
Lower Saxony is a German state (Land) situated in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with 47,624 km2 (18,388 sq mi), and fourth-largest in population among the 16 Länder federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, but the number of speakers is declining.

Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of 18,413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants.

The Ore Mountains or Ore Mountain Range in Central Europe have formed a natural border between Bohemia and Saxony for around 800 years, from the 12th to the 20th centuries. Today, the border between the Czech Republic and Germany runs just north of the main crest of the mountain range. The highest peaks are the Klínovec in the Czech Republic, which rises to 1,244 metres (4,081 ft) above sea level and the Fichtelberg in Germany.
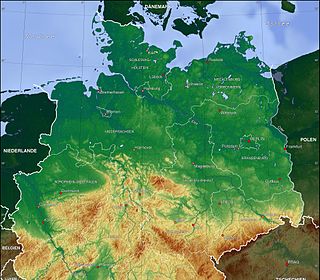
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east.
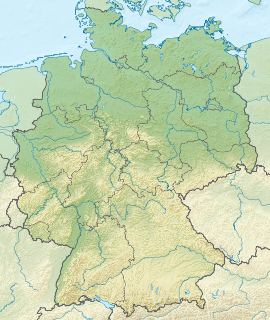
Germany is a country in west-central Europe, that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Germany has the second largest population in Europe and is seventh largest in area. The territory of Germany covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of waters.

This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Political boundaries play no part in this, apart from defining the national border.
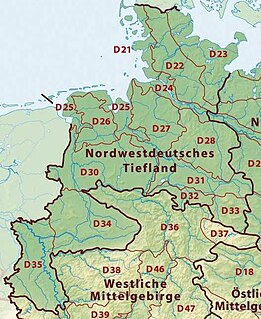
The Westphalian Lowland, also known as the Westphalian Basin is a flat landscape that mainly lies within the German region of Westphalia, although small areas also fall within North Rhine and in Lower Saxony. Together with the neighbouring Lower Rhine Plain to the west, it represents the second most southerly region of the North German Plain, after the Cologne Bight. It is variously known in German as the Westfälische Bucht, the Münsterländer or Westfälische Tieflands- or Flachlandsbucht.

The Saxon Uplands, Saxon Hills or Ore Mountain Foreland is a strip of countryside of about 200 m to 500 m above sea level (NN) high, in the German state of Saxony, that lies immediately north of the German Ore Mountains and runs mainly through the areas of Zwickauer Land, Zwickau, Chemnitzer Land, Chemnitz, Mittelsachsen and the country south of Dresden. It borders on the Upper Pleißeland to the extreme west, the Ore Mountain Basin in the south and the Mulde Loess Hills to the north and east.
The Saxon Loess Fields refer to a natural region that lies mainly within the state of Saxony in central Germany. In addition, small areas of this region extend to the northwest and west into Saxony-Anhalt, to the southeast into Thuringia and to the northeast into Brandenburg. It more-or-less combines the BfN's major regions listed as D19 Saxon Upland and Ore Mountain Foreland, and D14, Upper Lusatia (Oberlausitz); only the range of Central Uplands hills, the Lusatian Mountains, has been excluded and instead forms part of the Saxon Highlands and Uplands.
The Saxon-Bohemian Chalk Sandstone Region is a natural region in south Saxony on the southern border with the Czech Republic. It forms part of the northern perimeter of the Bohemian Massif and comprises Saxon Switzerland, the German part of the Elbsandsteingebirge and the Zittau Hills, a small section of the Lusatian Mountains on German soil. Because the boundary between the Elbsandsteingebirge and the Lusatian Uplands is on Czech territory, the two natural regions are physically separated.
The Saxon Highlands and Uplands refer to a natural region mainly in the south of Saxony with small elements also in southeast Thuringia and northeast Bavaria. It comprises, from (south)west to (north)east, of the Vogtland, the Ore Mountains, Saxon Switzerland, the Upper Lusatian Plateau and the Zittau Hills.

The Eastern Ore Mountains form a natural region of Saxony that covers the eastern part of the Saxon Ore Mountains range. Together with the Western and Central Ore Mountains, it is part of the larger Saxon Highlands and Uplands region. Its southern continuation beyond the German border covers an area of roughly the same extent in the Czech Republic.

The Western Ore Mountains is a natural region that forms the westernmost part of the Ore Mountains in the German federal state of Saxony. It is also part of the major landscape unit known as the Saxon Highlands and Uplands. It extends eastwards to include the valley of the Schwarzwasser, and, below its mouth, that of the Zwickauer Mulde, and incorporates the western parts of the former major units known as the Lower and Upper Western Ore Mountains, no. 423, as well as the Southern Slopes of the Ore Mountains, no. 420.
The Ore Mountain Basin or Erzgebirge Basin is a natural region in the German federal state of Saxony, that is part of the Saxon Lowland. To the north it borders on the Mulde Loess Hills and to the south on several natural regions in the Saxon Highlands and Uplands.
Wendland and Altmark, named after the German regions of Wendland and Altmark, is the name of a natural regional major landscape unit group in Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt, North Germany. In the Handbook of Natural Region Divisions of Germany it is given serial number 86, the Bundesamt für Naturschutz gives the same region the serial number D29.

The Harz Nature Park or just Harz Nature Park lies in the districts of Goslar and Göttingen in South Lower Saxony. The nature park in the Harz Mountains was founded in 1960 and is covers an area of around 790 km². It is run by the Harz Regional Association.

The classification of natural regions of Saxony shown here was produced between 1994 and 2001 by a working group called "Ecosystem and Regional Character" at the Saxonian Academy of Sciences in Leipzig as part of the research and development project "Natural Regions and Natural Region Potential of the Free State of Saxony" at a scale of 1:50,000 as the basis for the rural development and regional planning. This was also supported by the Saxon State Ministry of the Environment and Agriculture and the Saxon Ministry of the Interior.

The Vogelsberg (help·info) is a large volcanic mountain range in the German Central Uplands in the state of Hesse, separated from the Rhön Mountains by the Fulda river valley. Emerging approximately 19 million years ago, the Vogelsberg is Central Europe's largest basalt formation, consisting of a multitude of layers that descend from their peak in ring-shaped terraces to the base.
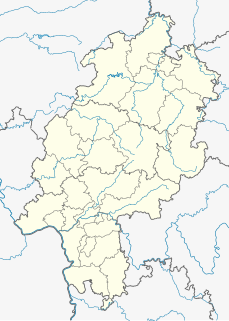
The Söhre is a forested hill range of the German Central Uplands and a subordinate natural region of the Fulda-Werra Uplands in North Hesse, Germany.













