This article needs additional citations for verification .(April 2009) |
A carbon nanotube quantum dot (CNT QD) is a small region of a carbon nanotube in which electrons are confined.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(April 2009) |
A carbon nanotube quantum dot (CNT QD) is a small region of a carbon nanotube in which electrons are confined.
A CNT QD is formed when electrons are confined to a small region within a carbon nanotube. This is normally accomplished by application of a voltage to a gate electrode, dragging the valence band of the CNT down in energy, thereby causing electrons to pool in a region in the vicinity of the electrode. Experimentally this is accomplished by laying a CNT on a silicon dioxide surface, sitting on a doped silicon wafer. This can be done by chemical vapor deposition using carbon monoxide. [1] The silicon wafer serves as the gate electrode. Metallic leads can then be laid over the nanotube in order to connect the CNT QD up to an electrical circuit.
The CNT QD has interesting properties as a result of the strong correlation between the confined electrons. In addition to this the electrons possess orbital angular momentum, as is characteristic of CNT electrons. spin–orbit coupling has also been shown to be significant in these systems. [2] [3] These properties are often probed by connecting the nanotube to two metallic leads and measuring the conductance of the system.
The CNT QD connected to metallic leads constitutes a genuine many-body system, due to the electron correlations. Therefore, Wilson's Numerical renormalization group is often used to study the CNT QD. The CNT QD is modelled as an Anderson-type model, which can be reduced by Schrieffer-Wolff transformation to an effective Kondo-type model at low temperature.
Similar mesoscopic devices have been constructed from elements other than carbon. So called copper nanotubes (CuNTs), developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, [4] are fabricated by closely aligning individual copper atoms on a surface.
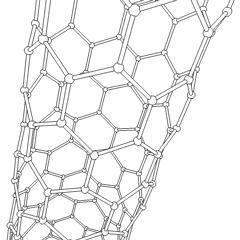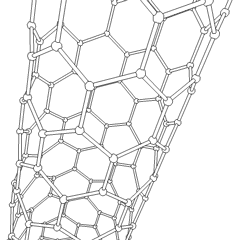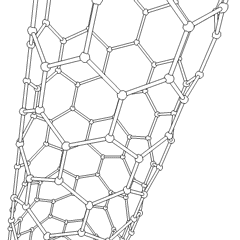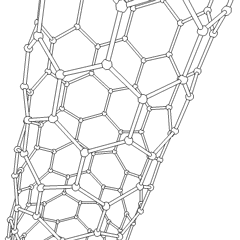
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometres.
Nano-RAM is a proprietary computer memory technology from the company Nantero. It is a type of nonvolatile random-access memory based on the position of carbon nanotubes deposited on a chip-like substrate. In theory, the small size of the nanotubes allows for very high density memories. Nantero also refers to it as NRAM.

Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) are a class of devices integrating electrical and mechanical functionality on the nanoscale. NEMS form the next logical miniaturization step from so-called microelectromechanical systems, or MEMS devices. NEMS typically integrate transistor-like nanoelectronics with mechanical actuators, pumps, or motors, and may thereby form physical, biological, and chemical sensors. The name derives from typical device dimensions in the nanometer range, leading to low mass, high mechanical resonance frequencies, potentially large quantum mechanical effects such as zero point motion, and a high surface-to-volume ratio useful for surface-based sensing mechanisms. Applications include accelerometers and sensors to detect chemical substances in the air.
Hybrid solar cells combine advantages of both organic and inorganic semiconductors. Hybrid photovoltaics have organic materials that consist of conjugated polymers that absorb light as the donor and transport holes. Inorganic materials in hybrid cells are used as the acceptor and electron transporter in the structure. The hybrid photovoltaic devices have a potential for not only low-cost by roll-to-roll processing but also for scalable solar power conversion.

Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are cylinders of one or more layers of graphene (lattice). Diameters of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) are typically 0.8 to 2 nm and 5 to 20 nm, respectively, although MWNT diameters can exceed 100 nm. CNT lengths range from less than 100 nm to 0.5 m.

In nanotechnology, a carbon nanobud is a material that combines carbon nanotubes and spheroidal fullerenes, both allotropes of carbon, forming "buds" attached to the tubes. Carbon nanobuds were discovered and synthesized in 2006.
Organic photovoltaic devices (OPVs) are fabricated from thin films of organic semiconductors, such as polymers and small-molecule compounds, and are typically on the order of 100 nm thick. Because polymer based OPVs can be made using a coating process such as spin coating or inkjet printing, they are an attractive option for inexpensively covering large areas as well as flexible plastic surfaces. A promising low cost alternative to conventional solar cells made of crystalline silicon, there is a large amount of research being dedicated throughout industry and academia towards developing OPVs and increasing their power conversion efficiency.
Molecular scale electronics, also called single-molecule electronics, is a branch of nanotechnology that uses single molecules, or nanoscale collections of single molecules, as electronic components. Because single molecules constitute the smallest stable structures imaginable, this miniaturization is the ultimate goal for shrinking electrical circuits.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are very prevalent in today's world of medical research and are being highly researched in the fields of efficient drug delivery and biosensing methods for disease treatment and health monitoring. Carbon nanotube technology has shown to have the potential to alter drug delivery and biosensing methods for the better, and thus, carbon nanotubes have recently garnered interest in the field of medicine.

