Related Research Articles

Yggdrasil, in Norse cosmology, is an immense and central sacred tree. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.

Brian Boru was an Irish king who ended the domination of the High Kingship of Ireland by the Uí Néill and probably ended Viking invasion/domination of Ireland. Brian built on the achievements of his father, Cennétig mac Lorcain, and especially his elder brother, Mathgamain. Brian first made himself king of Munster, then subjugated Leinster, eventually becoming High King of Ireland. He was the founder of the O'Brien dynasty, and is widely regarded as one of the most successful and unifying monarchs in medieval Ireland.

The Battle of Clontarf took place on 23 April 1014 at Clontarf, near Dublin, on the east coast of Ireland. It pitted an army led by Brian Boru, High King of Ireland, against a Norse-Irish alliance comprising the forces of Sigtrygg Silkbeard, King of Dublin; Máel Mórda mac Murchada, King of Leinster; and a Viking army from abroad led by Sigurd of Orkney and Brodir of Mann. It lasted from sunrise to sunset, and ended in a rout of the Viking and Leinster armies.

Thor is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of mankind, hallowing, and fertility. Besides Old Norse Þórr, the deity occurs in Old English as Þunor, in Old Frisian as Thuner, in Old Saxon as Thunar, and in Old High German as Donar, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Þun(a)raz, meaning 'Thunder'.

Ár nDraíocht Féin: A Druid Fellowship, Inc. is a non-profit religious organization dedicated to the study and further development of modern Druidry.

Sacred groves or sacred woods are groves of trees and have special religious importance within a particular culture. Sacred groves feature in various cultures throughout the world. They were important features of the mythological landscape and cult practice of Celtic, Estonian, Baltic, Germanic, ancient Greek, Near Eastern, Roman, and Slavic polytheism; they also occur in locations such as India, Japan, and West Africa. Examples of sacred groves include the Greco-Roman temenos, various Germanic words for sacred groves, and the Celtic nemeton, which was largely but not exclusively associated with Druidic practice. During the Northern Crusades of the Middle Ages, conquering Christians commonly built churches on the sites of sacred groves. The Lakota and various other North American tribes regard particular forests or other natural landmarks as sacred places. Singular trees which a community deems to hold religious significance are known as sacred trees.

Donar's Oak was a sacred tree of the Germanic pagans located in an unclear location around what is now the region of Hesse, Germany. According to the 8th century Vita Bonifatii auctore Willibaldi, the Anglo-Saxon missionary Saint Boniface and his retinue cut down the tree earlier in the same century. Wood from the oak was then reportedly used to build a church at the site dedicated to Saint Peter. Sacred trees and sacred groves were widely venerated by the Germanic peoples.

The history of Ireland 800–1169 covers the period in the history of Ireland from the first Viking raids to the Norman invasion. The first two centuries of this period are characterised by Viking raids and the subsequent Norse settlements along the coast. Viking ports were established at Dublin, Wexford, Waterford, Cork and Limerick, which became the first large towns in Ireland.
Bróðir and Óspak of Man were two Danish brothers who were active in the Isle of Man and Ireland in the 11th century. They are mentioned in the 12th century Irish Cogadh Gaedhil re Gallaibh and the 13th century Icelandic Njal's Saga as key leaders who fought on opposite sides in the Battle of Clontarf in 1014. The latter account names Bróðir as the killer of Brian Boru, the High King of Ireland. Both Boru and Bróðir died in the battle, although accounts differ as to who killed whom. Óspak fought on the side of Boru, was injured, and lost his two sons in the battle.
Sigtrygg II Silkbeard Olafsson was a Hiberno-Norse king of Dublin of the Uí Ímair dynasty. He was caught up in the abortive Leinster revolt of 999–1000, after which he was forced to submit to the King of Munster, Brian Boru. His family also conducted a double marriage alliance with Boru, although he later realigned himself with the main leaders of the Leinster revolt of 1012–1014. He has a prominent role in the 12th-century Irish Cogadh Gaedhil re Gallaibh and the 13th century Icelandic Njal's Saga, as the main Norse leader at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014.
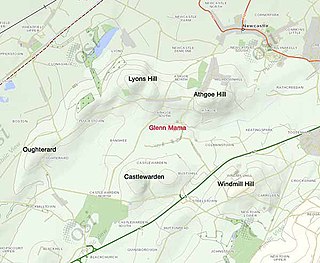
The Battle of Glenn Máma or Glenmama took place most probably near Lyons Hill in Ardclough, County Kildare, Ireland, in AD 999 between Windmill Hill and Blackchurch. It was the decisive and only engagement of the brief Leinster revolt of 999–1000 against the King of Munster, Brian Boru. In it, the combined forces of the Kingdoms of Munster and Meath, under King Brian Boru and the High King of Ireland, Máel Sechnaill II, inflicted a crushing defeat on the allied armies of Leinster and Dublin, led by King Máel Mórda of Leinster.
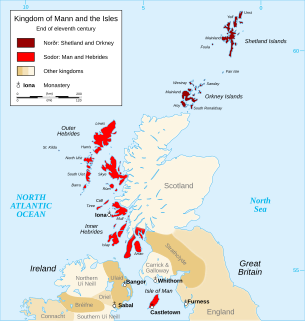
The Norse–Gaels also known as Hiberno-Scandinavian were a people of mixed Gaelic and Norse ancestry and culture. They emerged in the Viking Age, when Vikings who settled in Ireland and in Scotland adopted Gaelic culture and intermarried with Gaels. The Norse–Gaels dominated much of the Irish Sea and Scottish Sea regions from the 9th to 12th centuries. They founded the Kingdom of the Isles which included the coveted Isle of Man, the Hebrides, the Kingdom of Dublin, the Lordship of Galloway, and a Norse-Gaelic family briefly ruled the Kingdom of York. The most powerful Norse–Gaelic dynasty were the Uí Ímair or House of Ivar.

