The Great Plains, sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located just to the east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. It is the western part of the Interior Plains, which also include the mixed grass prairie, the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. Great Plains or Western Plains is also used to describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains.

Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east.

Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The predominant vegetation in this biome consists of grass and/or shrubs. The climate is temperate and ranges from semi-arid to semi-humid. The habitat type differs from tropical grasslands in the annual temperature regime as well as the types of species found here.

The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachment of trees, recycling soil nutrients, and facilitating seed dispersal and germination. Prior to widespread use of the steel plow, which enabled large scale conversion to agricultural land use, tallgrass prairies extended throughout the American Midwest and smaller portions of southern central Canada, from the transitional ecotones out of eastern North American forests, west to a climatic threshold based on precipitation and soils, to the southern reaches of the Flint Hills in Oklahoma, to a transition into forest in Manitoba.

The Flint Hills, historically known as Bluestem Pastures or Blue Stem Hills, are a region in eastern Kansas and north-central Oklahoma named for the abundant residual flint eroded from the bedrock that lies near or at the surface. It consists of a band of hills stretching from Kansas to Oklahoma, extending from Marshall and Washington Counties in the north to Cowley County, Kansas and Kay and Osage Counties in Oklahoma in the south, to Geary and Shawnee Counties west to east. Oklahomans generally refer to the same geologic formation as the Osage Hills or "the Osage."

Aspen parkland refers to a very large area of transitional biome between prairie and boreal forest in two sections, namely the Peace River Country of northwestern Alberta crossing the border into British Columbia, and a much larger area stretching from central Alberta, all across central Saskatchewan to south central Manitoba and continuing into small parts of the US states of Minnesota and North Dakota. Aspen parkland consists of groves of aspen, poplar and spruce, interspersed with areas of prairie grasslands, also intersected by large stream and river valleys lined with aspen-spruce forests and dense shrubbery. This is the largest boreal-grassland transition zone in the world and is a zone of constant competition and tension as prairie and woodlands struggle to overtake each other within the parkland.

The Texas Blackland Prairies are a temperate grassland ecoregion located in Texas that runs roughly 300 miles (480 km) from the Red River in North Texas to San Antonio in the south. The prairie was named after its rich, dark soil. Less than 1% of the original Blackland prairie vegetation remains, scattered across Texas in parcels.

The Loess Hills are a formation of wind-deposited loess soil in the westernmost parts of Iowa and Missouri, and the easternmost parts of Nebraska and Kansas, along the Missouri River.

Sorghastrum nutans, commonly known as either Indiangrass or yellow Indiangrass, is a North American prairie grass found in the Central United States, the Eastern United States, and Canada, especially in the Great Plains and tallgrass prairies.

The Northern short grasslands includes parts of the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan, and the American Great Plains states of Montana, North Dakota, Wyoming, South Dakota and Nebraska. One of 867 terrestrial ecoregions defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) further breaks this ecoregion into the Northwestern Glaciated Plains and Northwestern Great Plains.

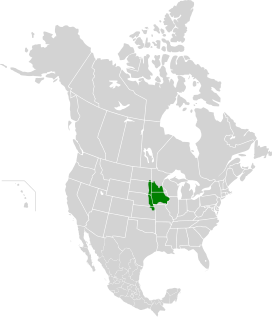
The Northern tall grasslands is one of 867 terrestrial ecoregions defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. This ecoregion largely follows the Red River Valley in the Canadian province of Manitoba and the American states of North Dakota and Minnesota.

The Western short grasslands is a temperate grassland ecoregion of the United States.

The Wyoming Basin shrub steppe ecoregion, within the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, is a shrub steppe in the northwestern United States.

The central forest–grasslands transition is a prairie ecoregion of the central United States, an ecotone between eastern forests and the North American Great Plains. It is a classification defined by the World Wildlife Fund.

The Montana valley and foothill grasslands are an ecoregion of northwestern North America in the northern United States and southern Canada.

A mixed-grass prairie is an ecotone located between the tallgrass prairies and shortgrass prairies. The mixed-grass prairie is richer in botanical diversity than either the tall- or shortgrass prairie. The mixed-grass prairie occurs in the central plains portion of the Great Plains, varying in width from central Texas in the United States up into southeastern Manitoba, Alberta and Saskatchewan in the northern mixed grasslands of Canada.
The ecology of the Great Plains is diverse, largely owing to their great size. Differences in rainfall, elevation, and latitude create a variety of habitats including short grass, mixed grass, and tall-grass prairies, and riparian ecosystems.

The Central Great Plains are a semiarid prairie ecoregion of the central United States, part of North American Great Plains. The region runs from west-central Texas through west-central Oklahoma, central Kansas, and south-central Nebraska.

The Northern Mixed Grasslands is one of 867 terrestrial ecoregions defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. This ecoregion includes parts of the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, north-central and eastern North Dakota, most of east South Dakota, and north-central Nebraska in the American Great Plains. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines this ecoregion as the Northern Glaciated Plains.