T-complex protein 1 subunit epsilon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT5 gene. [5]
T-complex protein 1 subunit epsilon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT5 gene. [5]
This gene encodes a molecular chaperone that is member of the TRiC complex. This complex consists of two identical stacked rings, each containing eight different proteins. Unfolded polypeptides enter the central cavity of the complex and are folded in an ATP-dependent manner. The complex folds various proteins, including actin and tubulin. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been observed but have not been thoroughly characterized. [5]
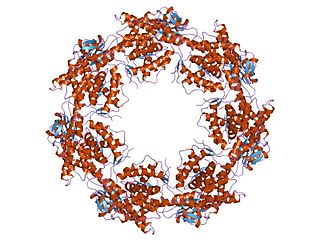
HSP60, also known as chaperonins (Cpn), is a family of heat shock proteins originally sorted by their 60kDa molecular mass. They prevent misfolding of proteins during stressful situations such as high heat, by assisting protein folding. HSP60 belong to a large class of molecules that assist protein folding, called molecular chaperones.

Prefoldin (GimC) is a superfamily of proteins used in protein folding complexes. It is classified as a heterohexameric molecular chaperone in both archaea and eukarya, including humans. A prefoldin molecule works as a transfer protein in conjunction with a molecule of chaperonin to form a chaperone complex and correctly fold other nascent proteins. One of prefoldin's main uses in eukarya is the formation of molecules of actin for use in the eukaryotic cytoskeleton.

Prostaglandin E synthase 3 (cytosolic) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES3 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 3, mitochondrial, also known as Tumorous imaginal disc 1 (TID1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJA3 gene on chromosome 16. This protein belongs to the DNAJ/Hsp40 protein family, which is known for binding and activating Hsp70 chaperone proteins to perform protein folding, degradation, and complex assembly. As a mitochondrial protein, it is involved in maintaining membrane potential and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) integrity, as well as cellular processes such as cell movement, growth, and death. Furthermore, it is associated with a broad range of diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, inflammatory diseases, and cancers.

T-complex protein 1 subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCP1 gene.

Phosducin-like protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCL gene.

Prefoldin subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PFDN1 gene.

T-complex protein 1 subunit theta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT8 gene. The CCT8 protein is a component of the TRiC complex.

Tubulin-specific chaperone D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBCD gene.

T-complex protein 1 subunit eta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT7 gene.

T-complex protein 1 subunit delta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT4 gene. The CCT4 protein is a component of the TRiC complex.

T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT6A gene.

T-complex protein 1 subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT2 gene.

Prefoldin subunit 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PFDN5 gene.

T-complex protein 1 subunit gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT3 gene.

Prefoldin subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PFDN2 gene.

Prefoldin subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PFDN4 gene.

T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCT6B gene.

The G beta-gamma complex (Gβγ) is a tightly bound dimeric protein complex, composed of one Gβ and one Gγ subunit, and is a component of heterotrimeric G proteins. Heterotrimeric G proteins, also called guanosine nucleotide-binding proteins, consist of three subunits, called alpha, beta, and gamma subunits, or Gα, Gβ, and Gγ. When a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) is activated, Gα dissociates from Gβγ, allowing both subunits to perform their respective downstream signaling effects. One of the major functions of Gβγ is the inhibition of the Gα subunit.

T-complex protein Ring Complex (TRiC), otherwise known as Chaperonin Containing TCP-1 (CCT), is a multiprotein complex and the chaperonin of eukaryotic cells. Like the bacterial GroEL, the TRiC complex aids in the folding of ~10% of the proteome, and actin and tubulin are some of its best known substrates. TRiC is an example of a biological machine that folds substrates within the central cavity of its barrel-like assembly using the energy from ATP hydrolysis.