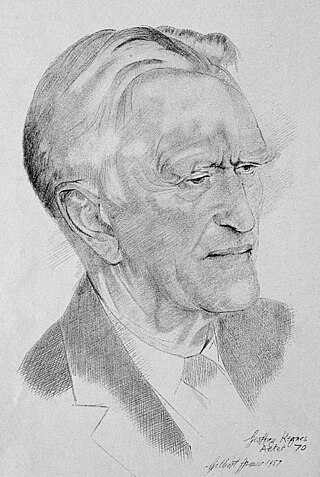Sir Thomas Browne was an English polymath and author of varied works which reveal his wide learning in diverse fields including science and medicine, religion and the esoteric. His writings display a deep curiosity towards the natural world, influenced by the Scientific Revolution of Baconian enquiry and are permeated by references to Classical and Biblical sources as well as the idiosyncrasies of his own personality. Although often described as suffused with melancholia, Browne's writings are also characterised by wit and subtle humour, while his literary style is varied, according to genre, resulting in a rich, unique prose which ranges from rough notebook observations to polished Baroque eloquence.

Down House is the former home of the English naturalist Charles Darwin and his family. It was in this house and garden that Darwin worked on his theory of evolution by natural selection, which he had conceived in London before moving to Down.
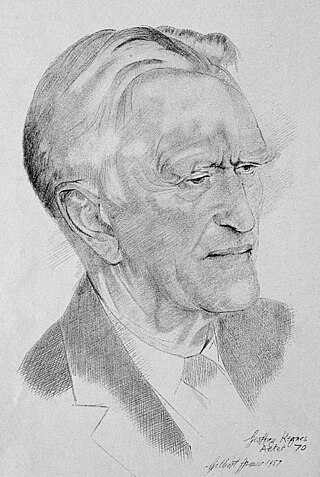
Sir Geoffrey Langdon Keynes was a British surgeon and author. He began his career as a physician in World War I, before becoming a doctor at St Bartholomew's Hospital in London, where he made notable innovations in the fields of blood transfusion and breast cancer surgery. Keynes was also a publishing scholar and bibliographer of English literature and English medical history, focusing primarily on William Blake and William Harvey.

Sir Robert Rowand Anderson, was a Scottish Victorian architect. Anderson trained in the office of George Gilbert Scott in London before setting up his own practice in Edinburgh in 1860. During the 1860s his main work was small churches in the 'First Pointed' style that is characteristic of Scott's former assistants. By 1880 his practice was designing some of the most prestigious public and private buildings in Scotland.

Edward Granville BrowneFBA was a British Iranologist. He published numerous articles and books, mainly in the areas of history and literature.
Sir Cecil Pembrey Grey Wakeley, 1st Baronet KBE CB PRCS FRSE was a 20th-century British surgeon.

Sir James Crichton-Browne FRS FRSE was a leading Scottish psychiatrist, neurologist and eugenicist. He is known for studies on the relationship of mental illness to brain injury and for the development of public health policies in relation to mental health. Crichton-Browne's father was the asylum reformer Dr William A.F. Browne, a prominent member of the Edinburgh Phrenological Society and, from 1838 until 1857, the superintendent of the Crichton Royal at Dumfries where Crichton-Browne spent much of his childhood.
The Cave, later Cave-Browne, later Cave-Browne-Cave Baronetcy, of Stanford in the County of Northampton, is a title in the Baronetage of England.
George Moreton Buckston was an English cricketer who played first-class cricket for Cambridge University in 1903, Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) and Derbyshire between 1905 and 1921.
Robin Henry Rowland Buckston was an English cricketer who played first-class cricket for Derbyshire between 1928 and 1939 and for Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in 1929 and 1930. He captained the Derbyshire team between 1937 and 1939.
Elliott Martin Browne CBE was a British theatre director, known for his production of twentieth century verse plays. He collaborated for many years with T. S. Eliot and was first producer of many of his plays including Murder in the Cathedral.

Sir William Browne FRS was an English medical doctor.

Sir George Washington Browne was a Scottish architect. He was born in Glasgow, and trained there and in London. He spent most of his career in Edinburgh, although his work can be found throughout Scotland and beyond. He was involved in nearly 300 projects, including many public and commercial buildings. One of his most notable buildings is Edinburgh's Central Library, and he became recognised as an authority on library planning and design. He came to national attention after winning a competition to design a bridge over the River Thames in London, although this was never realised. He was the first architect to be elected as President of the Royal Scottish Academy. He also served as President of the Edinburgh Architectural Association, and was instrumental in setting up the Royal Fine Art Commission for Scotland.

Sir Hugh Lett, 1st Baronet, was a British surgeon with a special interest in urology and headed the London Hospital's genito-urinary department for many years.

Sir Anthony Arthur Duncan Montague Browne was a British diplomat who was private secretary to Sir Winston Churchill during the last ten years of the latter's life.
Sir Nicholas Walker Browne, KBE, CMG was a British diplomat. He served as Ambassador to Iran from 1999 to 2002 and Ambassador to Denmark from 2003 to 2006.

The Harveian Society of London, named after the physician William Harvey, is a medical society and registered charity, founded in 1831. Doctors assemble regularly at the Medical Society of London, Chandos Street, Cavendish Square to converse and discuss medical matters through the medium of lectures and conferences.

William James Dempster was a British surgeon and researcher in organ transplantation at St Mary’s Hospital, London. He published more than 100 scientific reviews and papers on kidney transplant rejection in dogs, confirming that rejection was an example of immune response, mediated by serum antibodies.
John Cavendish Browne, 3rd Baron Kilmaine was an Anglo-Irish politician and landowner. He was an Irish representative peer (1849–73).