Related Research Articles

The Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited is a Japanese multinational pharmaceutical company. It is the third largest pharmaceutical company in Asia, behind Sinopharm and Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, and one of the top 20 largest pharmaceutical companies in the world by revenue. The company has over 49,578 employees worldwide and achieved US$19.299 billion in revenue during the 2018 fiscal year. The company is focused on oncology, rare diseases, neuroscience, gastroenterology, plasma-derived therapies and vaccines. Its headquarters is located in Chuo-ku, Osaka, and it has an office in Nihonbashi, Chuo, Tokyo. In January 2012, Fortune Magazine ranked the Takeda Oncology Company as one of the 100 best companies to work for in the United States. As of 2015, Christophe Weber was appointed as the CEO and president of Takeda.

F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche, is a Swiss multinational holding healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, Roche Holding AG, has shares listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange. The company headquarters are located in Basel. Roche is the fifth-largest pharmaceutical company in the world by revenue and the leading provider of cancer treatments globally. In 2023, the company’s seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 76.

Amgen Inc. is an American multinational biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Thousand Oaks, California. One of the world's largest independent biotechnology companies, As of 2022, Amgen has approximately 24,000 staff in total.
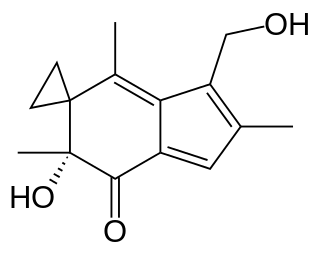
Irofulven or 6-hydroxymethylacylfulvene is an experimental antitumor agent. It belongs to the family of drugs called alkylating agents.
Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. is a medical research and drug development company with corporate offices and research facilities in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Incorporated in 1980 as AntiVirals, shortly before going public the company changed its name from AntiVirals to AVI BioPharma soon with stock symbol AVII and in July 2012 changed name from AVI BioPharma to Sarepta Therapeutics and SRPT respectively. As of 2023, the company has four approved drugs.

Astellas Pharma Inc. is a Japanese multinational pharmaceutical company, formed on 1 April 2005 from the merger of Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd..

Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of Camptotheca acuminata, a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today: topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also been found in other plants including Chonemorpha fragrans.
Insert Therapeutics, Inc., now Calando Pharmaceuticals, Inc., is a medical research company that uses nanobiotechnology specializing in therapeutic agents that are conjugated, to facilitate and enhance drug delivery. The small company was founded in 2000, is located in Pasadena, California, and is owned by Arrowhead Research Corporation.
Glembatumumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) that targets cancer cells expressing transmembrane glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB).

Jindřich Henry Kopeček was born in Strakonice, Czech Republic, as the son of Jan and Herta Zita (Krombholz) Kopeček. He is distinguished professor of pharmaceutical chemistry and distinguished professor of biomedical engineering at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, Utah. Kopeček is also an honorary professor at Sichuan University in Chengdu, China. His research focuses on biorecognition of macromolecules, bioconjugate chemistry, drug delivery systems, self-assembled biomaterials, and drug-free macromolecular therapeutics.

