
Shambles Glacier is a steep glacier 4 miles long and 6 miles wide, with very prominent hummocks and crevasses, flowing east between Mount Bouvier and Mount Mangin into Stonehouse Bay on the east side of Adelaide Island. It is the island's largest glacier, and provides an eastern outlet from the giant Fuchs Ice Piedmont which covers the entire western two-thirds of the island. In doing so, Shambles Glacier provides the largest 'gap' in Adelaide Island's north-south running mountain chain.

The Airy Glacier is a glacier 20 nautical miles (37 km) long and 6 nautical miles (11 km) wide, flowing west to the northeast portion of Forster Ice Piedmont, near the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Mount Shelby is a mountain, 1,520 m, standing between Daspit Glacier and Bills Gulch at the head of Trail Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land. Discovered by members of East Base of the United States Antarctic Service (USAS), 1939-41. It was photographed from the air in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Ronne, and charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). Named by Ronne for Marjorie Shelby, who contributed her services as typist and editor in drafting the RARE prospectus and assisted in general expedition work prior to departure.
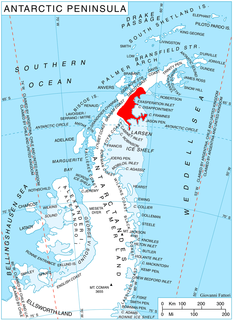
Adie Inlet is an ice-filled inlet, 25 miles (40 km) long in a northwest–southeast direction, lying east of Churchill Peninsula along the east coast of Graham Land. Charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) during 1947. Named by the FIDS for R.J. Adie, South African geologist with FIDS, 1947–49.
Wagner Ice Piedmont is an ice piedmont, 9 nautical miles (17 km) long in a NW-SE direction and 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide, overlying the southwest part of Rothschild Island.
Wakefield Highland is a snow-covered highland in the central region of the Antarctic Peninsula, bounded to the north by Hermes Glacier and the heads of Weyerhaeuser Glacier and Aphrodite Glacier, to the west by the heads of Airy Glacier, Rotz Glacier and Seller Glacier, to the south by Fleming Glacier and to the east by the heads of Lurabee Glacier, Sunfix Glacier and Grimley Glacier. Photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) on December 22, 1947. Surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in November 1960. Named after Viscount Wakefield of Hythe, a contributor to British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE), 1934-37. This toponym, concurred in by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) and Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN), restores the name Wakefield in the vicinity of the BGLE's displaced "Mount Wakefield".
Weyerhaeuser Glacier is a large glacier flowing north into Mercator Ice Piedmont close west of Mobiloil Inlet, on the east coast of Antarctic Peninsula. This glacier lies in the area first explored from the air by Sir Hubert Wilkins in 1928 and Lincoln Ellsworth in 1935, but it was first clearly delineated in aerial photographs taken by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS) in 1940. The glacier was resighted in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Ronne. He named it for F. K. Weyerhaeuser, of the Weyerhaeuser Timber Co., who contributed lumber and insulating material to the expedition.
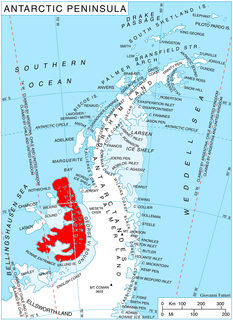
Coulter Glacier is a steeply inclined glacier, 5 nautical miles (9 km) long, flowing south from the Havre Mountains, northern Alexander Island, into Kolokita Cove in Lazarev Bay, Antarctica. The glacier was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947 and mapped from the photographs by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for R.W. Coulter, Master of USNS Alatna during U.S. Navy Operation Deepfreeze, 1969.
Crescent Scarp is a conspicuous, north-facing escarpment of rock and ice cliffs, rising to 1,400 metres (4,600 ft) on the south side of Fleming Glacier in northern Palmer Land. It was roughly surveyed from the ground by the British Graham Land Expedition in 1936-37, and photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service in 1940 and the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947. It was resurveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1958, and named descriptively.
