
Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931 and 1936 during the Great Depression and was dedicated on September 30, 1935, by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. Its construction was the result of a massive effort involving thousands of workers, and cost over one hundred lives. It was referred to as Hoover Dam after President Herbert Hoover in bills passed by Congress during its construction; it was named Boulder Dam by the Roosevelt administration. The Hoover Dam name was restored by Congress in 1947.

The Deschutes River in central Oregon is a major tributary of the Columbia River. The river provides much of the drainage on the eastern side of the Cascade Range in Oregon, gathering many of the tributaries that descend from the drier, eastern flank of the mountains. The Deschutes provided an important route to and from the Columbia for Native Americans for thousands of years, and then in the 19th century for pioneers on the Oregon Trail. The river flows mostly through rugged and arid country, and its valley provides a cultural heart for central Oregon. Today the river supplies water for irrigation and is popular in the summer for whitewater rafting and fishing.
The Truckee–Carson Irrigation District (TCID) is a political subdivision of the State of Nevada, which operates dams at Lake Tahoe, diversion dams on the Truckee River in Washoe County, and the Lake Lahontan reservoir.
The Salt River Project (SRP) is the umbrella name for two separate entities: the Salt River Project Agricultural Improvement and Power District, an agency of the state of Arizona that serves as an electrical utility for the Phoenix metropolitan area, and the Salt River Valley Water Users' Association, a utility cooperative that serves as the primary water provider for much of central Arizona. It is one of the primary public utility companies in Arizona.

Central Oregon is a geographic region in the U.S. state of Oregon and is traditionally considered to be made up of Deschutes, Jefferson, and Crook counties. Other definitions include larger areas, often encompassing areas to the north towards the Columbia River, eastward towards Burns, or south towards Klamath Falls. These three counties have a combined population of 200,431 as of the 2010 census, with Deschutes the largest of the three counties, having approximately four times the population of the other two counties combined. As of 2015, the most populous city in the region is Bend, with an estimated 87,014 residents. As defined by the three county definition, Central Oregon covers 7,833 square miles (20,290 km2) of land. Central Oregon has had 3 record tourism years beginning in 2012. Over 2.2 million people visited Central Oregon in 2012 and again in 2013.

Kachess Lake is a lake and reservoir along the course of the Kachess River in Washington state, US. The upper part of the lake, north of a narrows, is called Little Kachess Lake. The Kachess River flows into the lake from the north, and out from the south. Kachess Lake is the middle of the three large lakes which straddle Interstate 90 north of the Yakima River in the Cascade Range. The other two are Cle Elum Lake, the easternmost which is also north of I-90 and Keechelus Lake, the westernmost, which is south of I-90.

The Crooked River is a tributary, 125 miles (201 km) long, of the Deschutes River in the U.S. state of Oregon. The river begins at the confluence of the South Fork Crooked River and Beaver Creek. Of the two tributaries, the South Fork Crooked River is the larger and is sometimes considered part of the Crooked River proper. A variant name of the South Fork Crooked River is simply "Crooked River". The Deschutes River flows north into the Columbia River.

Milner Dam is a rockfill dam near Burley in south central Idaho. It impounds the Snake River in a reservoir named Milner Lake. The dam spans the river across two islands, with three embankments.

The Granite Reef Diversion Dam is a concrete diversion dam located 22 miles (35 km) Northeast of Phoenix, Arizona. It impounds the Salt River for irrigation purposes.
The Central Utah Project is a US federal water project that was authorized for construction under the Colorado River Storage Project Act of April 11, 1956, as a participating project. In general, the Central Utah Project develops a portion of Utah's share of the yield of the Colorado River, as set out in the Colorado River Compact of 1922.

The Carlsbad Irrigation District, also known as Carlsbad Reclamation Project or Irrigation system of the Pecos Irrigation and Improvement Company, is a major early water reclamation project located near Carlsbad in southeastern New Mexico. Begun in the 1880s, it is now managed by the United States Bureau of Reclamation, and provides irrigation water to a large area around Carlsbad, diverted from the Pecos River and the Black River. The late 19th and early 20th-century elements of the project were designated a National Historic Landmark District in 1964.

