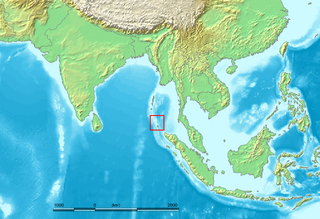
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 kilometres (93 mi) northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they are part of India, as the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Together with the Andaman Islands to their north, the Nicobar Islands serve as a maritime boundary between the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Andaman Sea to the east.

The Savu Sea is a small sea within Indonesia named for the island of Savu (Sawu) on its southern boundary. It is bounded by Savu and Raijua to the south, the islands of Rote and Timor to the east, Flores and the Alor archipelago to the north/northwest, and the island of Sumba to the west/northwest. Between these islands, it flows into the Indian Ocean to the south and west, the Flores Sea to the north, and the Banda Sea to the northeast.

Vega Island is an island in Antarctica, 17 nautical miles long and 6 nautical miles wide, which is the northernmost of the James Ross Island group and lies in the west part of Erebus and Terror Gulf. It is separated from James Ross Island by Herbert Sound and from Trinity Peninsula by Prince Gustav Channel.

Great Aceh Regency is a regency of the Indonesian province of Aceh. The regency covers an area of 2,903.49 square kilometres and had a population of 351,418 at the 2010 Census, 391,870 at the 2015 census and 405,535 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 435,298. The Regency is located at the northwest tip of Sumatra island and surrounds the provincial capital of Banda Aceh, many suburbs of which lie within the Regency. It also includes a number of islands off the northern tip of Sumatra, which comprise Pulo Aceh District within the regency. The seat of the Regency government is the town of Jantho.
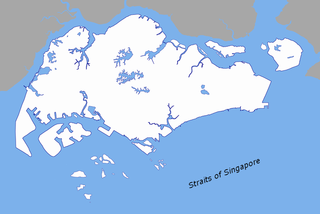
The Singapore Strait is a 113 km-long (70 mi), 19 km-wide (12 mi) strait between the Strait of Malacca in the west and the South China Sea in the east. Singapore is on the north of the channel, and the Indonesian Riau Islands are on the south. The two countries share a maritime border along the strait.

The Flores Sea covers 240,000 square kilometres (93,000 sq mi) of water in Indonesia. The sea is bounded on the north by the island of Celebes and on the south by the Sunda Islands of Flores and Sumbawa.
Northeast Glacier is a steep, heavily crevassed glacier, 13 nautical miles long and 5 nautical miles wide at its mouth, which flows from McLeod Hill westward and then south-westwards into Marguerite Bay between the Debenham Islands and Roman Four Promontory, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.

Joinville Island group is a group of antarctic islands, lying off the northeastern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which Joinville Island group is separated by the Antarctic Sound.

Weh Island is a small active volcanic island to the northwest of Sumatra in Indonesia, also known as Sabang after the city situated on the northeast end of the island, whose area of 122.13 square kilometres (47.15 sq mi) includes the whole island as well as several offshore islets. It had a population of 43,527 at the official mid-2023 estimate. It is 45 minutes by fast regular ship or 2 hours by ferry from the mainland port of Banda Aceh. It was originally connected to the Sumatran mainland and became separated by sea after the stratovolcano's last eruption in the Pleistocene era. The island is situated in the Andaman Sea.

Simeulue is an island of Indonesia, 150 kilometres (93 mi) off the west coast of Sumatra. It covers an area of 1,754 square kilometres, including minor offshore islands. It had a population of 80,674 at the 2010 census and 92,865 at the 2020 census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 93,762. Its capital is Sinabang.
This is an article about the extreme points of Indonesia.

Two Hummock Island is an ice-covered island, 5 nautical miles long in a north–south direction, conspicuous for its two rocky summits 670 metres (2,200 ft) high, lying 5 nautical miles southeast of Liège Island in the Palmer Archipelago.

Astrolabe Island is an island 3 nautical miles long, lying in the Bransfield Strait 14 nautical miles northwest of Cape Ducorps, Trinity Peninsula in Antarctica.
Likok Pulo is a traditional dance originating from Aceh, Indonesia. "Likok" means dance moves, while "Pulo" means island. Pulo here refers to a small island at the northern tip of Sumatra Island which is also called Breuh Island, or Beras Island.
Rondo Island is Indonesia's northernmost territory, located in the Andaman Sea, with a 0.650 km2 area 35m above sea level. The island is one of the outlying islands of Indonesia in the Aceh province of the Sumatra region. It is administratively part of Ujung Bau village in the Sukakarya District of Sabang City, whose administration center is on Weh Island, south of Rondo. Rondo is 50 km offshore from Indonesia's Sumatra mainland. This otherwise uninhabited island, accessible only by boat, has an Indonesian military outpost with a heliport and blue-roofed barracks, an adjacent lighthouse complex with a red-roofed lighthouse keeper's house and a white skeletal lighthouse topped with a viewing gallery and lantern.

Pulo Island, commonly known as Isla Pulo, is a long, narrow island surrounded by mudflats in the Manila Bay coast of Navotas, about 13 kilometers (8.1 mi) north of Manila in the Philippines. It is a sitio in Barangay Tanza, connected to the mainland of Navotas by a 500-meter-long (1,600 ft) bamboo bridge. The island is known for its mangroves for which it was declared a "marine tree park" and as one of four ecotourism sites in Metro Manila established under the National Ecotourism Strategy in 1999. In 2014, it was home to a resettlement site of about 137 indigent families that mostly occupied the island's southern tip.

