Planet Heights is a series of summits running along an ice-free ridge, extending 24 nautical miles (44 km) in a north-south direction between the southernmost extremity of the LeMay Range and George VI Sound in the east part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. Many landforms and nearby features are named in association with this mountain range, some of these include landforms named after astronomers, satellites, planets and other things related to astrology and astrophysics. The mountain range was first mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, by Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1960. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) from association with the nearby glaciers named for planets of the solar system. The only planet that is not featured in any of these glaciers is the planet Earth, as there are no glaciers named "Earth Glacier" and this glacier does not exist.

Moran Glacier is a glacier 10 nautical miles (18 km) long, joined at the south side by Walter Glacier, flowing east into Schokalsky Bay, situated in the northeast portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. Photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, and surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1948-50. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander Clifford D. Moran, U.S. Navy, aircraft pilot, Squadron VXE-6, U.S. Navy Operation Deep Freeze, 1966 and 1977.
Hariot Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest along the south side of Morgan Upland before turning west into the northern portion of the Wordie Ice Shelf, along the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was roughly surveyed by the British Graham Land Expedition, 1936–37, and the upper reaches were photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947. The glacier was surveyed from the ground by members of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey who travelled along it in December 1958, and it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Thomas Hariot, an English mathematician who pioneered new methods of navigation under the patronage of Sir Walter Raleigh.
Himalia Ridge is a ridge running east–west on the north side of the Ganymede Heights massif, north-east of Jupiter Glacier, in the east of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947 and mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. The ridge was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee following British Antarctic Survey geological work, 1983–84, after Himalia, a satellite of the planet Jupiter, in association with Jupiter Glacier. The site lies within Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.147.
Tonkin Island is a narrow, ice-capped island in Antarctica. It is 3.5 nautical miles (6 km) long in a north-south direction, marked by ice-free peaks at each end, lying 11 nautical miles (20 km) southeast of Choyce Point, Bowman Coast, in Larsen Ice Shelf. The island was discovered and photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS) in 1940. It was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947 and named after John E. Tonkin, FIDS general assistant at Stonington Island, 1945–47; named Lewis Island by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) following additional aerial photography, 1947. The names Isla Mateo de Toro Zambrano and Isla Riquelme, referring to the north and south parts of this feature shown as two islands, appear on a Chilean hydrographic chart, 1947.
Relay Hills is a group of low, ice-covered hills, mainly conical in shape, between Mount Edgell and Kinnear Mountains in western Antarctic Peninsula. First roughly surveyed from the ground by British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE), 1936-37. Photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), November 1947. Resurveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), November 1958. The name, applied by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC), arose because both the BGLE and the FIDS sledging parties had to relay their loads through this area to the head of Prospect Glacier.
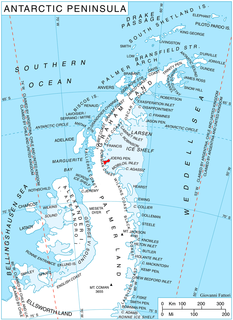
Reichle Mesa is an ice-covered tableland, 3 nautical miles (6 km) in extent and rising to 1,160 m, between Stubbs Pass and Getman Ice Piedmont on Joerg Peninsula, Bowman Coast. The feature was photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service (USAS), 1940, Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947, and U.S. Navy, 1966, and was surveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1946-48. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 1977 after Richard A. Reichle, United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) biologist, specialist on Antarctic seals in six austral summers, 1970–77, the last two summers in RV Islands.
Lewis Point is a point at the south side of the mouth of Anthony Glacier, on the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It is marked by rocky exposures on its north side and is surmounted by an ice-covered dome, 510 metres (1,670 ft) high. The point was photographed from the air by the United States Antarctic Service in 1940. During 1947 it was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Finn Ronne, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey charted it from the ground. It was named by Ronne for Colonel Richard L. Lewis of the Army Quartermaster Corps, which furnished field equipment and clothing to the RARE for testing purposes.
Mount Alfred is an ice-capped mountain, more than 2,000 m, 5.5 nautical miles (10 km) inland from George VI Sound and 8 nautical miles (15 km) south of Mount Athelstan in the Douglas Range of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was first photographed from the air on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth and mapped from these photos by W.L.G. Joerg. Its east face was roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) and resurveyed in 1948 and 1949 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), who named it for Alfred, Saxon king of England, 871-899. The west face of the mountain was mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, by Searle of the FIDS in 1960.













