
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with others to conserve, protect, and enhance fish, wildlife, plants and their habitats for the continuing benefit of the American people."

A swamp is a forested wetland. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in creating this environment. Swamps vary in size and are located all around the world. The water of a swamp may be fresh water, brackish water, or seawater. Freshwater swamps form along large rivers or lakes where they are critically dependent upon rainwater and seasonal flooding to maintain natural water level fluctuations. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Some swamps have hammocks, or dry-land protrusions, covered by aquatic vegetation, or vegetation that tolerates periodic inundation or soil saturation. The two main types of swamp are "true" or swamp forests and "transitional" or shrub swamps. In the boreal regions of Canada, the word swamp is colloquially used for what is more formally termed a bog, fen, or muskeg. Some of the world's largest swamps are found along major rivers such as the Amazon, the Mississippi, and the Congo.

A fen is a type of peat-accumulating wetland fed by mineral-rich ground or surface water. It is one of the main types of wetlands along with marshes, swamps, and bogs. Bogs and fens, both peat-forming ecosystems, are also known as mires. The unique water chemistry of fens is a result of the ground or surface water input. Typically, this input results in higher mineral concentrations and a more basic pH than found in bogs. As peat accumulates in a fen, groundwater input can be reduced or cut off, making the fen ombrotrophic rather than minerotrophic. In this way, fens can become more acidic and transition to bogs over time.

A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials – often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; alkaline mires are called fens. A bayhead is another type of bog found in the forest of the Gulf Coast states in the United States. They are often covered in heath or heather shrubs rooted in the sphagnum moss and peat. The gradual accumulation of decayed plant material in a bog functions as a carbon sink.
Montezuma National Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife preserve operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, encompassing part of the Montezuma Swamp at the north end of Cayuga Lake. The 10,004-acre preserve is composed of swamps, pools and channels and is a stopping point for migratory birds. It is the largest contiguous wetland complex in the northeastern United States and comprises a portion of the larger Montezuma Wetlands Complex, which is a partnership between the USFWS, the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, as well as several other non-profit support organizations.

The Baca National Wildlife Refuge is a 78,697-acre (31,848 ha) United States National Wildlife Refuge located in southern Colorado. It is within the Sangre de Cristo National Heritage Area.

The Seney National Wildlife Refuge is a managed wetland in Schoolcraft County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It has an area of 95,212 acres (385 km2). It is bordered by M-28 and M-77. The nearest town of any size is Seney, Michigan. The refuge contains the Seney Wilderness Area and the Strangmoor Bog National Natural Landmark within its boundaries.

The Erie National Wildlife Refuge is an 8,777-acre (3,552 ha) National Wildlife Refuge located in Crawford County, Pennsylvania. Named after the Erie tribe, it was established to provide waterfowl and other migratory birds with nesting, feeding, brooding, and resting habitat.

The copperbelly water snake or copperbelly is a subspecies of nonvenomous colubrid snake endemic to the Central United States.
Minerotrophic refers to environments that receive nutrients primarily through groundwater that flows through mineral-rich soils or rock, or surface water flowing over land. Minerotrophic, “minerogenous”, and “geogenous” are now often used interchangeably, although the latter two terms refer primarily to hydrological systems, while the former refers to nutrient dynamics. The hydrologic process behind minerotrophic wetlands results in water that has acquired dissolved chemicals which raise the nutrient levels and reduce the acidity. This in turn affects vegetation assemblages and diversity in the wetland in question. If dissolved chemicals include chemical bases such as calcium or magnesium ions, the water is referred to as base-rich and is neutral or alkaline. In contrast to minerotrophic environments, ombrotrophic environments get their water mainly from precipitation, and so are very low in nutrients and more acidic. Of the various wetland types, fens and rich fens are often minerotrophic while poor fens and bogs are often ombrotrophic. Marshes and swamps may also be fed through groundwater sources to a degree.

Folly Mills Creek Fen Natural Area Preserve is a Natural Area Preserve located in Augusta County, Virginia. The preserve was dedicated in 1998, and was the first privately owned Natural Area Preserve to be dedicated in the state.

Leslie Canyon National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge of the United States located in Arizona. The 2,770-acre (11.2 km2) refuge was established in 1988 to protect habitat for the endangered Yaqui Chub and Yaqui Topminnow. The refuge also protects a rare velvet ash-cottonwood-black walnut gallery forest.

The San Bernardino National Wildlife Refuge is located on the U.S.-Mexico border in Cochise County, Arizona. Situated at 3,720 to 3,920 feet (1,130–1,190 m) elevation in the bottom of a wide valley, the refuge encompasses a portion of the headwaters of the Yaqui River, which drains primarily western Chihuahua and eastern Sonora, Mexico. The 2,309-acre (9.34 km2) ranch was acquired by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service in 1982 to protect the water resources and provide habitat for endangered native fishes.

Sunkhaze Meadows National Wildlife Refuge is located in the Town of Milford, Penobscot County, Maine, approximately fourteen miles north of Bangor. The refuge was established in 1988 to ensure the ecological integrity of the Sunkhaze Meadows peat bog and the continued availability of its wetland, stream, forest and wildlife resources to the citizens of the United States. The purpose of acquisition, under the authority of the Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956 was "... for the development, advancement, management, conservation, and protection of fish and wildlife resources ..." and "... for the benefit of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, in performing its activities and services. Such acceptance may be subject to the terms of any restrictive or affirmative covenant, or condition of servitude ..." The Land and Water Conservation Fund was the source of funding for the purchase

The Warner Lakes are a chain of shallow lakes and marshes in the Warner Valley of eastern Lake County, Oregon, United States. The lakes extend the length of the valley, covering approximately 90,000 acres (360 km2).
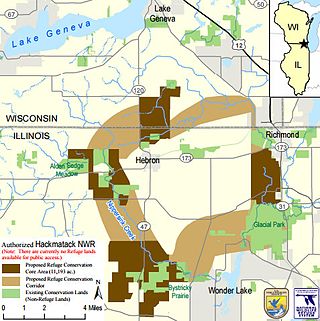
The Hackmatack National Wildlife Refuge is a newly established United States national wildlife refuge that will include noncontiguous properties, especially tallgrass prairie patches, wetland properties, and oak savanna parcels, located in the northwestern region of the Chicago metropolitan area and the southern part of the Milwaukee area. The refuge's boundaries encompass parts of McHenry County, Illinois, and Walworth County, Wisconsin. The refuge will be operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, known as USFWS. 85 percent of the refuge will be in Illinois, and 15 percent in Wisconsin.

Trail Creek is a 7.3-mile-long (11.7 km) north- by northwest-flowing stream whose main stem begins at the confluence of the West Branch Trail Creek and the East Branch Trail Creek in LaPorte County, Indiana, United States. Its mouth is a Lake Michigan harbor and marina adjacent to Washington Park in Michigan City, Indiana.

Salt Creek is a 24.0-mile-long (38.6 km) tributary of the East Arm Little Calumet River that begins south of Valparaiso in Porter County, Indiana and flows north until it joins the East Arm Little Calumet River just before it exits to Lake Michigan via the Port of Indiana-Burns Waterway.
Jackson Bog or Jackson Bog State Nature Preserve is a 58 acres (23 ha) State Nature Preserve in the U.S. state of Ohio. It is owned by the Jackson Township Local Board of Education and the Ohio Division of Natural Areas and Preserves.

Appalachian bogs are boreal or hemiboreal ecosystems, which occur in many places in the Appalachian Mountains, particularly the Allegheny and Blue Ridge subranges. Though popularly called bogs, many of them are technically fens.


















