
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate Branchiostoma.
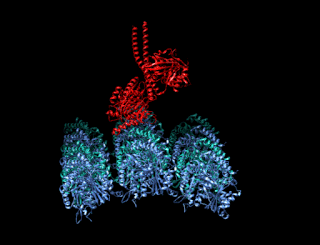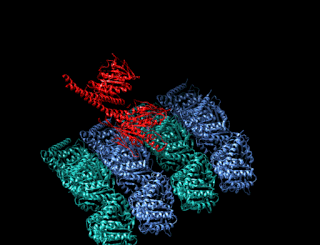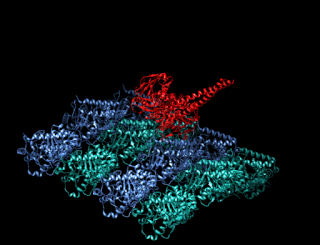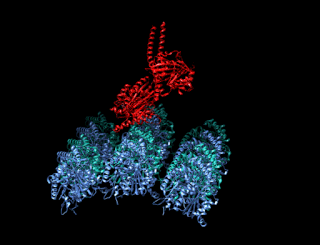
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells.
In cell biology, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are proteins that interact with the microtubules of the cellular cytoskeleton. MAPs are integral to the stability of the cell and its internal structures and the transport of components within the cell.
Plectin is a giant protein found in nearly all mammalian cells which acts as a link between the three main components of the cytoskeleton: actin microfilaments, microtubules and intermediate filaments. In addition, plectin links the cytoskeleton to junctions found in the plasma membrane that structurally connect different cells. By holding these different networks together, plectin plays an important role in maintaining the mechanical integrity and viscoelastic properties of tissues.

Stathmin, also known as metablastin and oncoprotein 18 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STMN1 gene.
The spindle pole body (SPB) is the microtubule organizing center in yeast cells, functionally equivalent to the centrosome. Unlike the centrosome the SPB does not contain centrioles. The SPB organises the microtubule cytoskeleton which plays many roles in the cell. It is important for organising the spindle and thus in cell division.
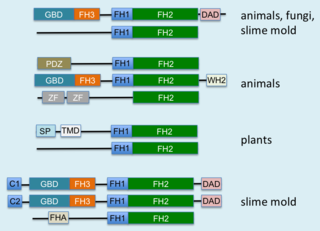
Formins (formin homology proteins) are a group of proteins that are involved in the polymerization of actin and associate with the fast-growing end (barbed end) of actin filaments. Most formins are Rho-GTPase effector proteins. Formins regulate the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton and are involved in various cellular functions such as cell polarity, cytokinesis, cell migration and SRF transcriptional activity. Formins are multidomain proteins that interact with diverse signalling molecules and cytoskeletal proteins, although some formins have been assigned functions within the nucleus.

Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DISC1 gene. In coordination with a wide array of interacting partners, DISC1 has been shown to participate in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, neuronal axon and dendrite outgrowth, mitochondrial transport, fission and/or fusion, and cell-to-cell adhesion. Several studies have shown that unregulated expression or altered protein structure of DISC1 may predispose individuals to the development of schizophrenia, clinical depression, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. The cellular functions that are disrupted by permutations in DISC1, which lead to the development of these disorders, have yet to be clearly defined and are the subject of current ongoing research. Although, recent genetic studies of large schizophrenia cohorts have failed to implicate DISC1 as a risk gene at the gene level, the DISC1 interactome gene set was associated with schizophrenia, showing evidence from genome-wide association studies of the role of DISC1 and interacting partners in schizophrenia susceptibility.

Microtubule-associated protein 2 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the MAP2 gene.

Dynactin is a 23 subunit protein complex that acts as a co-factor for the microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein-1. It is built around a short filament of actin related protein-1 (Arp1).

Alpha II-spectrin, also known as Spectrin alpha chain, brain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTAN1 gene. Alpha II-spectrin is expressed in a variety of tissues, and is highly expressed in cardiac muscle at Z-disc structures, costameres and at the sarcolemma membrane. Mutations in alpha II-spectrin have been associated with early infantile epileptic encephalopathy-5, and alpha II-spectrin may be a valuable biomarker for Guillain–Barré syndrome and infantile congenital heart disease.

Microtubule-actin cross-linking factor 1, isoforms 1/2/3/5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MACF1 gene.

Citron Rho-interacting kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CIT gene.

Microtubule-associated protein 6 (MAP6) or stable tubule-only polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAP6 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1A, also known as axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles or microtubule-based motor KIF1A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1A gene.
In molecular biology, the protein domain named the Shugoshin N-terminal coiled-coil region is a domain found on the N-terminal region of the Shugoshin protein in eukaryotes. It has a role in attaching to the kinetochores, structures on the chromatids where microtubules attach. Shugoshin has a conserved coiled-coil N-terminal domain and a highly conserved C-terminal region. Shugoshin is a crucial target of Bub1 kinase that plays a central role in the cohesion of chromosomes during cell division.
The XMAP215/Dis1 family is a highly conserved group of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) in eukaryotic organisms. These proteins are unique MAPs because they primarily interact with the growing-end (plus-end) of microtubules. This special property classifies this protein family as plus-end tracking proteins (+TIPs).

Calmodulin regulated spectrin associated protein family member 2 (CAMSAP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAMSAP2 gene. It acts as a microtubule minus-end anchor, and binds microtubules through its CKK domain.

Calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein family member 3 (CAMSAP3) is a human protein encoded by the gene CAMSAP3. The protein is commonly referred to as Nezha.

Calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 1 (CAMSAP1) is a human protein encoded by the gene CAMSAP1. Like other CAMSAP-family proteins, it is a microtubule minus-end anchor, and binds microtubules through its CKK domain.













