
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.

The Grand Canyon Railway is a heritage railroad which carries passengers between Williams, Arizona, and the South Rim of Grand Canyon National Park.

Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe 3751 is a class "3751" 4-8-4 "Heavy Mountain" type steam locomotive built in May 1927 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Eddystone (Philadelphia), Pennsylvania for the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). No. 3751 was the first 4-8-4 steam locomotive built for the Santa Fe and was referenced in documentation as type: "Heavy Mountain", "New Mountain", or "Mountain 4-wheel trailer". No. 3751 served in passenger duties until being retired in 1953.

Cadiz is an unincorporated community in the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. It is located just south of the Marble Mountains near the National Trails Highway. Cadiz was a water stop on the railroad.

Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe 2926 is a class "2900" 4-8-4 type steam locomotive built in May 1944 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works for the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). It was used to pull passenger and fast freight trains, mostly throughout New Mexico, until it was retired from revenue service in 1953. Three years later, it was donated to Coronado Park in Albuquerque for static display.
The California, Arizona and Santa Fe Railway was a non-operating subsidiary of Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). It was incorporated in 1911, and was merged into the ATSF in 1963.

The Barnwell and Searchlight Railway is a defunct 23-mile (37 km) short-line railroad that operated from 1906 to 1911. The railroad ran from Barnwell, California to Searchlight, Nevada. It was always operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.

The Copper Basin Railway is an Arizona short-line railroad that operates from a connection with the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) at Magma to Winkelman, in 54 miles (87 km) of length. The railroad also has a 7-mile (11 km) branch line that runs from Ray Junction to Ray, Arizona. There was formerly an interchange with the San Manuel Arizona Railroad (SMA) at Hayden. The CBRY exists primarily to serve a copper mine. L. S. “Jake” Jacobson was the President and Chief Operating Officer, retiring in 2020 after more than 30 years in his position. In summer 2006, ASARCO Copper Corporation purchased the entire railroad.
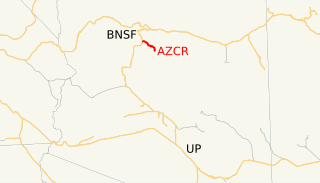
The Clarkdale Arizona Central Railroad is an Arizona short-line railroad that operates from a connection with the BNSF Railway at Drake, Arizona. The AZCR runs 37.8 miles (60.8 km) from Drake to Clarkdale, Arizona. An excursion train also runs on the line through Verde Canyon and is operated by the same owners under the Verde Canyon Railroad. The AZCR is owned by David L. Durbano.
The Bradshaw Mountain Railroad was a subsidiary of the Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway (SFP&P) in Arizona. The 35.65-mile (57.37 km) railroad was built to serve the mines in the Bradshaw Mountains. The railroad built from a connection at Poland Junction and at Mayer with the Prescott and Eastern Railroad. The Prescott and Eastern was also operated by the SFP&P.
The Prescott and Eastern Railroad (P&E) was a non-operating subsidiary of the Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway (SFP&P) in Arizona. The 26.4 mile (42.5 km) common carrier railroad was built to serve the mines in the region. The railroad built from a connection with the SFP&P at Entro and extended south to Poland Junction and terminated at Mayer. At Poland Junction and Mayer the P&E connected with the Bradshaw Mountain Railroad, also a non-operating subsidiary of the SFP&P. After various mergers the P&E was merged into the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. The line was later abandoned by the Santa Fe Railway. The first four miles of the line are now the Iron King Trail to Prescott Valley, Arizona.

Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway No. 1010 is a 2-6-2 type steam locomotive built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1901 for Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. It started out as a Vauclain compound locomotive before it was rebuilt into a conventional locomotive in the 1910s. It was primarily used for various passenger trains across the Southwestern United States, including the record breaking 1905 Scott Special on the segment between Needles, California, and Seligman, Arizona, before it was reassigned to freight service in the 1940s. It was retired in 1955 and was kept by the Santa Fe for several years for preservation purposes. In 1979, Santa Fe donated No. 1010 to the California State Railroad Museum, where the locomotive resides there in Sacramento as of 2024.

Williams Junction station was an Amtrak train station on the Southwest Chief route, located three miles (4.8 km) southeast of Williams, Arizona in the Kaibab National Forest. The station primarily served passengers travelling to the Grand Canyon via the Grand Canyon Railway.

Williams Depot is a privately owned train station in Williams, Arizona. It is the southern terminus of the Grand Canyon Railway line.

Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe No. 5 Little Buttercup is an 0-4-0 steam locomotive.
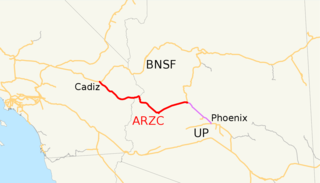
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.

Ash Fork Station is a former railway station of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, located in Ash Fork, Yavapai County, Arizona. The large and "grand" Harvey House Escalante Hotel and restaurant were part of the station complex.
The Phoenix and Eastern Railroad was a railroad company in the state of Arizona. It was chartered in 1901 to construct a line from Phoenix, Arizona to Benson, Arizona via the Gila River, a distance of 185 miles (298 km). The company would be leased by the Arizona Eastern Railroad, a subsidiary of the Southern Pacific, in 1910. A portion of its original line remains in service and is operated by the Copper Basin Railway.
The Hassayampa Flyer, also known as the Hassayampa Chief, was a passenger train operated by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway between Ash Fork and Phoenix in Arizona, United States.

Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe No. 769 is a preserved 769 class 2-8-0 "consolidation" type steam locomotive originally built by the Richmond Locomotive Works in 1900 as one of the Santa Fe Pacific Railroad's final locomotives. It was originally numbered 266 before the SFP had completely merged into its parent company, the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, and the locomotive was renumbered 3045, and it was eventually renumbered again to 769. The locomotive was put into use for short-distance freight trains and for yard switching before being sold again in 1950 to the Albuquerque and Cerrillos Coal Company in Madrid, New Mexico for more yard switching and short distance coal trains. As the 1950s progressed, however, the company shut down due to bankruptcy, and No. 769 was abandoned along with the rest of the locomotive yard and the rest of Madrid. In the late 1970s the town was recovered and converted into a heritage town, and No. 769 was then put on static display just behind the shed it was stored in, which was converted to the Engine House Theatre. In early 2020, No. 769 was selected for a future project to restore it to operating condition to eventually run on reconstructed trackage between Madrid and a nearby BNSF interchange near Los Cerrillos.

