Trees are significant in many of the world's mythologies, and have been given deep and sacred meanings throughout the ages. Human beings, observing the growth and death of trees, and the annual death and revival of their foliage, have often seen them as powerful symbols of growth, death and rebirth. Evergreen trees, which largely stay green throughout these cycles, are sometimes considered symbols of the eternal, immortality or fertility. The image of the Tree of life or world tree occurs in many mythologies.

Máel Sechnaill mac Domnaill, also called Máel Sechnaill Mór or Máel Sechnaill II, was King of Mide and High King of Ireland. His great victory at the Battle of Tara against Olaf Cuaran in 980 resulted in Gaelic Irish control of the Kingdom of Dublin.

Cogad Gáedel re Gallaib is a medieval Irish text that tells of the depredations of the Vikings and Uí Ímair dynasty in Ireland and the Irish king Brian Boru's great war against them, beginning with the Battle of Sulcoit in 967 and culminating in the Battle of Clontarf in 1014, in which Brian was slain but his forces were victorious. The chronicle, which compares King Brian to Augustus and Alexander the Great, was written in the early twelfth century, at least a hundred years after the events it describes. Much of the narrative is drawn from the earlier Annals of Ulster.
Events from the 10th century in Ireland.
Ivar of Limerick, was the last Norse king of the city-state of Limerick, and penultimate King of the Foreigners of Munster, reigning during the rise to power of the Dál gCais and the fall of the Eóganachta.
The Battle of Sulcoit was fought in the year 968 between the Irish of the Dál gCais, led by Brian Boru, and the Vikings of Limerick, led by Ivar of Limerick. It was a victory for the Dál gCais and marked the end of Norse expansion in Ireland. It was also the first of three battles that highlight the career of Brian Boru. The battle took place during a military campaign led by Ivar of Limerick into Dál gCais territory. After the battle, the Dál gCais seized and burned the Viking stronghold of Limerick.
Annals of Inisfallen AI967.2: "A defeat of the foreigners of Luimnech by Mathgamain, son of Cennétig, at Sulchuait, and Luimnech was burned by him before noon on the following day."
Annals of Ulster U967.5: "Mathgamain son of Cennáitig, king of Caisel, plundered and burned Luimnech."

The O'Brien dynasty is a noble house of Munster, founded in the 10th century by Brian Boru of the Dál gCais (Dalcassians). After becoming King of Munster, through conquest he established himself as Ard Rí na hÉireann. Brian's descendants thus carried the name Ó Briain, continuing to rule the Kingdom of Munster until the 12th century where their territory had shrunk to the Kingdom of Thomond which they would hold for just under five centuries.

Trees hold a particular role in Germanic paganism and Germanic mythology, both as individuals and in groups. The central role of trees in Germanic religion is noted in the earliest written reports about the Germanic peoples, with the Roman historian Tacitus stating that Germanic cult practices took place exclusively in groves rather than temples. Scholars consider that reverence for and rites performed at individual trees are derived from the mythological role of the world tree, Yggdrasil; onomastic and some historical evidence also connects individual deities to both groves and individual trees. After Christianization, trees continue to play a significant role in the folk beliefs of the Germanic peoples.
References
- Holm, Poul. 2000. "Viking Dublin and the City-State Concept. Parameters and Significance of the Hiberno-Norse Settlement" in Hansen, Mogens Herman. A Comparative Study of Thirty City-state Cultures, pp. 251–262. The Royal Danish Academy of Science and Letters. ISBN 87-7876-177-8
