
Balance of trade can be measured in terms of commercial balance, or net exports. Balance of trade is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance of trade for goods versus one for services. The balance of trade measures a flow variable of exports and imports over a given period of time. The notion of the balance of trade does not mean that exports and imports are "in balance" with each other.

In economics, inflation is a general increase of the prices of goods and services in an economy. This is usually measured using the consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of CPI inflation is deflation, a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. As prices faced by households do not all increase at the same rate, the consumer price index (CPI) is often used for this purpose.

The global financial system is the worldwide framework of legal agreements, institutions, and both formal and informal economic action that together facilitate international flows of financial capital for purposes of investment and trade financing. Since emerging in the late 19th century during the first modern wave of economic globalization, its evolution is marked by the establishment of central banks, multilateral treaties, and intergovernmental organizations aimed at improving the transparency, regulation, and effectiveness of international markets. In the late 1800s, world migration and communication technology facilitated unprecedented growth in international trade and investment. At the onset of World War I, trade contracted as foreign exchange markets became paralyzed by money market illiquidity. Countries sought to defend against external shocks with protectionist policies and trade virtually halted by 1933, worsening the effects of the global Great Depression until a series of reciprocal trade agreements slowly reduced tariffs worldwide. Efforts to revamp the international monetary system after World War II improved exchange rate stability, fostering record growth in global finance.

Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability. Further purposes of a monetary policy may be to contribute to economic stability or to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies. Today most central banks in developed countries conduct their monetary policy within an inflation targeting framework, whereas the monetary policies of most developing countries' central banks target some kind of a fixed exchange rate system. A third monetary policy strategy, targeting the money supply, was widely followed during the 1980s, but has diminished in popularity since that, though it is still the official strategy in a number of emerging economies.
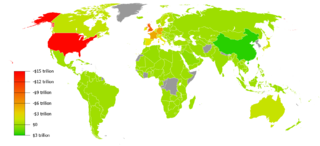
In international economics, the balance of payments of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.

In macroeconomics and international finance, a country's current account records the value of exports and imports of both goods and services and international transfers of capital. It is one of the two components of the balance of payments, the other being the capital account. Current account measures the nation's earnings and spendings abroad and it consists of the balance of trade, net primary income or factor income and net unilateral transfers, that have taken place over a given period of time. The current account balance is one of two major measures of a country's foreign trade. A current account surplus indicates that the value of a country's net foreign assets grew over the period in question, and a current account deficit indicates that it shrank. Both government and private payments are included in the calculation. It is called the current account because goods and services are generally consumed in the current period.

The Plaza Accord was a joint agreement signed on September 22, 1985, at the Plaza Hotel in New York City, between France, West Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States, to depreciate the U.S. dollar in relation to the French franc, the German Deutsche Mark, the Japanese yen and the British pound sterling by intervening in currency markets. The U.S. dollar depreciated significantly from the time of the agreement until it was replaced by the Louvre Accord in 1987. Some commentators believe the Plaza Accord contributed to the Japanese asset price bubble of the late 1980s.

The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, and Australia among 44 other countries after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretton Woods system was the first example of a fully negotiated monetary order intended to govern monetary relations among independent states. The Bretton Woods system required countries to guarantee convertibility of their currencies into U.S. dollars to within 1% of fixed parity rates, with the dollar convertible to gold bullion for foreign governments and central banks at US$35 per troy ounce of fine gold. It also envisioned greater cooperation among countries in order to prevent future competitive devaluations, and thus established the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to monitor exchange rates and lend reserve currencies to nations with balance of payments deficits.
The economies of Canada and the United States are similar because both are developed countries. While both countries feature in the top ten economies in the world in 2022, the U.S. is the largest economy in the world, with US$24.8 trillion, with Canada ranking ninth at US$2.2 trillion.
Economic forecasting is the process of making predictions about the economy. Forecasts can be carried out at a high level of aggregation—for example for GDP, inflation, unemployment or the fiscal deficit—or at a more disaggregated level, for specific sectors of the economy or even specific firms. Economic forecasting is a measure to find out the future prosperity of a pattern of investment and is the key activity in economic analysis. Many institutions engage in economic forecasting: national governments, banks and central banks, consultants and private sector entities such as think-tanks, companies and international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund, World Bank and the OECD. A broad range of forecasts are collected and compiled by "Consensus Economics". Some forecasts are produced annually, but many are updated more frequently.

