This biographical article is written like a résumé .(September 2022) |
Carl O. Pabo is a biophysicist. He is the founder and president of Humanity 2050, a nonprofit institute. [1] [2]
This biographical article is written like a résumé .(September 2022) |
Carl O. Pabo is a biophysicist. He is the founder and president of Humanity 2050, a nonprofit institute. [1] [2]
Pabo has been a professor at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (1982–1991) and at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1991–2001) and an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (1986–2001). [4] He's been a visiting professor at Caltech, Stanford, Berkeley and Harvard. [5] At Caltech, he taught a course called “The World in 2050.” [6]
In 1991, he used X-ray crystallography to show how Zinc finger nucleases attach to DNA. In 1994, after moving to the MIT, he showed how zinc fingers could be custom built to grab onto any desired three-base pair DNA sequence. This was an important step toward building the full library of zinc fingers for all 64 sequences. [7] He was chief scientific officer at Sangamo BioSciences from 2001–2003. [8]
In 2018, he founded Humanity 2050 to “to advocate a more comprehensive, coherent way of thinking about the human future.” [9] He also serves as a scientific advisor for NanoDimension. [10]
Pabo became a Guggenheim Fellow in 2005. [11] He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences [12] and of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. [13] Was awarded the Pfizer Award in Enzyme Chemistry in 1992. He has also won the Protein Society Young Investigator Award and the Pfizer Award in enzymology. [14]

David Baltimore is an American biologist, university administrator, and 1975 Nobel laureate in Physiology or Medicine. He is a professor of biology at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), where he served as president from 1997 to 2006. He founded the Whitehead Institute and directed it from 1982 to 1990. In 2008, he served as president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2008.

Leroy "Lee" Edward Hood is an American biologist who has served on the faculties at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the University of Washington. Hood has developed ground-breaking scientific instruments which made possible major advances in the biological sciences and the medical sciences. These include the first gas phase protein sequencer (1982), for determining the sequence of amino acids in a given protein; a DNA synthesizer (1983), to synthesize short sections of DNA; a peptide synthesizer (1984), to combine amino acids into longer peptides and short proteins; the first automated DNA sequencer (1986), to identify the order of nucleotides in DNA; ink-jet oligonucleotide technology for synthesizing DNA and nanostring technology for analyzing single molecules of DNA and RNA.
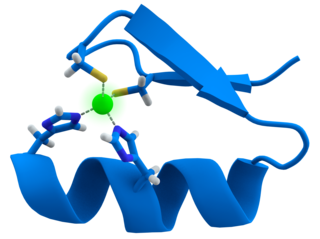
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) which stabilizes the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. Xenopus laevis TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in Drosophila. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins.

EGR-1 also known as ZNF268 or NGFI-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EGR1 gene.
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.

Pamela Jane Bjorkman NAS, AAAS is an American biochemist. She is the David Baltimore Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), Her research centers on the study of the three-dimensional structures of proteins related to Class I MHC, or Major Histocompatibility Complex, proteins of the immune system and proteins involved in the immune responses to viruses. Bjorkman is most well known as a pioneer in the field of structural biology.
John Norman Abelson is an American molecular biologist with expertise in biophysics, biochemistry, and genetics. He was a professor at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech).

Sir Thomas Leon Blundell, is a British biochemist, structural biologist, and science administrator. He was a member of the team of Dorothy Hodgkin that solved in 1969 the first structure of a protein hormone, insulin. Blundell has made contributions to the structural biology of polypeptide hormones, growth factors, receptor activation, signal transduction, and DNA double-strand break repair, subjects important in cancer, tuberculosis, and familial diseases. He has developed software for protein modelling and understanding the effects of mutations on protein function, leading to new approaches to structure-guided and Fragment-based lead discovery. In 1999 he co-founded the oncology company Astex Therapeutics, which has moved ten drugs into clinical trials. Blundell has played central roles in restructuring British research councils and, as President of the UK Science Council, in developing professionalism in the practice of science.

Jeremy Mark Berg was founding director of the University of Pittsburgh's Institute for Personalized Medicine. He holds positions as Associate Senior Vice Chancellor for Science Strategy and Planning and Professor of Computational and Systems Biology at the University of Pittsburgh. From 2016 - 2019, Berg was editor in chief of the Science journals.

Peter B. Dervan is the Bren Professor of Chemistry at the California Institute of Technology. The primary focus of his research is the development and study of small organic molecules that can sequence-specifically recognize DNA, a field in which he is an internationally recognized authority. The most important of these small molecules are pyrrole–imidazole polyamides. Dervan is credited with influencing "the course of research in organic chemistry through his studies at the interface of chemistry and biology" as a result of his work on "the chemical principles involved in sequence-specific recognition of double helical DNA". He is the recipient of many awards, including the National Medal of Science (2006).
Zinc finger protein chimera are chimeric proteins composed of a DNA-binding zinc finger protein domain and another domain through which the protein exerts its effect. The effector domain may be a transcriptional activator (A) or repressor (R), a methylation domain (M) or a nuclease (N).

Daniela Bargellini Rhodes FRS is an Italian structural and molecular biologist. She was a senior scientist at the Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, England, where she worked, and later studied for her PhD under the supervision of Nobel laureate Aaron Klug. Continuing her work under the tutelage of Aaron Klug at Cambridge, she was appointed group leader in 1983, obtained tenure in 1987 and was promoted to senior scientist in 1994. Subsequently, she served as director of studies between 2003 and 2006. She has also been visiting professor at both "La Sapienza" in Rome, Italy and the Rockefeller University in NY, USA.

Zinc finger protein 804A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF804A gene. The human gene maps to chromosome 2 q32.1 and consists of 4 exons that code for a protein of 1210 amino acids.

Richard H. Scheller is the former Chief Science Officer and Head of Therapeutics at 23andMe and the former Executive Vice President of Research and Early Development at Genentech. He was a professor at Stanford University from 1982 to 2001 before joining Genentech. He has been awarded the Alan T. Waterman Award in 1989, the W. Alden Spencer Award in 1993 and the NAS Award in Molecular Biology in 1997, won the 2010 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience with Thomas C. Südhof and James E. Rothman, and won the 2013 Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research with Thomas Südhof. He was also given the Life Sciences Distinguished Alumni Award from University of Wisconsin–Madison. He is a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and a Member of the National Academy of Sciences.
Marvin H. Caruthers is an American biochemist who is a distinguished professor at the University of Colorado Boulder.
James Michael Berger is an American academic working as a professor of biophysics and biophysical chemistry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, where he is also the co-director of the Cancer Chemical and Structural Biology Program at the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center and the director of the Johns Hopkins Institute for Basic Biomedical Sciences. His main area of research is the functions of molecular cellular machinery.
Lila Mary Gierasch is an American biochemist and biophysicist. At present, she is a distinguished Professor working on "protein folding in the cell" in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the College of Natural Sciences, University of Massachusetts—Amherst.
Edward John Rebar is an American biologist, and is Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer of Sana Biotechnology.

Carlos F. Barbas III was chair professor of the Janet and Keith Kellogg II and a chemist at the Scripps Research Institute. Barbas developed new therapies that can target HIV-1 and some kinds of cancer which went into clinical trials.
David Nathan Beratan is an American chemist and physicist, the R.J. Reynolds Professor of Chemistry at Duke University. He has secondary appointments in the departments of Physics and Biochemistry. He is the director of the Center for Synthesizing Quantum Coherence, a NSF Phase I Center for Chemical Innovation.