Arrowrock Dam is a concrete arch dam in the western United States, on the Boise River in southwestern Idaho, east of Boise. Opened 107 years ago in 1915, it is located on the border of Boise and Elmore counties, upstream of the Lucky Peak Dam and reservoir. The spillway elevation for Arrowrock is 3,219 feet (981 m) above sea level and its primary purpose is to provide irrigation water for agriculture.

Tieton Dam is an earth and concrete type dam on the Tieton River in Yakima County, in the U.S. state of Washington. The dam began operation in 1925. Its reservoir, Rimrock Lake, has a total capacity of 203,600 acre-feet (0.2511 km3) with a normal operating capacity of 198,000 acre-feet (0.244 km3) to provides water for agricultural irrigation. This dam is a component of the Yakima Project. Tieton Dam also produces electricity for Burbank Water and Power and Glendale Water and Power, near Los Angeles. The Southern California Public Power Agency installed two 7 megawatt generators in a project started in 2010. The power is transmitted over the DC Intertie that runs from Celilo, Oregon to Sylmar, California. Upstream from the dam, the river is impounded by Clear Creek Dam, another element of the Yakima Project. About 8 miles (13 km) downstream from the dam, the Tieton River is tapped for the Tieton Main Canal.
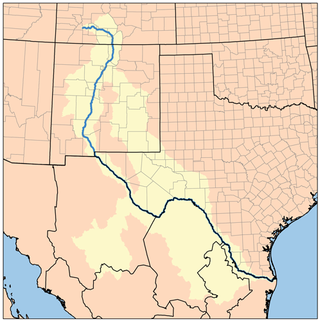
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

Guernsey Dam is an earthfill dam on the North Platte River in Platte County in the U.S. State of Wyoming. The dam creates Guernsey Reservoir, the last of the 5 major reservoirs on the North Platte River in Wyoming. The dam contains a hydroelectric plant capable of 6.4 megawatts of electricity. The total capacity of the reservoir is 71,040 acre-feet (87,630,000 m3) of water which is used mainly for irrigation. Morrison-Knudsen and Utah Construction Company constructed Guernsey Dam and the hydroelectric plant as part of the North Platte Project to provide irrigation to eastern Wyoming and western Nebraska. Guernsey helps control the river flow and stores water released from the project's primary storage upstream at Pathfinder Reservoir. About 8 miles (13 km) downstream of the dam the Whalen Diversion Dam diverts water into the Fort Laramie and Interstate Canals that service farms in Wyoming and Nebraska.

Alexander McClurg Drake was a Minnesota investor and Oregon pioneer. He was the founder of Bend, Oregon.

Mirror Pond is an impoundment of the Deschutes River in Bend, in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is between Pacific Power's Bend Hydro dam and the Colorado dam, between RM 166 and 167. The pond is flanked by Drake, Harmon, Pageant, Brooks, Columbia, Miller's Landing, and McKay parks, as well as a number of buildings such as Pine Tavern and private homes. Some people mistakenly consider the Galveston (Tumalo) bridge the upper boundary of Mirror Pond; others call the portion of the lake between Galveston bridge and the Colorado dam "upper Mirror Pond".

The Grand Valley Diversion Dam is a diversion dam in the De Beque Canyon of the Colorado River, about 15 miles (24 km) northeast of Grand Junction, Colorado in the United States. It is a 14-foot (4.3 m) high, 546-foot (166 m) long concrete roller dam with six gates, which were the first and largest of their kind to be installed in the United States.
The Crooked River Railroad Bridge, part of a BNSF Railway line between the Columbia River and Bend, Oregon, crosses Oregon's Crooked River Canyon in southern Jefferson County. The bridge is 320 feet (98 m) above the river and when it was completed in 1911, it was the second-highest railroad bridge in the United States. It is a steel two-hinge arch span with a total length of 460 feet (140 m).

The Swalley Irrigation District supplies water to irrigators through a network of pipes and canals fed by the Deschutes River near Bend in the U.S. state of Oregon. The network, begun in 1899, is a closed system with an intake behind North Canal Dam in Bend and a main canal, the Swalley Canal, that runs north from the city for about 13 miles (21 km). The only covered bridge east of the Cascade Range in Oregon crosses the Swalley Canal.

