Money creation, or money issuance, is the process by which the money supply of a country, or of an economic or monetary region, is increased. In most modern economies, money is created by both central banks and commercial banks. Money issued by central banks is termed base money. Central banks can increase the quantity of base money directly, by engaging in open market operations or quantitative easing. However, the majority of the money supply is created by the commercial banking system in the form of bank deposits. Bank loans issued by commercial banks that practice fractional reserve banking expands the quantity of broad money to more than the original amount of base money issued by the central bank.
International economics is concerned with the effects upon economic activity from international differences in productive resources and consumer preferences and the international institutions that affect them. It seeks to explain the patterns and consequences of transactions and interactions between the inhabitants of different countries, including trade, investment and transaction.
Peter Bain Kenen was an American economist, who was the Walker Professor of Economics and International Finance at Princeton University, and senior fellow in international economics at the Council on Foreign Relations.

Anna Jacobson Schwartz was an American economist who worked at the National Bureau of Economic Research in New York City and a writer for The New York Times. Paul Krugman has said that Schwartz is "one of the world's greatest monetary scholars."
Robert, Baron Triffin was a Belgian-American economist best known for his critique of the Bretton Woods system of fixed currency exchange rates. His critique became known later as Triffin's dilemma.
Modern monetary theory or modern money theory (MMT) is a heterodox macroeconomic theory that describes currency as a public monopoly and unemployment as evidence that a currency monopolist is overly restricting the supply of the financial assets needed to pay taxes and satisfy savings desires. According to MMT, governments do not need to worry about accumulating debt since they can create new money by using fiscal policy in order to pay interest. MMT argues that the primary risk once the economy reaches full employment is inflation, which acts as the only constraint on spending. MMT also argues that inflation can be addressed by increasing taxes on everyone to reduce the spending capacity of the private sector.
The Global Interdependence Center (GIC) is a Philadelphia-based non-profit organization that holds conferences and programming to increase global dialogue and promote free trade, in order to improve cooperation and understanding among nation states, with the goal of reducing international conflicts and improving worldwide living standards.

The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline observed in national economies globally, i.e. a recession, that occurred in the late 2000s. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country. At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations.
A global saving glut is a situation in which desired saving exceeds desired investment. By 2005 Ben Bernanke, chairman of the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, expressed concern about the "significant increase in the global supply of saving" and its implications for monetary policies, particularly in the United States. Although Bernanke's analyses focused on events in 2003 to 2007 that led to the 2007–2009 financial crisis, regarding GSG countries and the United States, excessive saving by the non-financial corporate sector (NFCS) is an ongoing phenomenon, affecting many countries. Bernanke's global saving glut (GSG) hypothesis argued that increased capital inflows to the United States from GSG countries were an important reason that U.S. longer-term interest rates from 2003 to 2007 were lower than expected.
Graciela Kaminsky is a professor of economics and international affairs at George Washington University and a faculty research associate at the National Bureau of Economic Research. Kaminsky studied economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology where she received her Ph.D. In 1984 she did a brief research stay at the Argentine Central Bank, later in 1985 she moved to San Diego as an assistant professor at the University of California. In 1992 she worked on the board of governors of the US Federal Reserve System, later in 1998 she was appointed a full professor at George Washington University, where she works at the Elliot School of International Affairs. Kaminsky has been a visiting scholar at the Bank of Japan, the Bank of Spain, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority, and the Central Bank of France.









