
The beta sheet is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies.
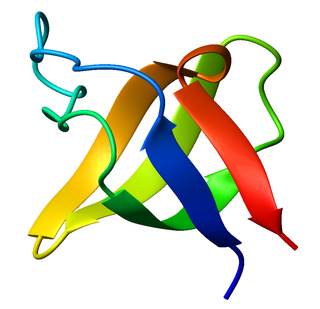
The SRC Homology 3 Domain is a small protein domain of about 60 amino acid residues. Initially, SH3 was described as a conserved sequence in the viral adaptor protein v-Crk. This domain is also present in the molecules of phospholipase and several cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases such as Abl and Src. It has also been identified in several other protein families such as: PI3 Kinase, Ras GTPase-activating protein, CDC24 and cdc25. SH3 domains are found in proteins of signaling pathways regulating the cytoskeleton, the Ras protein, and the Src kinase and many others. The SH3 proteins interact with adaptor proteins and tyrosine kinases. Interacting with tyrosine kinases, SH3 proteins usually bind far away from the active site. Approximately 300 SH3 domains are found in proteins encoded in the human genome. In addition to that, the SH3 domain was responsible for controlling protein-protein interactions in the signal transduction pathways and regulating the interactions of proteins involved in the cytoplasmic signaling.

Chloride channels are a superfamily of poorly understood ion channels specific for chloride. These channels may conduct many different ions, but are named for chloride because its concentration in vivo is much higher than other anions. Several families of voltage-gated channels and ligand-gated channels have been characterized in humans.
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings. CAMs are crucial components in maintaining tissue structure and function. In fully developed animals, these molecules play an integral role in generating force and movement and consequently ensuring that organs are able to execute their functions normally. In addition to serving as "molecular glue", CAMs play important roles in the cellular mechanisms of growth, contact inhibition, and apoptosis. Aberrant expression of CAMs may result in a wide range of pathologies, ranging from frostbite to cancer.

In molecular biology, CD4 is a glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). CD4 is found on the surface of immune cells such as helper T cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It was discovered in the late 1970s and was originally known as leu-3 and T4 before being named CD4 in 1984. In humans, the CD4 protein is encoded by the CD4 gene.

Gelsolin is an actin-binding protein that is a key regulator of actin filament assembly and disassembly. Gelsolin is one of the most potent members of the actin-severing gelsolin/villin superfamily, as it severs with nearly 100% efficiency.
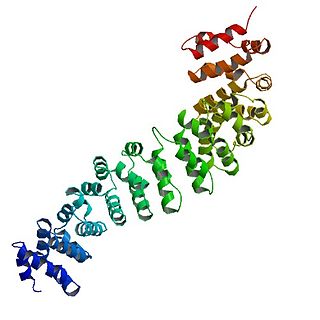
Catenin beta-1, also known as β-catenin (beta-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene.

Endoglin (ENG) is a type I membrane glycoprotein located on cell surfaces and is part of the TGF beta receptor complex. It is also commonly referred to as CD105, END, FLJ41744, HHT1, ORW and ORW1. It has a crucial role in angiogenesis, therefore, making it an important protein for tumor growth, survival and metastasis of cancer cells to other locations in the body.
The sodium-calcium exchanger (often denoted Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, exchange protein, or NCX) is an antiporter membrane protein that removes calcium from cells. It uses the energy that is stored in the electrochemical gradient of sodium (Na+) by allowing Na+ to flow down its gradient across the plasma membrane in exchange for the countertransport of calcium ions (Ca2+). A single calcium ion is exported for the import of three sodium ions. The exchanger exists in many different cell types and animal species. The NCX is considered one of the most important cellular mechanisms for removing Ca2+.

Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1), also known as CD29, is a cell surface receptor that in humans is encoded by the ITGB1 gene. This integrin associates with integrin alpha 1 and integrin alpha 2 to form integrin complexes which function as collagen receptors. It also forms dimers with integrin alpha 3 to form integrin receptors for netrin 1 and reelin. These and other integrin beta 1 complexes have been historically known as very late activation (VLA) antigens.

ADGRV1, also known as G protein-coupled receptor 98 (GPR98) or Very Large G-protein coupled receptor 1 (VLGR1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR98 gene. Several alternatively spliced transcripts have been described.

Cav2.1, also called the P/Q voltage-dependent calcium channel, is a calcium channel found mainly in the brain. Specifically, it is found on the presynaptic terminals of neurons in the brain and cerebellum. Cav2.1 plays an important role in controlling the release of neurotransmitters between neurons. It is composed of multiple subunits, including alpha-1, beta, alpha-2/delta, and gamma subunits. The alpha-1 subunit is the pore-forming subunit, meaning that the calcium ions flow through it. Different kinds of calcium channels have different isoforms (versions) of the alpha-1 subunit. Cav2.1 has the alpha-1A subunit, which is encoded by the CACNA1A gene. Mutations in CACNA1A have been associated with various neurologic disorders, including familial hemiplegic migraine, episodic ataxia type 2, and spinocerebellar ataxia type 6.
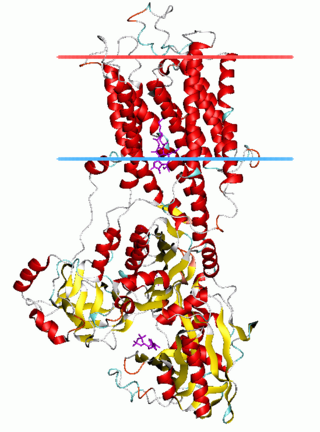
The P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases, are a large group of evolutionarily related ion and lipid pumps that are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. P-type ATPases are α-helical bundle primary transporters named based upon their ability to catalyze auto- (or self-) phosphorylation (hence P) of a key conserved aspartate residue within the pump and their energy source, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E1 and E2. P-type ATPases fall under the P-type ATPase (P-ATPase) Superfamily (TC# 3.A.3) which, as of early 2016, includes 20 different protein families.

AP-2 complex subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP2B1 gene.

Cytohesin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYTH2 gene.

Cytohesin-1 formerly known as Pleckstrin homology, Sec7 and coiled/coil domains 1 (PSCD1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYTH1 gene.

Myopodin protein, also called Synaptopodin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYNPO2 gene. Myopodin is expressed in cardiac, smooth muscle and skeletal muscle, and localizes to Z-disc structures.

Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A12 gene. Aralar is an integral membrane protein located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Its primary function as an antiporter is the transport of cytoplasmic glutamate with mitochondrial aspartate across the inner mitochondrial membrane, dependent on the binding of one calcium ion. Mutations in this gene cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy 39 (EIEE39), symptomized by global hypomyelination of the central nervous system, refractory seizures, and neurodevelopmental impairment. This gene has connections to autism.

Cluster of differentiation CD79A also known as B-cell antigen receptor complex-associated protein alpha chain and MB-1 membrane glycoprotein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD79A gene.

The aldo-keto reductase family is a family of proteins that are subdivided into 16 categories; these include a number of related monomeric NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases, such as aldehyde reductase, aldose reductase, prostaglandin F synthase, xylose reductase, rho crystallin, and many others.


















