In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla.

The alveolates are a group of protists, considered a major clade and superphylum within Eukarya. They are currently grouped with the stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria, the group being referred to as SAR.

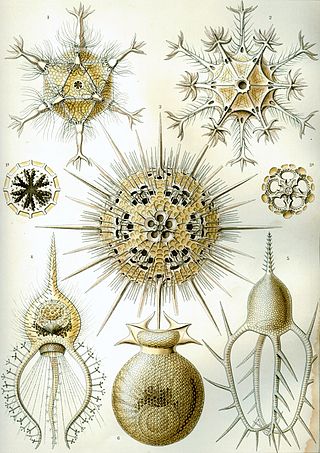
The centrohelids or centroheliozoa are a large group of heliozoan protists. They include both mobile and sessile forms, found in freshwater and marine environments, especially at some depth.

Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic forms, and also includes some important parasites of humans, including Giardia and Trichomonas. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now obsolete Protista kingdom. They are classified based on their flagellar structures, and they are considered to be the most basal flagellate lineage. Phylogenomic analyses split the members of Excavata into three different and not all closely related groups: Discobids, Metamonads and Malawimonads. Except for Euglenozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic.

Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes (protists) with stiff arms (axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule-supported projections from the amoeboid cell body, and are variously used for capturing food, sensation, movement, and attachment. They are similar to Radiolaria, but they are distinguished from them by lacking central capsules and other complex skeletal elements, although some produce simple scales and spines. They may be found in both freshwater and marine environments.

Chromista is a proposed but seemingly polyphyletic biological kingdom consisting of single-celled and multicellular eukaryotic species that share similar features in their photosynthetic organelles (plastids). It includes all protists whose plastids contain chlorophyll c, such as some algae, diatoms, oomycetes, and protozoans. It is probably a polyphyletic group whose members independently arose as a separate evolutionary group from the common ancestor of all eukaryotes. As it is assumed the last common ancestor already possessed chloroplasts of red algal origin, the non-photosynthetic forms evolved from ancestors able to perform photosynthesis. Their plastids are surrounded by four membranes, and are believed to have been acquired from some red algae.

Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow, was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford.

Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of bacteria. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria.

The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foraminifera and radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, Guttulinopsis vulgaris, a cellular slime mold, has also been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters (synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeletons, which are in different clades within Rhizaria made out of opal, celestite, or calcite. Certain species can attain sizes of more than a centimeter with some species being able to form cylindrical colonies approximately 1 cm in diameter and greater than 1 m in length. They feed by capturing and engulfing prey with the extensions of their pseudopodia; forms that are symbiotic with unicellular algae contribute significantly to the total primary production of the ocean.
Phaeodarea, or Phaeodaria, is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell.

Discicristata is a proposed eukaryotic clade. It consists of Euglenozoa plus Percolozoa.

A bikont is any of the eukaryotic organisms classified in the group Bikonta. Many single-celled members of the group, and the presumed ancestor, have two flagella.

Corticata, in the classification of eukaryotes, is a clade suggested by Thomas Cavalier-Smith to encompass the eukaryote supergroups of the following two groups:

Retaria is a clade within the supergroup Rhizaria containing the Foraminifera and the Radiolaria. In 2019, the Retaria were recognized as a basal Rhizaria group, as sister of the Cercozoa.

Malawimonadidae is a group of unicellular eukaryotes of outsize importance in understanding eukaryote phylogeny.

The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade of eukaryotic organisms that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon.

Diaphoretickes is a major group of eukaryotic organisms, with over 400,000 species. The majority of the earth's biomass that carries out photosynthesis belongs to Diaphoretickes.

Eukaryota, whose members are known as eukaryotes, is a diverse domain of organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea make up the other two domains.

Halvaria is a taxonomic grouping of protists that includes Alveolata and Stramenopiles (Heterokonta).
The biological classification system of life introduced by British zoologist Thomas Cavalier-Smith involves systematic arrangements of all life forms on earth. Following and improving the classification systems introduced by Carl Linnaeus, Ernst Haeckel, Robert Whittaker, and Carl Woese, Cavalier-Smith's classification attempts to incorporate the latest developments in taxonomy. His classification has been a major foundation in modern taxonomy, particularly with revisions and reorganisations of kingdoms and phyla.
