Transparent conducting films (TCFs) are thin films of optically transparent and electrically conductive material. They are an important component in a number of electronic devices including liquid-crystal displays, OLEDs, touchscreens and photovoltaics. While indium tin oxide (ITO) is the most widely used, alternatives include wider-spectrum transparent conductive oxides (TCOs), conductive polymers, metal grids and random metallic networks, carbon nanotubes (CNT), graphene, nanowire meshes and ultra thin metal films.
Self-assembling peptides are a category of peptides which undergo spontaneous assembling into ordered nanostructures. Originally described in 1993, these designer peptides have attracted interest in the field of nanotechnology for their potential for application in areas such as biomedical nanotechnology, tissue cell culturing, molecular electronics, and more.
A device generating linear or rotational motion using carbon nanotube(s) as the primary component, is termed a nanotube nanomotor. Nature already has some of the most efficient and powerful kinds of nanomotors. Some of these natural biological nanomotors have been re-engineered to serve desired purposes. However, such biological nanomotors are designed to work in specific environmental conditions. Laboratory-made nanotube nanomotors on the other hand are significantly more robust and can operate in diverse environments including varied frequency, temperature, mediums and chemical environments. The vast differences in the dominant forces and criteria between macroscale and micro/nanoscale offer new avenues to construct tailor-made nanomotors. The various beneficial properties of carbon nanotubes makes them the most attractive material to base such nanomotors on.
Ultra-high-purity steam, also called the clean steam, UHP steam or high purity water vapor, is used in a variety of industrial manufacturing processes that require oxidation or annealing. These processes include the growth of oxide layers on silicon wafers for the semiconductor industry, originally described by the Deal-Grove model, and for the formation of passivation layers used to improve the light capture ability of crystalline photovoltaic cells. Several methods and technologies can be employed to generate ultra high purity steam, including pyrolysis, bubbling, direct liquid injection and purified steam generation. The level of purity, or the relative lack of contamination, affects the quality of the oxide layer or annealed surface. The method of delivery affects growth rate, uniformity and electrical performance. Oxidation and annealing are common steps in the manufacture of such devices as microelectronics and solar cells.
A carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNTFET) is a field-effect transistor that utilizes a single carbon nanotube or an array of carbon nanotubes as the channel material instead of bulk silicon in the traditional MOSFET structure. First demonstrated in 1998, there have been major developments in CNTFETs since.
Single-walled carbon nanotubes in the fields of quantum mechanics and nanoelectronics, have the ability to conduct electricity. This conduction can be ballistic, diffusive, or based on scattering. When ballistic in nature conductance can be treated as if the electrons experience no scattering.

Single-walled carbon nanohorn is the name given by Sumio Iijima and colleagues in 1999 to horn-shaped sheath aggregate of graphene sheets. Very similar structures had been observed in 1994 by Peter J.F. Harris, Edman Tsang, John Claridge and Malcolm Green. Ever since the discovery of the fullerene, the family of carbon nanostructures has been steadily expanded. Included in this family are single-walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, carbon onions and cones and, most recently, SWNHs. These SWNHs with about 40–50 nm in tubule length and about 2–3 nm in diameter are derived from SWNTs and ended by a five-pentagon conical cap with a cone opening angle of ~20o. Moreover, thousands of SWNHs associate with each other to form the ‘dahlia-like' and ‘bud-like’ structured aggregates which have an average diameter of about 80–100 nm. The former consists of tubules and graphene sheets protruding from its surface like petals of a dahlia, while the latter is composed of tubules developing inside the particle itself. Their unique structures with high surface area and microporosity make SWNHs become a promising material for gas adsorption, biosensing, drug delivery, gas storage and catalyst support for fuel cell. Single-walled carbon nanohorns are an example of the family of carbon nanocones.

Carbon nanotube supported catalyst is a novel supported catalyst, using carbon nanotubes as the support instead of the conventional alumina or silicon support. The exceptional physical properties of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) such as large specific surface areas, excellent electron conductivity incorporated with the good chemical inertness, and relatively high oxidation stability makes it a promising support material for heterogeneous catalysis.
In nanotechnology, carbon nanotube interconnects refer to the proposed use of carbon nanotubes in the interconnects between the elements of an integrated circuit. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) can be thought of as single atomic layer graphite sheets rolled up to form seamless cylinders. Depending on the direction on which they are rolled, CNTs can be semiconducting or metallic. Metallic carbon nanotubes have been identified as a possible interconnect material for the future technology generations and to replace copper interconnects. Electron transport can go over long nanotube lengths, 1 μm, enabling CNTs to carry very high currents (i.e. up to a current density of 109 A∙cm−2) with essentially no heating due to nearly one dimensional electronic structure. Despite the current saturation in CNTs at high fields, the mitigation of such effects is possible due to encapsulated nanowires.

Techniques have been developed to produce carbon nanotubes in sizable quantities, including arc discharge, laser ablation, high-pressure carbon monoxide disproportionation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Most of these processes take place in a vacuum or with process gases. CVD growth of CNTs can occur in vacuum or at atmospheric pressure. Large quantities of nanotubes can be synthesized by these methods; advances in catalysis and continuous growth are making CNTs more commercially viable.
Vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays (VANTAs) are a unique microstructure consisting of carbon nanotubes oriented with their longitudinal axis perpendicular to a substrate surface. These VANTAs effectively preserve and often accentuate the unique anisotropic properties of individual carbon nanotubes and possess a morphology that may be precisely controlled. VANTAs are consequently widely useful in a range of current and potential device applications.