
Borneo is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra.

Sulawesi, also known as Celebes, is one of the four Greater Sunda Islands. It is governed by Indonesia. The world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago. Within Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger populations.

The Karimata Strait also spelled Carimata or Caramata is the wide strait that connects the South China Sea to the Java Sea, separating the Indonesian islands of Belitung and Borneo (Kalimantan). It is bordered by the Belitung island in the west and Borneo in the east. It is the widest strait that connects the South China Sea and the Java Sea, but its numerous islands and reefs reduce its navigability. Its weather and current is influenced by the annual southeast and northwest monsoon.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.

East Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. Its territory comprises the eastern portion of Borneo. It had a population of about 3.03 million at the 2010 Census, 3.42 million at the 2015 Census, and 3.766 million at the 2020 census. Its capital is the city of Samarinda.
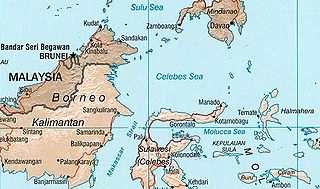
The Celebes Sea of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and on the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Cape Mangkalihat, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.

Makassar Strait is a strait between the islands of Borneo and Sulawesi in Indonesia. To the north it joins the Celebes Sea, while to the south it meets the Java Sea. To the northeast, it forms the Sangkulirang Bay south of the Mangkalihat Peninsula. The strait is an important regional shipping route in Southeast Asia.

The Mahakam River is a river in Kalimantan, Indonesia. It flows 980 kilometers from the district of Long Apari in the highlands of Borneo, to its mouth at the Makassar Strait.

Bontang is a city on the eastern coast of the island of Borneo in Indonesia, in the province of East Kalimantan. It occupies an area of 161.88 km2 (62.50 sq mi), and the population was 140,787 at the 2010 Census, and 178,917 at the 2020 Census. It is also the third most densely populated place in the province after Balikpapan and Samarinda.

Hose's langur is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae endemic to the island of Borneo, including Brunei, Kalimantan (Indonesia), and East Malaysia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss. It was first identified in Kutai National Park and Sangkulirang Peninsula, East Kalimantan, Indonesia, in 1985.

Kutai is a historical region in East Kalimantan, Indonesia on the island of Borneo and is also the name of the native ethnic of the region, numbering around 300,000 who have their own language of the same name and their own rich history. Today the name is preserved in the names of three regencies in East Kalimantan, the Kutai Kartanegara Regency, the West Kutai Regency and the East Kutai Regency. The major river of the region is the Mahakam River.
Kutai or Kutai Malay is a Malayan language spoken by 300,000 to 500,000 people. It is the native language of Kutai people, the indigenous ethnic group which lives along the Mahakam River in Borneo, especially in North Kalimantan, Indonesia. They are the principal population in the regencies of West Kutai, Kutai Kartanegara, and East Kutai within North Kalimantan province.

Sangkulirang is a town and sub district of East Kalimantan, Indonesia. The town lies in the northern part of the Makassar Strait and at the base of the Mangkalihat Peninsula. Sangkulirang is situated in the delta of the Karangan River, which forms the Sangkulirang bay on the east coast of Borneo. Most of the regency is vegetated with mangrove forest and has some notable karst areas with steep limestone cliffs.

North Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. North Kalimantan borders the Malaysian states of Sabah to the north and Sarawak to the west, and by the Indonesian province of East Kalimantan to the south. Tanjung Selor serves as the capital of the province, while Tarakan is the largest city and the financial centre.
The Kutai sedimentary basin extends from the central highlands of Borneo, across the eastern coast of the island and into the Makassar Strait. With an area of 60,000 km2, and depths up to 15 km, the Kutai is the largest and deepest Tertiary age basin in Indonesia. Plate tectonic evolution in the Indonesian region of SE Asia has produced a diverse array of basins in the Cenozoic. The Kutai is an extensional basin in a general foreland setting. Its geologic evolution begins in the mid Eocene and involves phases of extension and rifting, thermal sag, and isostatic subsidence. Rapid, high volume, sedimentation related to uplift and inversion began in the Early Miocene. The different stages of Kutai basin evolution can be roughly correlated to regional and local tectonic events. It is also likely that regional climate, namely the onset of the equatorial ever wet monsoon in early Miocene, has affected the geologic evolution of Borneo and the Kutai basin through the present day. Basin fill is ongoing in the lower Kutai basin, as the modern Mahakam River delta progrades east across the continental shelf of Borneo.

The Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat Karst is a karstique area in Sub Kelay, Biatan, Talisayan, Batu Putih, and Biduk-biduk Berau districts of East Kalimantan province on the island of Borneo in Indonesia. It covers an area of 105,000 hectares, including the Mangkalihat Peninsula.

The Laut Strait separates Laut Island and Kalimantan, the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It is an important commercial waterway to the port of Kotabaru from nearby Makassar Strait.

Lubang Jeriji Saléh is a limestone cave complex in the Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat Karst located in the remote jungle of Bengalon district in East Kutai, East Kalimantan province on Borneo island, Indonesia. In a 2018 publication a team of researchers announced to have found the then-oldest known work of figurative art in the world among the cave paintings, at 40,000 years old. However, the same team has since found and dated an elaborate therianthrope rock art panel in the Leang Bulu’ Sipong 4 cave in Sulawesi's Maros-Pangkep karst to around 44,000 years old, older than the figurative art in Lubang Jeriji Saléh.

Beras Basah Island is a small island located in the Straits of Makassar and approximately 10 kilometers (6.2 mi) east off the coast of Borneo. Administratively, this island is under the City of Bontang government and Province of East Kalimantan. The island is known to be a tourist destination as a dive site that provides tropical underwater life.

















