Related Research Articles
The Clinchfield Railroad was an operating and holding company for the Carolina, Clinchfield and Ohio Railway. The line ran from the coalfields of Virginia and Elkhorn City, Kentucky, to the textile mills of South Carolina. The 35-mile segment from Dante, Virginia, to Elkhorn City, opening up the coal lands north of Sandy Ridge Mountains and forming a connection with the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway at Elkhorn City, was completed in 1915.
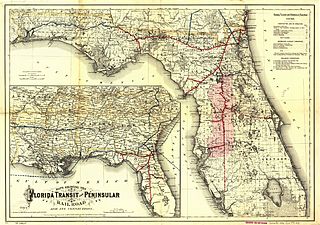
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.
The Columbus Southern Railway is a historic railroad that operated in the U.S. state of Georgia. The railroad operated an 88-mile line from Columbus to Albany that opened in 1890.

The Riceboro Southern Railway began operations in 2004 operating on about 33 miles of track, some of which is leased from CSX Transportation. The track on which it operates is part of the ex-Seaboard Air Line route from Savannah, Georgia to Jacksonville, Florida. It runs generally from Ogeechee, Georgia, where the line splits from the CSX Savannah Subdivision, which is the former Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Savannah-Jacksonville route, and Riceboro. It does not have any of its own locomotives; it uses Georgia Central power.
The Piedmont & Northern Railway was a heavy electric interurban company operating over two disconnected divisions in North and South Carolina. Tracks spanned 128 miles (206 km) total between the two segments, with the northern division running 24 miles (39 km) from Charlotte, to Gastonia, North Carolina, including a three-mile (5 km) spur to Belmont. The southern division main line ran 89 miles (143 km) from Greenwood to Spartanburg, South Carolina, with a 12 mi (19 km) spur to Anderson. Initially the railroad was electrified at 1500 volts DC, however, much of the electrification was abandoned when dieselisation was completed in 1954.
The Raleigh and Gaston Railroad was a Raleigh, North Carolina, based railroad opened in April 1840 between Raleigh and the town of Gaston, North Carolina, on the Roanoke River. It was North Carolina's second railroad. The length was 100 miles (160 km) and built with 4 ft 8 in gauge. Part of the Raleigh and Gaston's tracks remains in service today as part of CSX's S Line as the Norlina Subdivision of CSX's Florence Division.
The Green Pond, Walterboro and Branchville Railroad was a railroad that ran from Green Pond, South Carolina northwest to Ehrhardt, South Carolina.
The Palmetto Railroad was a Southeastern railroad that served South Carolina and North Carolina in the late 19th century.
The South Carolina Western Railway was a Southeastern railroad that operated in the early 20th century.
The Raleigh and Augusta Air Line Railroad was a North Carolina railroad that operated in the second half of the 19th century.
CSX Transportation's Valrico Subdivision is a railroad line in Central Florida. It serves as CSX's main route through a region of Central Florida known as the Bone Valley, which contains the largest known deposits of phosphate in the United States.
CSX Transportation's Atlanta Terminal Subdivision comprises the company's railroad lines and infrastructure operating in and around Atlanta, Georgia. The Atlanta Terminal Subdivision consists of five lines and a number of yards. Most of the lines in the Atlanta Terminal Subdivision date back to the 1800s.
The Augusta Subdivision is a railroad line owned by CSX Transportation in the U.S. states of Georgia and South Carolina. The line runs from CSX's A Line at Yemassee, South Carolina to Augusta, Georgia, for a total of 87.7 miles (141.1 km). At its north end it connects with Norfolk Southern Railway and CSX's McCormick Subdivision.

The Charleston Subdivision is a railroad territory owned by CSX Transportation in the U.S. states of South Carolina and Georgia. The line from Florence, South Carolina, to Savannah, Georgia, for a total of 195.8 miles. At its north end it continues south from the South End Subdivision and at its south end it continues south as the Savannah Subdivision of the Jacksonville Division.
The Monroe Subdivision is a railroad line owned by CSX Transportation in the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina. The line runs from Pee Dee, North Carolina to Abbeville, South Carolina, for a total of 177 miles. The full line is dispatched by Centralized traffic control.
The Winston and Bone Valley Railroad was a railroad line running the Bone Valley region of Central Florida. It connected to the South Florida Railroad main line near Lakeland. A vast majority of the line remains in service by CSX Transportation, who operates it today as their Bone Valley Subdivision.
The W&W Subdivision is a railroad line owned by CSX Transportation in the U.S. state of North Carolina. The line today runs from just south of Wilson, North Carolina, to Wallace, North Carolina, for a total of 69.1 miles. At its north end the line connects to CSX's A Line. The line's name stands for the Wilmington and Weldon Railroad, the company that originally built the line.

The Seaboard Air Line Railroad's Sarasota Subdivision was a rail line that ran from the company's main line at Turkey Creek south to Palmetto, Bradenton, Sarasota, and Venice. The line was built in phases from 1901 to 1911.
The Seaboard Air Line Railroad’s Main Line was the backbone of the Seaboard Air Line Railroad's network in the southeastern United States. The main line ran from Richmond, Virginia to Tampa, Florida, a distance of over 800 miles. Along its route it passed through Petersburg, Raleigh, Columbia, Savannah, Jacksonville, and Ocala, Florida. While some segments of the line have been abandoned as of 2023, most of the line is still in service and is owned by the Seaboard Air Line's successor, CSX Transportation as their S-Line.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Parkton—Sumter Line was one of the company's secondary main lines running between Parkton, North Carolina and Sumter, South Carolina.
References
- ↑ South Carolina Railroads, Catawba Valley Railway Archived 2010-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ South Carolina Railroads, Catawba Valley Railway Archived 2010-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Seaboard Air Line Expands, New York Times, October 13, 1909
- 1 2 Seaboard Air Line Railroad Georgia Division Timetable (1955)
- ↑ "Spence to Great Falls, SC". Abandoned Rails. Retrieved 25 July 2023.