
The Florida East Coast Railway is a Class II railroad operating in the U.S. state of Florida, currently owned by Grupo México.

The South Florida Railroad was a railroad from Sanford, Florida, to Tampa, Florida, becoming part of the Plant System in 1893 and the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. It served as the southernmost segment of the Atlantic Coast Line's main line. The line remains in service today and is now part of the Central Florida Rail Corridor in the Orlando metro area. The rest of the line remains under the ownership of CSX Transportation as part of their A Line.
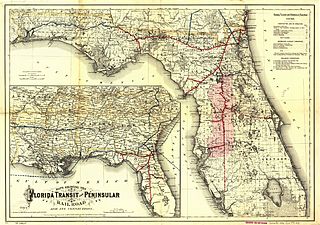
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.

The Plant System, named after its owner, Henry B. Plant, was a system of railroads and steamboats in the U.S. South, taken over by the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. The original line of the system was the Savannah, Florida and Western Railway, running across southern Georgia. The Plant Investment Company was formed in 1882 to lease and buy other railroads and expand the system. Other major lines incorporated into the system include the Savannah and Charleston Railroad and the Brunswick and Western Railroad.

The Central of Georgia Railway started as the Central Rail Road and Canal Company in 1833. As a way to better attract investment capital, the railroad changed its name to Central Rail Road and Banking Company of Georgia. This railroad was constructed to join the Macon and Western Railroad at Macon, Georgia, in the United States, and run to Savannah. This created a rail link from Chattanooga, on the Tennessee River, to seaports on the Atlantic Ocean. It took from 1837 to 1843 to build the railroad from Savannah to the eastern bank of the Ocmulgee River at Macon; a bridge into the city was not built until 1851.
Chartered in 1897, the Atlantic, Valdosta and Western Railway operated from Valdosta, Georgia, to Jacksonville, Florida, and was nicknamed the Jacksonville Short Line. The line was opened in July 1899, prefaced by a "bohemian smoker" banquet in Valdosta on June 27, 1899. In May 1902, the railroad was purchased by the Georgia Southern and Florida Railway and their parent company Southern Railway. The line was quickly integrated into Southern's passenger schedules with travel between Valdosta and Jacksonville advertised at about 31⁄2 hours. Southern took control of the AV&W on July 1, 1902.

The Valdosta Railway is a shortline railroad in the U.S. state of Georgia, connecting Clyattville to CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway at Valdosta. The company began operations in 1992 as a subsidiary of the Rail Management and Consulting Corporation, and was acquired by Genesee & Wyoming Inc. in 2005.
Elko is an unincorporated community in Houston County, Georgia, United States, south of the city of Perry. Founded circa 1890 as a railroad town, Elko prospered in the early 1900s as a local depot and trading center for cotton planters in southern Houston County.

Palatka station is a historic train station that was built in Palatka, Florida in 1908. The station currently serves Amtrak's Silver Service line and also houses the Palatka Railroad Preservation Society and the David Browning Railroad Museum. It is located at 220 North Eleventh Street, at the corner of North Eleventh Street's intersection with US 17/SR 100.

The Royal Palm was a named train of the Southern Railway that ran from Cincinnati, Ohio, to Jacksonville, Florida, and then on the Florida East Coast Railway's East Coast Champion to Miami, Florida. The train was discontinued in 1970.
The Florida Southern Railway was a railroad that operated in Florida in the late 1800s. It was one of Florida's three notable narrow gauge railway when it was built along with the South Florida Railroad and the Orange Belt Railway. The Florida Southern was originally chartered to run from Lake City south through central Florida to Charlotte Harbor. However, with the influence of Henry B. Plant, it operated with two discontinuous segments that would be part of the Plant System, which would later become part of the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad.

The Palatka-Lake Butler State Trail (PLB) corridor stretches nearly 47 miles (76 km) from the vicinity of Lake Butler, Florida to Palatka, Florida. The project is located along the former Georgia Southern and Florida Railway right-of-way and the trail is being constructed on top of the existing abandoned railroad bed through Putnam, Clay, Bradford, and Union counties.
The Cape Fear and Yadkin Valley Railway was a Southeastern railroad that operated in the Carolinas immediately after Reconstruction. It ran from Mount Airy, North Carolina, southeast through Greensboro and Fayetteville to the Atlantic port of Wilmington, North Carolina. A significant branch also ran from Fayetteville south to Bennettsville, South Carolina.
The Jacksonville & Southwestern Railroad (J&SW) was a railroad that served Florida from 1899 to 1904. It was purchased by the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1904. The Atlantic Coast Line would extend the line further west and it would become their Jacksonville—Wilcox Line. Some of the original right-of-way was converted to a recreational path in the rails to trails program in the 1990s.
The Live Oak, Tampa and Charlotte Harbor Railroad was a historic railroad in Florida chartered by railroad tycoon Henry B. Plant. It was built as an extension of Plant's Live Oak and Rowlands Bluff Railroad. Together, the two lines ran from Live Oak, Florida to Gainesville via High Springs. The lines were completed in 1884.
The Waycross Short Line was the unofficial name of a railroad line built by Henry B. Plant that ran from Waycross, Georgia to Jacksonville, Florida on the St. Johns River. The line through Georgia was chartered by Plant as the Waycross and Florida Railroad and the Florida segment was chartered as the East Florida Railway. The line crossed the Georgia/Florida border just south of Folkston, Georgia at the St. Marys River.

The Macon, Dublin and Savannah Railroad was chartered in 1885 as the Macon and Dublin Railroad. It was built to connect its namesake towns, Macon and Dublin. Eventually, it became a 96-mile short line operating between Macon and Vidalia.
The Seaboard Air Line Railroad’s Main Line was the backbone of the Seaboard Air Line Railroad's network in the southeastern United States. The main line ran from Richmond, Virginia to Tampa, Florida, a distance of over 800 miles. Along its route it passed through Petersburg, Raleigh, Columbia, Savannah, Jacksonville, and Ocala, Florida. While some segments of the line have been abandoned as of 2023, most of the line is still in service and is owned by the Seaboard Air Line's successor, CSX Transportation as their S-Line.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's High Springs—Croom Line was a historic rail line in northern Florida. The line dates back to the late 1800s and was used for both passengers and freight.










