A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
Ukrainian–Armenian relations are bilateral diplomatic relations between Ukraine and Armenia, which were established on 25 December 1991. Until then, both were member republics of the Soviet Union. Today, the countries are both members of the World Trade Organization, Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the United Nations, and the Eastern Partnership initiative of the EU. Currently, Ukraine has the 5th largest Armenian community in the world. The Embassy of Armenia in Kyiv opened in 1993. The Embassy of Ukraine in Yerevan opened in 1996. The current Ambassador of Armenia to Ukraine is Andranik Manukyan. The current Ambassador of Ukraine to Armenia is Ivan Khukhta.

Diplomatic relations between the Argentine Republic and Ukraine, have existed for decades. The importance of relations centers on the history of Ukrainian migration to Argentina. Ukrainians in Argentina form the second largest Ukrainian community in Latin America numbering approximately 250,000 Ukrainians and their descendants. Both nations are members of the World Trade Organization.

Serbia–Ukraine relations are foreign relations between Serbia and Ukraine. Serbia, as a direct successor to the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, recognized Ukraine on 15 April 1994. Diplomatic relations between Ukraine and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia were established on 15 April 1994.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution 62/243, titled "The Situation in the Occupied Territories of Azerbaijan", is a resolution of the United Nations General Assembly about the situation in Nagorno-Karabakh, which was adopted on March 14, 2008 at the 62nd session of the General Assembly. It became the seventh United Nations document concerning Nagorno-Karabakh and the third and last United Nations General Assembly document on it.

International reactions to the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation have largely been condemnatory of Russia's actions, supportive of Ukraine's sovereignty and territorial integrity, and supportive of finding a quick end to the crisis. The United States and the European Union responded by enacting sanctions against Russia for its role in the crisis, and urged Russia to withdraw. Russia has accused the United States and the EU of funding and directing the revolution and retaliated to the sanctions by imposing its own.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution 68/262 was adopted on 27 March 2014 by the sixty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly in response to the Russian annexation of Crimea and entitled "territorial integrity of Ukraine". The nonbinding resolution, which was supported by 100 United Nations member states, affirmed the General Assembly's commitment to the territorial integrity of Ukraine within its internationally recognized borders and underscored the invalidity of the 2014 Crimean referendum. Eleven nations voted against the resolution, while 58 abstained, and a further 24 states were absent when the vote took place.
Ukraine was one of the founding members of the United Nations when it joined in 1945 as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic; along with the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukraine signed the United Nations Charter when it was part of the Soviet Union. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the newly independent Ukraine retained its seat.

Georgia–Slovenia relations are the bilateral relations between Georgia and Slovenia, two European nations with a communist past that established their bilateral ties in 1993. Their relations have been highly represented with a close diplomatic partnership, with Slovenia being one of the staunch supporters of Georgia's territorial integrity and pro-Western path. Both nations are members of the Council of Europe.

Iran–Ukraine relations are the bilateral relations between Iran and Ukraine. Iran has an embassy in Kyiv and Ukraine has an embassy in Tehran. Prior to 2020, the relationship between the Islamic Republic of Iran and Ukraine was friendly but has since sharply deteriorated due to Iran supplying its Shahed military drones to Russia during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine as well as the downing of Ukraine International Airlines Flight 752 by Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps in 2020.

Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Russia has been involved in territorial disputes with a number of countries. These disputes are primarily an aspect of the post-Soviet conflicts, and have led to some countries losing parts of their sovereign territory to what a large portion of the international community designates as a Russian military occupation. As such, these lands are commonly described as Russian-occupied territories, regardless of what their status is in Russian law. The term is applied to Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine.

The eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly opened on 28 February 2022 at the United Nations headquarters. It addresses the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Maldivian politician Abdulla Shahid served as President of the body during this time.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2623 called for the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly on the subject of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Albania and the United States introduced the resolution before the United Nations Security Council, which adopted it on 27 February 2022. Russia voted against while China, India and the United Arab Emirates abstained. As this was a procedural resolution, no permanent member could exercise their veto power.

Eritrea and Russia relations are diplomatic relations between the State of Eritrea and the Russian Federation. Russia has an embassy in Asmara and Eritrea has its own in Moscow.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine violated international law. The invasion has also been called a crime of aggression under international criminal law, and under some countries' domestic criminal codes – including those of Ukraine and Russia – although procedural obstacles exist to prosecutions under these laws.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/4 is the fourth resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 12 October 2022, following Resolution ES-11/3 which was adopted on 7 April 2022.
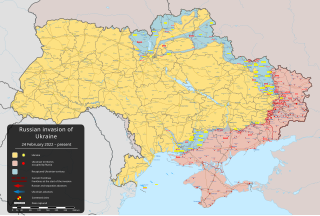
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Russo-Ukrainian War:
Belarus and Sudan established diplomatic relations on 15 July 1999.
Belarus–Syria relations refer to the relationship between Belarus and the Syrian Arab Republic. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1992. Belarus has an embassy in Damascus and Syria has an embassy in Minsk.
The Federated States of Micronesia and Ukraine established diplomatic relations on 17 September 1999.
















