Route

It owned the ATSF lines between Phoenix–Ash Fork and Phoenix–Mojave. It leased/purchased the tracks built by the Southern Pacific Railroad across the Mojave Desert between Needles and Mojave in Southern California.
The California, Arizona and Santa Fe Railway was a non-operating subsidiary (paper railroad) of Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). It was incorporated in 1911, and was merged into the ATSF in 1963. [1]
California, Arizona and Santa Fe would ultimately be absorbed by Burlington Northern Santa Fe Railway.

It owned the ATSF lines between Phoenix–Ash Fork and Phoenix–Mojave. It leased/purchased the tracks built by the Southern Pacific Railroad across the Mojave Desert between Needles and Mojave in Southern California.

The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.

Thomas Nickerson was an American railroad executive. He served as the eighth president of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF), between 1874 and 1880. He was also president of the Atlantic and Pacific Railroad.

Cadiz is an unincorporated community in the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is located just south of the Marble Mountains near the National Trails Highway. Cadiz was a water stop on the railroad.

The Barnwell and Searchlight Railway is a defunct 23-mile (37 km) short-line railroad that operated from 1906 to 1911. The railroad ran from Barnwell, California to Searchlight, Nevada. It was always operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
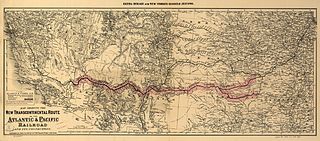
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Needles in Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.

The Copper Basin Railway is an Arizona short-line railroad that operates from a connection with the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) at Magma to Winkelman, in 54 miles (87 km) of length. The railroad also has a 7-mile (11 km) branch line that runs from Ray Junction to Ray, Arizona. There was formerly an interchange with the San Manuel Arizona Railroad (SMA) at Hayden. The CBRY exists primarily to serve a copper mine. L. S. “Jake” Jacobson was the President and Chief Operating Officer, retiring in 2020 after more than 30 years in his position. In summer 2006, ASARCO Copper Corporation purchased the entire railroad.
The Bradshaw Mountain Railroad was a subsidiary of the Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway (SFP&P) in Arizona. The 35.65-mile (57.37 km) railroad was built to serve the mines in the Bradshaw Mountains. The railroad built from a connection at Poland Junction and at Mayer with the Prescott and Eastern Railroad. The Prescott and Eastern was also operated by the SFP&P.
The Prescott and Eastern Railroad (P&E) was a non-operating subsidiary of the Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway (SFP&P) in Arizona. The 26.4 mile (42.5 km) common carrier railroad was built to serve the mines in the region. The railroad built from a connection with the SFP&P at Entro and extended south to Poland Junction and terminated at Mayer. At Poland Junction and Mayer the P&E connected with the Bradshaw Mountain Railroad, also a non-operating subsidiary of the SFP&P. After various mergers the P&E was merged into the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. The line was later abandoned by the Santa Fe Railway.

The Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway (SFP&P) was a common carrier railroad that later became an operating subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway in Arizona. At Ash Fork, Arizona, the SFP&P connected with Santa Fe's operating subsidiary, the Atlantic & Pacific Railroad mainline, that ran from California to Chicago. The SFP&P's 195-mile (314 km) line extended the Santa Fe Railway south into Phoenix. The SFP&P extended another 100 miles (160 km) to the east from Phoenix to Florence and Winkelman via the Phoenix and Eastern Railroad. The SFP&P also served several mines in the Prescott area, including the Derby Mine by way of the Summit (flag) Station at 'Prieta' in the Sierra Prieta range, through its various subsidiary railroads.
The Santa Fe and Grand Canyon Railroad (SF&GC) was a 56-mile railroad that ran from Williams, Arizona to take mining supplies and people to the copper mines near Anita. In 1901, the SF&GC was sold at foreclosure and became the Grand Canyon Railway, a subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. Today the line is a heritage railway owned by the Grand Canyon Railway providing excursions to the Grand Canyon.

Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway No. 1010 is a 2-6-2 type steam locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1901 for Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. It started out as a Vauclain compound locomotive before it was rebuilt into a conventional locomotive in the 1910s. It was primarily used for various passenger trains across the Southwestern United States, including the record breaking 1905 Scott Special on the segment between Needles, California, and Seligman, Arizona, before it was reassigned to freight service in the 1940s. It was retired in 1955 and was kept by the Santa Fe for several years for preservation purposes. In 1979, Santa Fe donated No. 1010 to the California State Railroad Museum, where the locomotive resides there in Sacramento as of 2024.

Paul Pardee Hastings was a prominent executive of the Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Railroad.

The Southern Transcon is a main line of the BNSF Railway comprising 11 subdivisions between Southern California and Chicago, Illinois. Completed in its current alignment in 1908 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, when it opened the Belen Cutoff in New Mexico and bypassed the steep grades of Raton Pass, it now serves as a mostly double-tracked intermodal corridor.

El Garces Intermodal Transportation Facility is an Amtrak intercity rail station and bus depot in downtown Needles, California. The structure was originally built in 1908 as El Garces, a Harvey House and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF) station. It is named for Francisco Garcés, a Spanish missionary who surveyed the area in the 1770s. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2002.
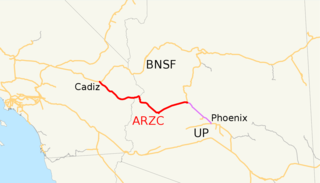
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.
The Phoenix and Eastern Railroad was a railroad company in the state of Arizona. It was chartered in 1901 to construct a line from Phoenix, Arizona to Benson, Arizona via the Gila River, a distance of 185 miles (298 km). The company would be leased by the Arizona Eastern Railroad, a subsidiary of the Southern Pacific, in 1910. A portion of its original line remains in service and is operated by the Copper Basin Railway.
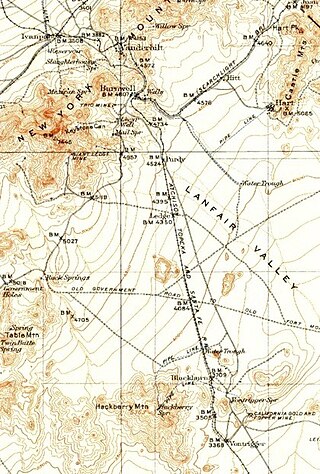
California Eastern Railway, is a defunct 45-mile (72 km) short-line railroad that operated from 1902 to 1911. The railroad ran from Goffs, California, to Ivanpah. It was first a private line operated by a mining company, that was acquired by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
Entro, also known as Entro Siding and P and E Junction, was a rail junction in Yavapai County, Arizona, United States. It has an estimated elevation of 5,141 feet (1,567 m) above sea level. It was the point at which the Prescott and Eastern Railroad met the Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway, eventually part of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. In 1917 it had a population of 15. The lines were eventually abandoned.
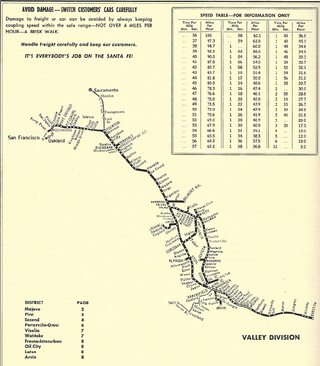
The Valley Division of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway ran from San Francisco to Barstow in California. It is currently in operation as the BNSF Railway's Stockton Subdivision and Bakersfield Subdivision.