Santaris Pharma A/S was a biopharmaceutical company founded in 2003 in Copenhagen, Denmark. The company also had a branch in San Diego, California that opened in 2009. Created by a merger between Cureon and Pantheco, Santaris developed RNA-targeted medicines using a Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) Drug Platform and Drug Development Engine.
AbbVie Inc. is an American pharmaceutical company headquartered in North Chicago, Illinois. It is ranked sixth on the list of largest biomedical companies by revenue. In 2023, the company's seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 74. The company's primary product is Humira (adalimumab), administered via injection. It is approved to treat autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, plaque psoriasis, and ulcerative colitis.
Polymer-drug conjugates are nano-medicine products under development for cancer diagnosis and treatment. There are more than 10 anticancer conjugates in clinical development. Polymer-drug conjugates are drug molecules held in polymer molecules, which act as the delivery system for the drug. Polymer drugs have passed multidrug resistance (MDR) testing and hence may become a viable treatment for endocrine-related cancers. A cocktail of pendant drugs could be delivered by water-soluble polymer platforms. The physical and chemical properties of the polymers used in polymer-drug conjugates are specially synthesized to flow through the kidneys and liver without being filtered out, allowing the drugs to be used more effectively. Traditional polymers used in polymer-drug conjugates can be degraded through enzymatic activity and acidity. Polymers are now being synthesized to be sensitive to specific enzymes that are apparent in diseased tissue. The drugs remain attached to the polymer and are not activated until the enzymes associated with the diseased tissue are present. This process significantly minimizes damage to healthy tissue.
Mark E. Davis is the Warren and Katherine Schlinger Professor of Chemical Engineering at the California Institute of Technology. He is a member of the City of Hope National Medical Center. He earned his B.S., M.S., and Ph.D. in chemical engineering all from the University of Kentucky. His lab focuses on the synthesis of materials for catalysis and biocompatible materials for drug delivery.
Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics for genetically defined diseases. The company was founded in 2002 and is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. In 2016, Forbes included the company on its "100 Most Innovative Growth Companies" list.

Andreas Bernkop-Schnürch is an Austrian scientist and entrepreneur, who is Head of the Department of Pharmaceutical Technology in the Institute of Pharmacy at the University of Innsbruck.

Hanmi Pharm Co., Ltd. is a South Korean pharmaceutical company that is headquartered in Seoul.

William H.Rastetter, a scientist, entrepreneur and venture capitalist, is the chair of Neurocrine Biosciences, of Fate Therapeutics, and of Daré Bioscience, Inc. in San Diego, California. He was a founding board member and investor in GRAIL, Inc. in Menlo Park, California, and served for a period as the company's interim CEO (2017) and chair (2017-2018). Rastetter is also a director of Regulus Therapeutics and Iambic Therapeutics. He was a partner in the venture firm Venrock (2006-2013), and a trustee at Caltech (2015-2018). He has served as a director (1998-2016) and as chair of Illumina (2005-2016). He advised SVB Leerink (2014-2019) and currently advises Illumina Ventures.
Hamid Ghandehari is an Iranian-American drug delivery research scientist, and a professor in the Departments of Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Biomedical Engineering at the University of Utah. His research is focused in recombinant polymers for drug and gene delivery, nanotoxicology of dendritic and inorganic constructs, water-soluble polymers for targeted delivery and poly(amidoamine) dendrimers for oral delivery.

Dextran drug delivery systems involve the use of the natural glucose polymer dextran in applications as a prodrug, nanoparticle, microsphere, micelle, and hydrogel drug carrier in the field of targeted and controlled drug delivery. According to several in vitro and animal research studies, dextran carriers reduce off-site toxicity and improve local drug concentration at the target tissue site. This technology has significant implications as a potential strategy for delivering therapeutics to treat cancer, cardiovascular diseases, pulmonary diseases, bone diseases, liver diseases, colonic diseases, infections, and HIV.
References
- ↑ Weiss GJ, Chao J, Neidhart JD, Ramanathan RK, Bassett D, Neidhart JA, Choi CH, Chow W, Chung V, Forman SJ, Garmey E, Hwang J, Kalinoski DL, Koczywas M, Longmate J, Melton RJ, Morgan R, Oliver J, Peterkin JJ, Ryan JL, Schluep T, Synold TW, Twardowski P, Davis ME, Yen Y (2013). "First-in-human phase 1/2a trial of CRLX101, a cyclodextrin-containing polymer-camptothecin nanopharmaceutical in patients with advanced solid tumor malignancies". Invest. New Drugs. 31 (4): 986–1000. doi:10.1007/s10637-012-9921-8. PMC 3774600 . PMID 23397498.
- ↑ "Survival". thirteen.org.