
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder that results in blood clots forming in small blood vessels throughout the body. This results in a low platelet count, low red blood cells due to their breakdown, and often kidney, heart, and brain dysfunction. Symptoms may include large bruises, fever, weakness, shortness of breath, confusion, and headache. Repeated episodes may occur.

Hemolytic–uremic syndrome (HUS) is a group of blood disorders characterized by low red blood cells, acute kidney failure, and low platelets. Initial symptoms typically include bloody diarrhea, fever, vomiting, and weakness. Kidney problems and low platelets then occur as the diarrhea progresses. Children are more commonly affected, but most children recover without permanent damage to their health, although some children may have serious and sometimes life-threatening complications. Adults, especially the elderly, may present a more complicated presentation. Complications may include neurological problems and heart failure.

The alternative pathway is a type of cascade reaction of the complement system and is a component of the innate immune system, a natural defense against infections.

Complement component 3, often simply called C3, is a protein of the immune system. It plays a central role in the complement system and contributes to innate immunity. In humans it is encoded on chromosome 19 by a gene called C3.
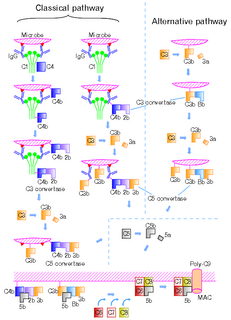
C5 convertase is an enzyme belonging to a family of serine proteases that play key role in the innate immunity. It participates in the complement system ending with cell death.

Thrombomodulin (TM), CD141 or BDCA-3 is an integral membrane protein expressed on the surface of endothelial cells and serves as a cofactor for thrombin. It reduces blood coagulation by converting thrombin to an anticoagulant enzyme from a procoagulant enzyme. Thrombomodulin is also expressed on human mesothelial cell, monocyte and a dendritic cell subset.
Complement factor B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFB gene.
Complement control protein are proteins that interact with components of the complement system.

Factor H is a member of the regulators of complement activation family and is a complement control protein. It is a large, soluble glycoprotein that circulates in human plasma. Its principal function is to regulate the alternative pathway of the complement system, ensuring that the complement system is directed towards pathogens or other dangerous material and does not damage host tissue. Factor H regulates complement activation on self cells and surfaces by possessing both cofactor activity for the Factor I mediated C3b cleavage, and decay accelerating activity against the alternative pathway C3-convertase, C3bBb. Factor H exerts its protective action on self cells and self surfaces but not on the surfaces of bacteria or viruses. This is thought to be the result of Factor H having the ability to adopt conformations with lower or higher activities as a cofactor for C3 cleavage or decay accelerating activity. The lower activity conformation is the predominant form in solution and is sufficient to control fluid phase amplification. The more active conformation is thought to be induced when Factor H binds to glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and or sialic acids that are generally present on host cells but not, normally, on pathogen surfaces ensuring that self surfaces are protected whilst complement proceeds unabated on foreign surfaces.

CD46 complement regulatory protein also known as CD46 and Membrane Cofactor Protein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CD46 gene. CD46 is an inhibitory complement receptor.

Complement factor I, also known as C3b/C4b inactivator, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFI gene. Complement factor I is a protein of the complement system, first isolated in 1966 in guinea pig serum, that regulates complement activation by cleaving cell-bound or fluid phase C3b and C4b. It is a soluble glycoprotein that circulates in human blood at an average concentration of 35 μg/mL.

C-C motif chemokine 4-like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL4L1 gene.

Complement factor H-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR1 gene.

CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPG gene.

CAMP responsive element binding protein-like 1, also known as CREBL1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CREBL1 gene.

Age-related maculopathy susceptibility protein 2, is a mitochondrial protein that in humans is encoded by the ARMS2 gene.

Complement factor H-related protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR3 gene.

Complement factor H-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR5 gene.

Complement factor H-related protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR2 gene.
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is an extremely rare, life-threatening, progressive disease that frequently has a genetic component. In most cases it can be effectively controlled by interruption of the complement cascade. Particular monoclonal antibodies, discussed later in the article, have proven efficacy in many cases.
















