Related Research Articles

Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum. Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, abdominal pain and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous.
A tumor marker is a biomarker that can be used to indicate the presence of cancer or the behavior of cancers. They can be found in bodily fluids or tissue. Markers can help with assessing prognosis, surveilling patients after surgical removal of tumors, and even predicting drug-response and monitor therapy.

Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly-related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is usually present at very low levels in the blood of healthy adults. However, the serum levels are raised in some types of cancer, which means that it can be used as a tumor marker in clinical tests. Serum levels can also be elevated in heavy smokers.
Technetium (99mTc) arcitumomab is a drug used for the diagnostic imaging of colorectal cancers, marketed by Immunomedics. It consists of the Fab' fragment of a monoclonal antibody and a radionuclide, technetium-99m.

Signal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule.

Chemokine receptor 6 also known as CCR6 is a CC chemokine receptor protein which in humans is encoded by the CCR6 gene. CCR6 has also recently been designated CD196. The gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 6 (6q27) on the Watson (plus) strand. It is 139,737 bases long and encodes a protein of 374 amino acids.
ALVAC-CEA vaccine is a cancer vaccine containing a canary pox virus (ALVAC) combined with the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) human gene.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) also known as CD66a, is a human glycoprotein, and a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) also known as CD66c, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family..

Pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein 1 (PSBG-1) also known as CD66f, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSG1 gene and is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family. Pregnancy-specific glycoproteins (PSGs) are a complex consisting of carbohydrate and protein, which is present in the mammalian body specifically during pregnancy. This glycoprotein is the most abundant protein found in the maternal bloodstream during the later stages of pregnancy and it is of vital importance in fetal development. The PSG functions primarily as an immunomodulator to protect the growing fetus.

Pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSG9 gene.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 3 (CEACAM3) also known as CD66d, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family..
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8 (CEACAM8) also known as CD66b, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family. Its main function is cell adhesion, cell migration, and pathogen binding.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEACAM7 gene.
Galectin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LGALS4 gene.

Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (CEACAM5) also known as CD66e, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family.
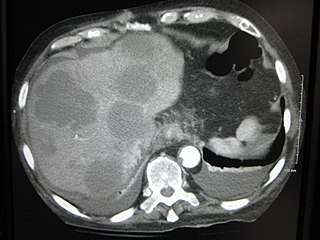
A liver metastasis is a malignant tumor in the liver that has spread from another organ affected by cancer. The liver is a common site for metastatic disease because of its rich, dual blood supply. Metastatic tumors in the liver are 20 times more common than primary tumors. In 50% of all cases the primary tumor is of the gastrointestinal tract; other common sites include the breast, ovaries, bronchus and kidney. Patients with Colorectal cancer will develop liver metastases during the disease

HOXA11-AS lncRNA is a long non-coding RNA from the antisense strand in the homeobox A. The HOX gene contains four clusters. The sense strand of the HOXA gene codes for proteins. Alternative names for HOXA11-AS lncRNA are: HOXA-AS5, HOXA11S, HOXA11-AS1, HOXA11AS, or NCRNA00076. This gene is 3,885 nucleotides long and resides at chromosome 7 (7p15.2) and is transcribed from an independent gene promoter. Being a lncRNA, it is longer than 200 nucleotides in length, in contrast to regular non-coding RNAs.
Kohzoh Imai is a Japanese physician and oncologist specializing in molecular diagnosis and novel medical treatment of cancer. He is well known for the discovery of a melanoma-related antigen by producing a monoclonal antibody. In addition, he produced monoclonal antibodies against CEA or ICAM-1 and found out they are usable in the diagnosis and the pathological analysis.
Mary E. Costanza is a retired doctor and professor at the University of Massachusetts Amherst medical school. She is known for her research in the field of cancer, cancer prevention, and leadership of the American Cancer Society in Massachusetts.
References
- ↑ Estiar, Mehrdad Asghari; Esmaeili, Rezvan; Zare, Ali-Akbar; Farahmand, Leila; Fazilaty, Hassan; Zekri, Ali; Jafarbeik-Iravani, Narges; Majidzadeh-A, Keivan (1 November 2017). "High expression of CEACAM19, a new member of carcinoembryonic antigen gene family, in patients with breast cancer". Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 17 (4): 547–553. doi:10.1007/s10238-016-0442-1. ISSN 1591-9528. PMID 27909883.
- ↑ Dongxui, Sui; Qinglong, Jiang; Bingjie, Qu; Guihua, Gao (5 January 2020). "Expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 19 and its prognostic significance in colorectal cancer". 中国医师进修杂志 (in Chinese). 43 (1): 70–75. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4904.2020.01.017. ISSN 1673-4904.