 |
|---|
This article lists international organizations of which Ukraine is a member or an observer.
 |
|---|
This article lists international organizations of which Ukraine is a member or an observer.
Ukraine is also a potential candidate for the following organizations:

After achieving independence from the Soviet Union, the Republic of Moldova established relations with other European countries. A course for European Union integration and neutrality define the country's foreign policy guidelines.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 31 member states – 29 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact, and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is animus in consulendo liber.

The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of 20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security, including cross-border crime prevention.

The European Union (EU) has expanded a number of times throughout its history by way of the accession of new member states to the Union. To join the EU, a state needs to fulfil economic and political conditions called the Copenhagen criteria, which require a stable democratic government that respects the rule of law, and its corresponding freedoms and institutions. According to the Maastricht Treaty, each current member state and the European Parliament must agree to any enlargement. The process of enlargement is sometimes referred to as European integration. This term is also used to refer to the intensification of co-operation between EU member states as national governments allow for the gradual harmonisation of national laws.
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integration has primarily come about through the European Union and its policies.

The politics of Europe deals with the continually evolving politics within the continent of Europe. It is a topic far more detailed than other continents due to a number of factors including the long history of nation states in the region as well as the modern day trend towards increased political unity amongst the European states.
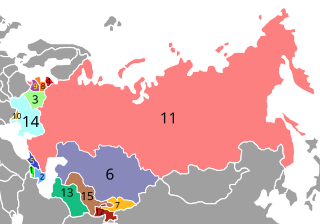
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet republics, and in Russia as the near abroad, are the 15 sovereign states that were union republics of the Soviet Union, which emerged and re-emerged from the Soviet Union following its dissolution in 1991.

International relations between the European Union (EU) and Ukraine are shaped through the Ukraine–European Union Association Agreement and the Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA). Ukraine is a priority partner within the Eastern Partnership and the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP). The EU and Ukraine have been seeking an increasingly close relationship, going beyond co-operation, to gradual economic integration and deepening of political co-operation. On 23 June 2022, the European Council granted Ukraine the status of a candidate for accession to the European Union.
Turkey is a founding member of the United Nations, the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, a member state of the Council of Europe since 1949, and of NATO since 1952. Since 2005, Turkey is in accession negotiations with the European Union, having been an associate member since 1963 and is also in European Customs Union. Turkey is also a member of the G20 industrial nations which brings together the 20 largest economies of the world.

Georgia and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) enjoy good relations. Georgia is not currently a member of NATO, but has been promised by NATO to be admitted in the future.

NATO is a military alliance of thirty-one European and North American countries that constitutes a system of collective defense. The process of joining the alliance is governed by Article 10 of the North Atlantic Treaty, which allows for the invitation of "other European States" only and by subsequent agreements. Countries wishing to join must meet certain requirements and complete a multi-step process involving political dialog and military integration. The accession process is overseen by the North Atlantic Council, NATO's governing body. NATO was formed in 1949 with twelve founding members and has added new members nine times. The first additions were Greece and Turkey in 1952. In May 1955, West Germany joined NATO, which was one of the conditions agreed to as part of the end of the country's occupation by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States, prompting the Soviet Union to form its own collective security alliance later that month. Following the end of the Franco regime, newly democratic Spain chose to join NATO in 1982.
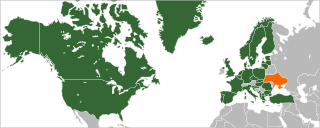
Relations between Ukraine and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) started in 1991. Ukraine applied to integrate with a NATO Membership Action Plan (MAP) in 2008. Plans for NATO membership were shelved by Ukraine following the 2010 presidential election in which Viktor Yanukovych, who preferred to keep the country closer to Russia, was elected President. Yanukovych fled Ukraine in February 2014 during the Revolution of Dignity. The interim Yatsenyuk Government initially said that it had no plans to join NATO. However, following the Russian annexation of Crimea and Russian military support for armed separatists in eastern Ukraine, the Second Yatsenyuk Government made joining NATO a priority. In February 2019, the Ukrainian parliament voted to amend the Constitution of Ukraine to state Ukraine's goal of NATO and European Union membership.
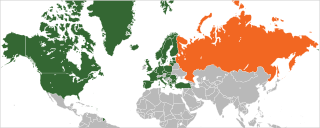
Relations between the NATO military alliance and the Russian Federation were established in 1991 within the framework of the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. In 1994, Russia joined the Partnership for Peace program, and on 27 May 1997, the NATO–Russia Founding Act (NRFA) was signed at a NATO Summit in Paris, France, enabling the creation of the NATO–Russia Permanent Joint Council (NRPJC). Through the early part of 2010s NATO and Russia signed several additional agreements on cooperation. The NRPJC was replaced in 2002 by the NATO–Russia Council (NRC), which was established in an effort to partner on security issues and joint projects together.
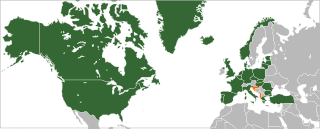
The accession of Albania to NATO took place in 2009. Albania's relationship with the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) began in 1992 when it joined the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. In 1994, it entered NATO's Partnership for Peace, which began Albania's process of accession into the alliance. In 1999, the country received a Membership Action Plan (MAP). The country received an invitation to join at the 2008 Bucharest Summit and became a full member on April 1, 2009.

Official relations between Moldova and NATO began in 1992 when Moldova joined the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. However, as Moldova's neutrality is enshrined in its constitution, there are no official plans for Moldova to join the organization.

On 28 February 2022, shortly after it was invaded by Russia, Ukraine applied for membership of the European Union (EU). Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy requested immediate admission under a "new special procedure", and the presidents of eight EU states called for an accelerated accession process. European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen stated that she supports Ukrainian accession, but that the process would take time. On 10 March 2022, the Council of the European Union asked the commission for its opinion on the application. On 8 April 2022, von der Leyen presented Zelenskyy with a legislative questionnaire, which Ukraine responded to on 9 May.

Belarus–NATO relations refers to relations between the Republic of Belarus and the NATO for the sake of security, realization of common interests under the individual partnership program, participation in the "Planning and Analysis Process".

Controversy in Russia regarding the legitimacy of eastward NATO expansion is one of the conflicting moments in relations between Russia and NATO. The Russian authorities claim that agreement on non-expansion of NATO to Eastern Europe took place orally and the alliance violated it with its expansion while the leaders of the alliance claim that no such promise was made and that such a decision could only be made in writing. Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev, who participated in the 1990 negotiations, subsequently spoke out about the existence of a "guarantee of non-expansion of NATO to the east" inconsistently, confirming its existence in some interviews and refuting in others. Among academic researchers, opinions on the existence or absence of a non-extension agreement also differ.
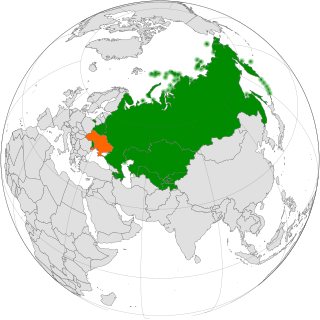
Relations between Ukraine and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) are multilateral international relations between a third state and a supranational organization.

Austria and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) have a close relationship. Austria is one of four members of the European Union that are not members of NATO. Austria has had formal relations with NATO since 1995, when it joined the Partnership for Peace programme.