| Bulinus reticulatus | |
|---|---|
 | |
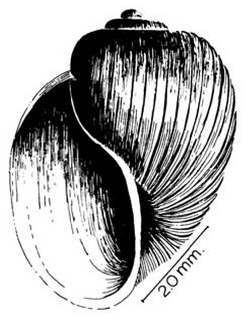
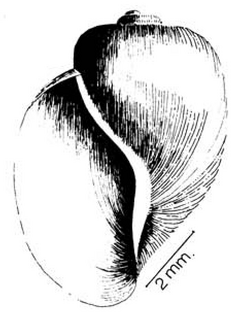
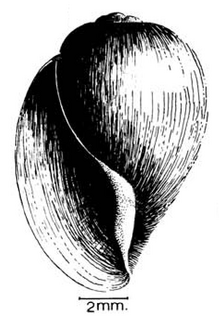
| Drawing of apertural view of the shell of Bulinus reticulatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| (unranked): | clade Heterobranchia clade Euthyneura clade Panpulmonata clade Hygrophila |
| Superfamily: | Planorboidea |
| Family: | Planorbidae |
| Subfamily: | Bulininae |
| Tribe: | Bulinini |
| Genus: | Bulinus |
| Species: | B. reticulatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Bulinus reticulatus Mandahl-Barth, 1954 | |
Bulinus reticulatus is a species group of a tropical freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ramshorn snails and their allies.

Freshwater snails are gastropod mollusks which live in freshwater. There are many different families. They are found throughout the world in various habitats, ranging from ephemeral pools to the largest lakes, and from small seeps and springs to major rivers. The great majority of freshwater gastropods have a shell, with very few exceptions. Some groups of snails that live in freshwater respire using gills, whereas other groups need to reach the surface to breathe air. In addition, some are amphibious and have both gills and a lung. Most feed on algae, but many are detritivors and some are filter feeders.

An aquatic animal is an animal, either vertebrate or invertebrate, which lives in the water for most or all of its lifetime. Many insects such as mosquitoes, mayflies, dragonflies and caddisflies have aquatic larvae, with winged adults. Aquatic animals may breathe air or extract oxygen that dissolved in water through specialised organs called gills, or directly through the skin. Natural environments and the animals that live in them can be categorized as aquatic (water) or terrestrial (land). This designation is paraphyletic.

Planorbidae, common name the ramshorn snails or ram's horn snails, is a family of air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonate gastropod molluscs. Unlike most molluscs, the blood of ram's horn snails contains iron-based hemoglobin instead of copper-based hemocyanin. As a result, planorbids are able to breathe oxygen more efficiently than other molluscs. The presence of hemoglobin gives the body a reddish colour. This is especially apparent in albino animals.